허퍼진 A
Huperzine A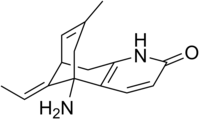 | |
 | |
| 임상 데이터 | |
|---|---|
| 기타 이름 | 후파 |
| 루트 행정부. | 오랄 |
| ATC 코드 | |
| 약동학 데이터 | |
| 반감기 제거 | 10[1]~14시간 |
| 식별자 | |
| |
| CAS 번호 | |
| PubChem CID | |
| 드러그뱅크 | |
| 켐스파이더 | |
| 유니 | |
| 체비 | |
| 첸블 | |
| CompTox 대시보드 (EPA ) | |
| ECHA 정보 카드 | 100.132.430 |
| 화학 및 물리 데이터 | |
| 공식 | C15H18N2O |
| 몰 질량 | 242.322 g/120−1 |
| 3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| 녹는점 | 217~219°C(423~426°F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Huperzine A는 Firmosh Huperzia serrata에서[2] 자연적으로 발생하는 세스키테르펜 알칼로이드 화합물이며 H. Elmeri, H. Carinat 및 H. Aqualupian을 [3]포함한 다른 식품 Huperzia 종에서 다양한 양으로 발견된다.Huperzine A는 알츠하이머병과 같은 신경학적 질환의 치료제로 연구되어 왔지만, 이러한 연구들의 메타 분석 결과, 방법론적인 품질이 떨어지는 것으로 결론지어졌고, 그 결과는 주의 [4][5]깊게 해석되어야 한다.허퍼진A는 아세틸콜린에스테라아제 효소에 의해 신경전달물질인 아세틸콜린의 분해를 억제한다.처방전 없이 살 수 있는 영양 보충제이며 기억력 및 집중력 향상을 위한 인지 증강제로 판매되고 있습니다.
약리학적 효과
Huperzia serrata에서 [2]Huperzine A를 추출한다.가역성 아세틸콜린에스테라아제[6][7][8][9] 억제제 및 혈액-뇌 [11]장벽을 가로지르는 NMDA 수용체[10] 길항제이다.아세틸콜린에스테라아제는 신경전달물질인 아세틸콜린과 신경전달물질로 기능하는 다른 콜린에스테르의 분해를 촉매하는 효소이다.Huperzine A와 아세틸콜린에스테라아제의 복합체 구조는 X선 결정학(PDB 코드: 1VOT, 3D [12]구조 참조)에 의해 결정되었다.
몇 년 동안, Huperzine A는 신경 변성으로 특징지어지는 질병,[2][13] 특히 알츠하이머병의 가능한 치료법으로 연구되어 왔다.2013년 메타 분석 결과, 후퍼진 A는 알츠하이머 병 환자의 인지 기능, 글로벌 임상 상태 및 일상생활 활동을 개선하는 데 효과적일 수 있는 것으로 나타났다.그러나 검토된 임상시험의 크기와 질이 낮기 때문에, 더 높은 품질의 연구로 유익한 [4]효과가 확인되지 않는 한, 후퍼진 A를 알츠하이머병 치료제로 권장해서는 안 된다.
Huperzine A는 또한 동물 연구와 임상 [14]연구의 긍정적인 결과를 바탕으로 기억력과 정신 기능을 향상시키는 능력에 대한 주장과 함께 식이 보조 식품으로 판매된다.
Huperzine A는 또한 자각몽을 [15]유도하는데 도움을 주는 것으로 알려져 있다.
부작용
Huperzine A는 메스꺼움, 구토, [5]설사와 같은 가벼운 콜린 작동성 부작용을 보일 수 있습니다.경미한 근육 경련과 침이 과도하게 분비되고 땀이 날 수 있을 뿐만 아니라 경미한 근육 경련과 흐릿한 말씨도 발생할 수 있다.임신 및 수유 중에는 충분한 안전 [16]데이터가 없으므로 Huperzine A를 사용하지 않는 것이 좋습니다.
약물 상호작용
Huperzine A는 심박수를 감소시킬 수 있는 베타 차단제와 [17]같이 서맥을 유발하는 약물과 함께 복용할 경우 첨가 효과가 있을 수 있다.이론적으로 후퍼진 A를 다른 아세틸콜린에스테라아제 억제제 [18]또는 콜린 작동제와 함께 복용하면 첨가성 콜린 작동 효과가 있을 수 있다.
안전.
Huperzine A는 콜린 작동성 부작용의 가능성에도 불구하고 안전성이 매우 높은 것으로 보입니다.독성학 연구에 따르면 Huperzine A는 인간 치료량의 50-100배에서 투여되어도 독성이 없는 것으로 나타났다.추출물은 2μg/kg 용량으로 6시간 동안 활성 상태이며 별다른 부작용은 없습니다.[19]
기타 가능한 용도
Huperzine A는 유기인산염 신경제 중독 치료에 유용하며, 이러한 약물에 의해 야기되는 중추신경계의 손상을 방지할 수 있다.[20] [21]
합성
Huperzine A의 확장 가능하고 효율적인 두 가지 총 합성이 [22][23]보고되었다.
레퍼런스
- ^ Li YX, Zhang RQ, Li CR, Jiang XH (2007). "Pharmacokinetics of huperzine A following oral administration to human volunteers". European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics. 32 (4): 183–187. doi:10.1007/BF03191002. PMID 18348466. S2CID 2702029.
- ^ a b c Zangara A (2003). "The psychopharmacology of huperzine A: an alkaloid with cognitive enhancing and neuroprotective properties of interest in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease". Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 75 (3): 675–686. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(03)00111-4. PMID 12895686. S2CID 36435892.
- ^ Lim WH, Goodger JQ, Field AR, Holtum JA, Woodrow IE (2010). "Huperzine alkaloids from Australasian and southeast Asian Huperzia". Pharmaceutical Biology. 48 (9): 1073–1078. doi:10.3109/13880209.2010.485619. PMID 20731560.
- ^ a b Yang G, Wang Y, Tian J, Liu J (2013). "Huperzine A for Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials". PLOS ONE. 8 (9): e74916. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...874916Y. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074916. PMC 3781107. PMID 24086396.
- ^ a b Li J, Wu HM, Zhou RL, Liu GJ, Dong BR (16 April 2008). "Huperzine A for Alzheimer's disease". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. CD005592 (2): CD005592. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005592.pub2. PMID 18425924.
- ^ Wang, R; Yan, H; Tang, XC (January 2006). "Progress in studies of huperzine A, a natural cholinesterase inhibitor from Chinese herbal medicine". Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 27 (1): 1–26. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7254.2006.00255.x. PMID 16364207. Retrieved 6 December 2017.
Huperzine A (HupA), a novel alkaloid isolated from the Chinese herb Huperzia serrata, is a potent, highly specific and reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase (AChE).
- ^ Meletis, Chris D.; Jason E. Barke (2004). Herbs and Nutrients for the Mind: A Guide to Natural Brain Enhancers. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 191. ISBN 978-0275983949.
- ^ Wang BS, Wang H, Wei ZH, Song YY, Zhang L, Chen HZ (2009). "Efficacy and safety of natural acetylcholinesterase inhibitor huperzine A in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: an updated meta-analysis". Journal of Neural Transmission. 116 (4): 457–465. doi:10.1007/s00702-009-0189-x. PMID 19221692. S2CID 8655284.
- ^ Tang X, He X, Bai D (1999). "Huperzine A: A novel acetylcholinesterase inhibitor". Drugs of the Future. 24 (6): 647. doi:10.1358/dof.1999.024.06.545143.
- ^ Coleman BR, Ratcliffe RH, Oguntayo SA, Shi X, Doctor BP, Gordon RK, Nambiar MP (2008). "[+]-Huperzine A treatment protects against N-methyl-d-aspartate-induced seizure/status epilepticus in rats". Chemico-Biological Interactions. 175 (1–3): 387–395. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2008.05.023. PMID 18588864.
- ^ Patocka J (1998). "Huperzine A - an interesting anticholinesterase compound from the Chinese herbal medicine" (PDF). Acta Medica. 41 (4): 155–7. doi:10.14712/18059694.2019.181. PMID 9951045.
- ^ Raves ML, Harel M, Pang YP, Silman I, Kozikowski AP, Sussman JL (1997). "Structure of acetylcholinesterase complexed with the nootropic alkaloid, (–)-huperzine A". Nature Structural & Molecular Biology. 4 (1): 57–63. doi:10.1038/nsb0197-57. PMID 8989325. S2CID 236518.
- ^ Bai DL, Tang XC, He XC (2000). "Huperzine A, A Potential Therapeutic Agent for Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease". Current Medicinal Chemistry. 7 (3): 355–374. doi:10.2174/0929867003375281. PMID 10637369.
- ^ Talbott, SM (2012). Huperzine A (HupA). A Guide to Understanding Dietary Supplements. Routledge. pp. 304–. ISBN 978-1-136-80570-7.
- ^ "Lucid Dreaming: A Beginner's Guide". The Four Hour Work Week. 22 September 2009. Retrieved 29 December 2016.
- ^ "Huperzine A". Natural Standard: The Authority on Integrative Medicine. Natural Standard. Retrieved 29 October 2014.
- ^ Pepping J (1 March 2000). "Huperzine A". American Journal of Health-System Pharmacy. 57 (6): 530, 533–534. doi:10.1093/ajhp/57.6.530. PMID 10754762.
- ^ Skolnick AA (12 March 1997). "Old Chinese Herbal Medicine Used for Fever Yields Possible New Alzheimer Disease Therapy". JAMA. 277 (10): 776. doi:10.1001/jama.1997.03540340010004. PMID 9052690.
- ^ Lallement, G.; Baille, V.; Baubichon, D.; Carpentier, P.; Collombet, J. M.; Filliat, P.; Foquin, A.; Four, E.; Masqueliez, C.; Testylier, G.; Tonduli, L.; Dorandeu, F. (May 2002). "Huperzine-A". Neurotoxicology. 23 (1): 1–5. doi:10.1016/S0161-813X(02)00015-3. PMID 12164543.
- ^ "Review of the Value of Huperzine as Pretreatment of Organophosphate Poisoning". Nutrition Review. 22 April 2013.
- ^ Liu, L.; Sun, J. X. (2005). "Advances on study of organophosphate poisoning prevented by Huperzine A". Wei Sheng Yan Jiu = Journal of Hygiene Research. 34 (2): 224–226. PMID 15952670.
- ^ Tun MK, Wüstmann D, Herzon SB (2011). "A robust and scalable synthesis of the potent neuroprotective agent (−)-huperzine A". Chemical Science. 2 (11): 2251–2253. doi:10.1039/C1SC00455G. S2CID 98224866.
- ^ Tudhope SR, Bellamy JA, Ball A, Rajasekar D, Azadi-Ardakani M, Meera HS, Gnanadeepam JM, Saiganesh R, Gibson F, He L, Behrens CH, Underiner G, Marfurt J, Favre N (2012). "Development of a Large-Scale Synthetic Route to Manufacture (−)-Huperzine A". Organic Process Research & Development. 16 (4): 635–642. doi:10.1021/op200360b.