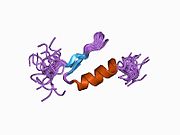
전사 팩터 2 활성화
Activating transcription factor 2ATF2라고도 알려진 활성화 전사인자 2는 인간에서 ATF2 [5]유전자에 의해 암호화되는 단백질이다.
기능.
이 유전자는 DNA 결합 단백질의 류신 지퍼 계열의 구성원인 전사 인자를 암호화합니다.이 단백질은 팔중미 회문인 cAMP-responsive element(CRE; cAMP-responsive element)에 결합합니다.단백질은 c-Jun과 호모디머 또는 헤테로디머를 형성한다.단백질은 또한 히스톤 H2B와 H4를 시험관내에서 특이적으로 아세틸화하는 히스톤 아세틸전달효소(HAT)이다. 따라서 염색질 성분에 대한 직접적인 영향에 의해 전사를 활성화하는 배열 특이적 인자의 클래스를 나타낼 수 있다.추가적인 전사 변형이 확인되었지만 생물학적 타당성은 [5]확인되지 않았다.
atf2 유전자는 인간 염색체 2q32에 [6]위치한다.ATF-2 단백질은 505개의 아미노산을 가지고 있습니다.쥐를 대상으로 한 연구는 신경계와 [7]골격 발달에서 ATF-2의 역할을 나타낸다.ATF-2는 일반적으로 스트레스 활성화 단백질 키나아제 p38 및 JNK에 [8]수렴하는 신호에 반응하여 활성화된다. ATF-2 인산화 반응은 종양 프로모터 포르볼 에스테르에 의한 세포 치료에 대한 반응으로 [9]입증되었다.
포유류의 피부종양의 [10][11]성장과 진행에 ATF-2의 비정상적인 활성화가 수반되는 여러 연구들이 있다.ATF-2는 돌연변이 Ras[12] 단백질에 의한 발암을 매개하여 상피세포의 공격적인 암 표현형의 유지를 규제할 수 있다.
ATF2는 또한 이중 가닥 [13]절단 시 ATM에 의해 C 말단(마우스에서는 세린 472 및 480, 인간에서는 세린 490 및 498)에서 인산화되는 것으로 나타났다.이 두 가지 세린의 돌연변이를 가진 생쥐는 방사선에 민감하고 p53 녹아웃 배경에서 종양 발생이 더 쉽다.
상호 작용
전사인자 2를 활성화하는 것은
- 씨준 [14][15][16]씨
- 카제인 키나아제2,[17] 알파1,
- CREB 결합 [18]단백질
- CSNK2A2,[17]
- JDP2,[19]
- MAPK14,[20][21][22]
- MAPK8,[20][21][22][23]
- 반신불수 호몰로그 3에 반대하는 엄마들[24]
- NCOA6,[25]
- RUVBL2,[26]
- UBE2I[27]
「 」를 참조해 주세요.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSG00000115966 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSMUSG000027104 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: ATF2 activating transcription factor 2".
- ^ Ozawa K, Sudo T, Soeda E, Yoshida MC, Ishii S (1991). "Assignment of the human CREB2 (CRE-BP1) gene to 2q32". Genomics. 10 (4): 1103–4. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90210-6. PMID 1833307.
- ^ Reimold AM, Grusby MJ, Kosaras B, Fries JW, Mori R, Maniwa S, Clauss IM, Collins T, Sidman RL, Glimcher MJ, Glimcher LH (1996). "Chondrodysplasia and neurological abnormalities in ATF-2-deficient mice". Nature. 379 (6562): 262–5. Bibcode:1996Natur.379..262R. doi:10.1038/379262a0. PMID 8538792. S2CID 4326412.
- ^ Gupta S, Campbell D, Dérijard B, Davis RJ (1995). "Transcription factor ATF2 regulation by the JNK signal transduction pathway". Science. 267 (5196): 389–93. Bibcode:1995Sci...267..389G. doi:10.1126/science.7824938. PMID 7824938. S2CID 40268838.
- ^ Yamasaki T, Takahashi A, Pan J, Yamaguchi N, Yokoyama KK (March 2009). "Phosphorylation of Activation Transcription Factor-2 at Serine 121 by Protein Kinase C Controls c-Jun-mediated Activation of Transcription". J. Biol. Chem. 284 (13): 8567–81. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808719200. PMC 2659215. PMID 19176525.
- ^ Leslie MC, Bar-Eli M (2005). "Regulation of gene expression in melanoma: new approaches for treatment". J. Cell. Biochem. 94 (1): 25–38. doi:10.1002/jcb.20296. PMID 15523674. S2CID 23515325.
- ^ Papassava P, Gorgoulis VG, Papaevangeliou D, Vlahopoulos S, van Dam H, Zoumpourlis V (2004). "Overexpression of activating transcription factor-2 is required for tumor growth and progression in mouse skin tumors". Cancer Res. 64 (23): 8573–84. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-0955. PMID 15574764.
- ^ Vlahopoulos SA, Logotheti S, Mikas D, Giarika A, Gorgoulis V, Zoumpourlis V (17 March 2008). "The role of ATF-2 in oncogenesis". BioEssays. 30 (4): 314–27. doi:10.1002/bies.20734. PMID 18348191. S2CID 678541.
- ^ Bhoumik A, Takahashi S, Breitweiser W, Shiloh Y, Jones N, Ronai Z (May 2005). "ATM-dependent phosphorylation of ATF2 is required for the DNA damage response". Mol. Cell. 18 (5): 577–87. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.04.015. PMC 2954254. PMID 15916964.
- ^ Newell CL, Deisseroth AB, Lopez-Berestein G (July 1994). "Interaction of nuclear proteins with an AP-1/CRE-like promoter sequence in the human TNF-alpha gene". J. Leukoc. Biol. 56 (1): 27–35. doi:10.1002/jlb.56.1.27. PMID 8027667. S2CID 85570533.
- ^ Kara CJ, Liou HC, Ivashkiv LB, Glimcher LH (April 1990). "A cDNA for a human cyclic AMP response element-binding protein which is distinct from CREB and expressed preferentially in brain". Mol. Cell. Biol. 10 (4): 1347–57. doi:10.1128/MCB.10.4.1347. PMC 362236. PMID 2320002.
- ^ Hai T, Curran T (May 1991). "Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (9): 3720–4. Bibcode:1991PNAS...88.3720H. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. PMC 51524. PMID 1827203.
- ^ a b Yamaguchi Y, Wada T, Suzuki F, Takagi T, Hasegawa J, Handa H (August 1998). "Casein kinase II interacts with the bZIP domains of several transcription factors". Nucleic Acids Res. 26 (16): 3854–61. doi:10.1093/nar/26.16.3854. PMC 147779. PMID 9685505.
- ^ Sano Y, Tokitou F, Dai P, Maekawa T, Yamamoto T, Ishii S (October 1998). "CBP alleviates the intramolecular inhibition of ATF-2 function". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (44): 29098–105. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.44.29098. PMID 9786917.
- ^ Murata T, Shinozuka Y, Obata Y, Yokoyama KK (May 2008). "Phosphorylation of two eukaryotic transcription factors, Jun dimerization protein 2 and activation transcription factor 2, in Escherichia coli by Jun N-terminal kinase 1". Anal. Biochem. 376 (1): 115–21. doi:10.1016/j.ab.2008.01.038. PMID 18307971.
- ^ a b Raingeaud J, Gupta S, Rogers JS, Dickens M, Han J, Ulevitch RJ, Davis RJ (March 1995). "Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (13): 7420–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.13.7420. PMID 7535770.
- ^ a b Chen Z, Cobb MH (May 2001). "Regulation of stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways by TAO2". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (19): 16070–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100681200. PMID 11279118.
- ^ a b Tournier C, Whitmarsh AJ, Cavanagh J, Barrett T, Davis RJ (July 1997). "Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 is an activator of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94 (14): 7337–42. Bibcode:1997PNAS...94.7337T. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.14.7337. PMC 23822. PMID 9207092.
- ^ Fuchs SY, Xie B, Adler V, Fried VA, Davis RJ, Ronai Z (December 1997). "c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases target the ubiquitination of their associated transcription factors". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (51): 32163–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.51.32163. PMID 9405416.
- ^ Sano Y, Harada J, Tashiro S, Gotoh-Mandeville R, Maekawa T, Ishii S (March 1999). "ATF-2 is a common nuclear target of Smad and TAK1 pathways in transforming growth factor-beta signaling". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (13): 8949–57. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.13.8949. PMID 10085140.
- ^ Hong S, Choi HM, Park MJ, Kim YH, Choi YH, Kim HH, Choi YH, Cheong J (April 2004). "Activation and interaction of ATF2 with the coactivator ASC-2 are responsive for granulocytic differentiation by retinoic acid". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (17): 16996–7003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M311752200. PMID 14734562.
- ^ Cho SG, Bhoumik A, Broday L, Ivanov V, Rosenstein B, Ronai Z (December 2001). "TIP49b, a regulator of activating transcription factor 2 response to stress and DNA damage". Mol. Cell. Biol. 21 (24): 8398–413. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.24.8398-8413.2001. PMC 100004. PMID 11713276.
- ^ Firestein R, Feuerstein N (March 1998). "Association of activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2) with the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme hUBC9. Implication of the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway in regulation of ATF2 in T cells". J. Biol. Chem. 273 (10): 5892–902. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.10.5892. PMID 9488727.
외부 링크
- UCSC Genome Browser의 인간 ATF2 게놈 위치 및 ATF2 유전자 세부 정보 페이지.
추가 정보
- Denys H, Desmet R, Stragier M, Vergison R, Lemahieu SF (1977). "Cystitis emphysematosa". Acta Urol Belg. 45 (4): 327–31. PMID 602896.
- Kim SJ, Wagner S, Liu F, O'Reilly MA, Robbins PD, Green MR (1992). "Retinoblastoma gene product activates expression of the human TGF-beta 2 gene through transcription factor ATF-2". Nature. 358 (6384): 331–4. Bibcode:1992Natur.358..331K. doi:10.1038/358331a0. PMID 1641004. S2CID 9770957.
- Hai T, Curran T (1991). "Cross-family dimerization of transcription factors Fos/Jun and ATF/CREB alters DNA binding specificity". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88 (9): 3720–4. Bibcode:1991PNAS...88.3720H. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.9.3720. PMC 51524. PMID 1827203.
- Hoeffler JP, Lustbader JW, Chen CY (1991). "Identification of multiple nuclear factors that interact with cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate response element-binding protein and activating transcription factor-2 by protein-protein interactions". Mol. Endocrinol. 5 (2): 256–66. doi:10.1210/mend-5-2-256. PMID 1828107.
- Ozawa K, Sudo T, Soeda E, Yoshida MC, Ishii S (1991). "Assignment of the human CREB2 (CRE-BP1) gene to 2q32". Genomics. 10 (4): 1103–4. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90210-6. PMID 1833307.
- Diep A, Li C, Klisak I, Mohandas T, Sparkes RS, Gaynor R, Lusis AJ (1991). "Assignment of the gene for cyclic AMP-response element binding protein 2 (CREB2) to human chromosome 2q24.1-q32". Genomics. 11 (4): 1161–3. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(91)90047-I. PMID 1838349.
- Kara CJ, Liou HC, Ivashkiv LB, Glimcher LH (1990). "A cDNA for a human cyclic AMP response element-binding protein which is distinct from CREB and expressed preferentially in brain". Mol. Cell. Biol. 10 (4): 1347–57. doi:10.1128/MCB.10.4.1347. PMC 362236. PMID 2320002.
- Gonzalez GA, Yamamoto KK, Fischer WH, Karr D, Menzel P, Biggs W, Vale WW, Montminy MR (1989). "A cluster of phosphorylation sites on the cyclic AMP-regulated nuclear factor CREB predicted by its sequence". Nature. 337 (6209): 749–52. Bibcode:1989Natur.337..749G. doi:10.1038/337749a0. PMID 2521922. S2CID 4345950.
- Maekawa T, Sakura H, Kanei-Ishii C, Sudo T, Yoshimura T, Fujisawa J, Yoshida M, Ishii S (1989). "Leucine zipper structure of the protein CRE-BP1 binding to the cyclic AMP response element in brain". EMBO J. 8 (7): 2023–8. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03610.x. PMC 401081. PMID 2529117.
- Raingeaud J, Gupta S, Rogers JS, Dickens M, Han J, Ulevitch RJ, Davis RJ (1995). "Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (13): 7420–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.13.7420. PMID 7535770.
- Livingstone C, Patel G, Jones N (1995). "ATF-2 contains a phosphorylation-dependent transcriptional activation domain". EMBO J. 14 (8): 1785–97. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07167.x. PMC 398272. PMID 7737129.
- van Dam H, Wilhelm D, Herr I, Steffen A, Herrlich P, Angel P (1995). "ATF-2 is preferentially activated by stress-activated protein kinases to mediate c-jun induction in response to genotoxic agents". EMBO J. 14 (8): 1798–811. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07168.x. PMC 398273. PMID 7737130.
- Zhou Q, Gedrich RW, Engel DA (1995). "Transcriptional repression of the c-fos gene by YY1 is mediated by a direct interaction with ATF/CREB". J. Virol. 69 (7): 4323–30. doi:10.1128/JVI.69.7.4323-4330.1995. PMC 189172. PMID 7769693.
- Newell CL, Deisseroth AB, Lopez-Berestein G (1994). "Interaction of nuclear proteins with an AP-1/CRE-like promoter sequence in the human TNF-alpha gene". J. Leukoc. Biol. 56 (1): 27–35. doi:10.1002/jlb.56.1.27. PMID 8027667. S2CID 85570533.
- Nomura N, Zu YL, Maekawa T, Tabata S, Akiyama T, Ishii S (1993). "Isolation and characterization of a novel member of the gene family encoding the cAMP response element-binding protein CRE-BP1". J. Biol. Chem. 268 (6): 4259–66. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)53604-8. PMID 8440710.
- Martin ML, Lieberman PM, Curran T (1996). "Fos-Jun dimerization promotes interaction of the basic region with TFIIE-34 and TFIIF". Mol. Cell. Biol. 16 (5): 2110–8. doi:10.1128/mcb.16.5.2110. PMC 231198. PMID 8628277.
- Yang L, Lanier ER, Kraig E (1997). "Identification of a novel, spliced variant of CREB that is preferentially expressed in the thymus". J. Immunol. 158 (6): 2522–5. PMID 9058782.
- Shuman JD, Cheong J, Coligan JE (1997). "ATF-2 and C/EBPalpha can form a heterodimeric DNA binding complex in vitro. Functional implications for transcriptional regulation". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (19): 12793–800. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.19.12793. PMID 9139739.
- Fukunaga R, Hunter T (1997). "MNK1, a new MAP kinase-activated protein kinase, isolated by a novel expression screening method for identifying protein kinase substrates". EMBO J. 16 (8): 1921–33. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.8.1921. PMC 1169795. PMID 9155018.
- Kumar S, McDonnell PC, Gum RJ, Hand AT, Lee JC, Young PR (1997). "Novel homologues of CSBP/p38 MAP kinase: activation, substrate specificity and sensitivity to inhibition by pyridinyl imidazoles". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 235 (3): 533–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1997.6849. PMID 9207191.
외부 링크
- PDBe-KB는 인간 순환 AMP 의존 전사인자 ATF-2에 대한 PDB에서 사용 가능한 모든 구조 정보의 개요를 제공합니다.