ZEB2
ZEB2아연핑거 E박스 결합 호메오박스2는 ZEB2 [5]유전자에 의해 인체 내에서 부호화되는 단백질이다.ZEB2 단백질은 초기 태아 [6]발달 동안 필수적인 변환 성장인자 β(TGFβ) 신호 경로에 역할을 하는 전사 인자이다.
기능.
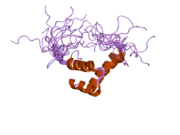
ZEB2(이전의 SMADIP1, SIP1)와 그 포유동물 패럴로그 ZEB1은 호메오도메인 전사 인자의 ZF(아연 핑거) 클래스 내의 Zeb 패밀리에 속합니다.ZEB2 단백질은 8개의 아연 손가락과 1개의 호메오도메인을 [7]가지고 있습니다.오른쪽에 나타난 호메오도메인의 구조.
ZEB2는 수용체 매개,[5] 활성화된 전장 SMAD와 상호작용합니다.TGFβ 수용체의 활성화는 세포 내 이펙터 분자인 R-SMADs의 인산화를 초래한다. ZEB2는 R-SMAD 결합 단백질로 전사 코어프레서 역할을 한다.그것은 인간과 다른 [8]포유동물들 사이의 뇌 크기에서 큰 차이를 허용하는 것으로 생각되는 메커니즘인 초기 발달에서 신경 상피 세포가 방사상 신경교 세포로 전환되는 타이밍에 관여한다.
ZEB2 전사물은 뇌신경절, 배근신경절, 교감신경절사슬, 장신경계 및 멜라노사이트와 같은 신경능과 구별되는 조직에서 발견된다.ZEB2는 또한 소화관, 신장, 골격근의 벽을 포함한 신경능에서 유래되지 않은 조직에서도 발견됩니다.
임상적 의의
ZEB2 유전자의 돌연변이는 모왓-윌슨 증후군과 관련이 있다.이 질병은 돌연변이와 심지어 ZEB2 유전자의 완전한 결실을 보인다.유전자의 돌연변이는 유전자가 기능하지 않는 ZEB2 단백질을 생성하게 하거나 기능 유전자 전체를 비활성화 시킬 수 있다.이러한 ZEB2 단백질의 결핍은 많은 장기의 발달을 방해한다.많은 증상들은 신경능으로부터 [9]불규칙한 구조의 발달로 설명될 수 있다.
허쉬스프룽병은 또한 소화관 신경이 발달하는 동안 ZEB2의 부족으로 설명될 수 있는 많은 증상들을 가지고 있다.이 병은 심한 변비와 [10]대장의 종창을 일으킨다.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSG00000169554 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSMUSG000026872 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: ZEB2 zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 2".
- ^ Bassez G, Camand OJ, Cacheux V, Kobetz A, Dastot-Le Moal F, Marchant D, Catala M, Abitbol M, Goossens M (March 2004). "Pleiotropic and diverse expression of ZFHX1B gene transcripts during mouse and human development supports the various clinical manifestations of the "Mowat-Wilson" syndrome". Neurobiology of Disease. 15 (2): 240–50. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2003.10.004. PMID 15006694. S2CID 25770329.
- ^ Bürglin TR, Affolter M (June 2016). "Homeodomain proteins: an update". Chromosoma. 125 (3): 497–521. doi:10.1007/s00412-015-0543-8. PMC 4901127. PMID 26464018.
- ^ Benito-Kwiecinski, Silvia; Giandomenico, Stefano L.; Sutcliffe, Magdalena; Riis, Erlend S.; Freire-Pritchett, Paula; Kelava, Iva; Wunderlich, Stephanie; Martin, Ulrich; Wray, Gregory A.; McDole, Kate; Lancaster, Madeline A. (2021). "An early cell shape transition drives evolutionary expansion of the human forebrain". Cell. 184 (8): 2084–2102.e19. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.050. PMC 8054913. PMID 33765444.
- ^ Dastot-Le Moal F, Wilson M, Mowat D, Collot N, Niel F, Goossens M (April 2007). "ZFHX1B mutations in patients with Mowat-Wilson syndrome". Human Mutation. 28 (4): 313–21. doi:10.1002/humu.20452. PMID 17203459. S2CID 37981110.
- ^ Saunders CJ, Zhao W, Ardinger HH (November 2009). "Comprehensive ZEB2 gene analysis for Mowat-Wilson syndrome in a North American cohort: a suggested approach to molecular diagnostics". American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A. 149A (11): 2527–31. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33067. PMID 19842203. S2CID 22472646.
추가 정보
- Mowat DR, Wilson MJ, Goossens M (May 2003). "Mowat-Wilson syndrome". Journal of Medical Genetics. 40 (5): 305–10. doi:10.1136/jmg.40.5.305. PMC 1735450. PMID 12746390.
- Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (February 1998). "Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. IX. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which can code for large proteins in vitro". DNA Research. 5 (1): 31–9. doi:10.1093/dnares/5.1.31. PMID 9628581.
- Ueki N, Oda T, Kondo M, Yano K, Noguchi T, Muramatsu M (December 1998). "Selection system for genes encoding nuclear-targeted proteins". Nature Biotechnology. 16 (13): 1338–42. doi:10.1038/4315. PMID 9853615. S2CID 20001769.
- Verschueren K, Remacle JE, Collart C, Kraft H, Baker BS, Tylzanowski P, Nelles L, Wuytens G, Su MT, Bodmer R, Smith JC, Huylebroeck D (July 1999). "SIP1, a novel zinc finger/homeodomain repressor, interacts with Smad proteins and binds to 5'-CACCT sequences in candidate target genes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (29): 20489–98. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.29.20489. PMID 10400677.
- Wakamatsu N, Yamada Y, Yamada K, Ono T, Nomura N, Taniguchi H, Kitoh H, Mutoh N, Yamanaka T, Mushiake K, Kato K, Sonta S, Nagaya M (April 2001). "Mutations in SIP1, encoding Smad interacting protein-1, cause a form of Hirschsprung disease". Nature Genetics. 27 (4): 369–70. doi:10.1038/86860. PMID 11279515. S2CID 39070888.
- Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, Verschueren K, van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, Mareel M, Huylebroeck D, van Roy F (June 2001). "The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1 downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion". Molecular Cell. 7 (6): 1267–78. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00260-X. PMID 11430829.
- Cacheux V, Dastot-Le Moal F, Kääriäinen H, Bondurand N, Rintala R, Boissier B, Wilson M, Mowat D, Goossens M (July 2001). "Loss-of-function mutations in SIP1 Smad interacting protein 1 result in a syndromic Hirschsprung disease". Human Molecular Genetics. 10 (14): 1503–10. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.14.1503. PMID 11448942.
- Tylzanowski P, Verschueren K, Huylebroeck D, Luyten FP (October 2001). "Smad-interacting protein 1 is a repressor of liver/bone/kidney alkaline phosphatase transcription in bone morphogenetic protein-induced osteogenic differentiation of C2C12 cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (43): 40001–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104112200. PMID 11477103.
- Yamada K, Yamada Y, Nomura N, Miura K, Wakako R, Hayakawa C, Matsumoto A, Kumagai T, Yoshimura I, Miyazaki S, Kato K, Sonta S, Ono H, Yamanaka T, Nagaya M, Wakamatsu N (December 2001). "Nonsense and frameshift mutations in ZFHX1B, encoding Smad-interacting protein 1, cause a complex developmental disorder with a great variety of clinical features". American Journal of Human Genetics. 69 (6): 1178–85. doi:10.1086/324343. PMC 1235530. PMID 11592033.
- Amiel J, Espinosa-Parrilla Y, Steffann J, Gosset P, Pelet A, Prieur M, Boute O, Choiset A, Lacombe D, Philip N, Le Merrer M, Tanaka H, Till M, Touraine R, Toutain A, Vekemans M, Munnich A, Lyonnet S (December 2001). "Large-scale deletions and SMADIP1 truncating mutations in syndromic Hirschsprung disease with involvement of midline structures". American Journal of Human Genetics. 69 (6): 1370–7. doi:10.1086/324342. PMC 1235547. PMID 11595972.
- Zweier C, Albrecht B, Mitulla B, Behrens R, Beese M, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Rott HD, Rauch A (March 2002). ""Mowat-Wilson" syndrome with and without Hirschsprung disease is a distinct, recognizable multiple congenital anomalies-mental retardation syndrome caused by mutations in the zinc finger homeo box 1B gene". American Journal of Medical Genetics. 108 (3): 177–81. doi:10.1002/ajmg.10226. PMID 11891681.
- Nagaya M, Kato J, Niimi N, Tanaka S, Wakamatsu N (August 2002). "Clinical features of a form of Hirschsprung's disease caused by a novel genetic abnormality". Journal of Pediatric Surgery. 37 (8): 1117–22. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2002.34455. PMID 12149685.
- Guaita S, Puig I, Franci C, Garrido M, Dominguez D, Batlle E, Sancho E, Dedhar S, De Herreros AG, Baulida J (October 2002). "Snail induction of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in tumor cells is accompanied by MUC1 repression and ZEB1 expression". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (42): 39209–16. doi:10.1074/jbc.M206400200. PMID 12161443.
- Espinosa-Parrilla Y, Amiel J, Augé J, Encha-Razavi F, Munnich A, Lyonnet S, Vekemans M, Attié-Bitach T (June 2002). "Expression of the SMADIP1 gene during early human development". Mechanisms of Development. 114 (1–2): 187–91. doi:10.1016/S0925-4773(02)00062-X. PMID 12175509. S2CID 18645909.
- Yoneda M, Fujita T, Yamada Y, Yamada K, Fujii A, Inagaki T, Nakagawa H, Shimada A, Kishikawa M, Nagaya M, Azuma T, Kuriyama M, Wakamatsu N (November 2002). "Late infantile Hirschsprung disease-mental retardation syndrome with a 3-bp deletion in ZFHX1B". Neurology. 59 (10): 1637–40. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000034842.78350.4e. PMID 12451214. S2CID 34389990.
- Postigo AA (May 2003). "Opposing functions of ZEB proteins in the regulation of the TGFbeta/BMP signaling pathway". The EMBO Journal. 22 (10): 2443–52. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg225. PMC 155983. PMID 12743038.
- Postigo AA, Depp JL, Taylor JJ, Kroll KL (May 2003). "Regulation of Smad signaling through a differential recruitment of coactivators and corepressors by ZEB proteins". The EMBO Journal. 22 (10): 2453–62. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg226. PMC 155984. PMID 12743039.
- Zweier C, Temple IK, Beemer F, Zackai E, Lerman-Sagie T, Weschke B, Anderson CE, Rauch A (August 2003). "Characterisation of deletions of the ZFHX1B region and genotype-phenotype analysis in Mowat-Wilson syndrome". Journal of Medical Genetics. 40 (8): 601–5. doi:10.1136/jmg.40.8.601. PMC 1735564. PMID 12920073.