코풀라 (확률론)
Copula (probability theory)확률 이론과 통계에서, 코풀라(copula)는 각 변수의 한계 확률 분포가 구간에서 균일한 다변량 누적 분포 함수다[0, 1]. 코플라는 무작위 변수들 사이의 의존성(상관간 상관성)을 설명/모형화하는 데 사용된다.[1] 1959년 응용 수학자 아베 스클라(Abe Sklar)가 도입한 이들의 이름은 언어학에서 문법 코플라와 유사하지만 관련이 없는 '링크(link)'나 '타이(tie)'를 위해 라틴어에서 유래했다. 코플라는 꼬리 위험과[2] 포트폴리오 최적화 애플리케이션을 모델링하고 최소화하기 위해 정량적 금융에서 널리 사용되어 왔다.[3]
Sclar의 정리에서는 모든 다변량 공동분포를 일변량 한계분포함수와 변수들 사이의 의존구조를 설명하는 코풀라 관점에서 작성할 수 있다고 기술하고 있다.
코풀라는 여백과 코풀라를 따로 추정해 무작위 벡터의 분포를 쉽게 모형화하고 추정할 수 있어 고차원 통계적 응용 분야에서 인기가 높다. 이용할 수 있는 많은 파라메트릭 코풀라 가족이 있는데, 이들은 대개 의존도의 강도를 조절하는 파라미터를 가지고 있다. 몇몇 인기 있는 파라메트릭 코풀라 모델은 아래에 요약되어 있다.
2차원 코플라는 퍼머톤과 두 배의 확률 측도라는 이름으로 수학의 다른 분야에서도 알려져 있다.
수학적 정의
Consider a random vector . Suppose its marginals are continuous, i.e. the marginal CDFs are continuous functions. 확률 적분 변환을 각 성분에 적용하여 랜덤 벡터
[0, 1] 구간에 균일하게 분포된 여백을 가진다.
The copula of is defined as the joint cumulative distribution function of :
코풀라 C는( 1, 2,… d )의성분들 사이의 의존 구조에 대한 모든 정보를 포함하고 있는 반면 누적 분포 함수 는 F_의 한계 분포에 대한 모든 정보를 포함하고 있다..
이러한 단계의 역방향은 다변량 확률 분포의 일반 등급에서 의사 랜덤 표본을 생성하는 데 사용할 수 있다. 즉, 코풀라 함수에서 샘플 , ,…, d) 을 생성하는 절차를 지정하면 필요한 샘플은 다음과 같이 생성될 수 있다.
F -1 {\i}^{-는 F i{\F_}}이(가) 연속적이라고 가정했기 때문에 문제가 없다. 또한 코풀라 함수에 대한 위의 공식은 다음과 같이 다시 쓸 수 있다.
정의
확률론적 용어로 :[ →[ 1] 1화살표 [ C가 단위 큐브[ d 의 d-차원 코풀라이다.[4]
분석적 로C: [ → [ ] C화살표 [는 다음과 같은 경우 d-차원 코풀라다.
- ,… - , + , d)= 인수 중 하나가 0이면 copula는 0이다.
- (,u, u, 1)= 하나의 주장이 u이고 다른 모든 1이라면 copula는 u와 동등하다.
- C is d-non-decreasing, i.e., for each hyperrectangle the C-volume of B is non-negative:
- 여기서 )=#{ k: = x N
For instance, in the bivariate case, is a bivariate copula if , and for all and .
스카라의 정리
아베 스클라(Abe Sklar)의 이름을 딴 스클라(Sklar)의 정리는 코플라(Copula)를 응용할 수 있는 이론적 토대를 제공한다.[5][6] Sklar의 정리에서는 모든 다변량 누적분포함수가
of a random vector can be expressed in terms of its marginals and a copula . Indeed:
다변량 분포에 밀도 이가) 있는 경우, 그리고 이 분포가 사용 가능한 경우 이 값을 더 유지한다.
서 c 은 코풀라의 밀도다.
The theorem also states that, given , the copula is unique on , which is the cartesian product of the ranges of the marginal cdf's. 이는 여백 가 연속적인 경우 코풀라가 고유함을 의미한다.
The converse is also true: given a copula and marginals then defines a d-dimensional cumula한계 분포 ( x) 이(가) 있는 tive 분포 함수
역점 조건
코플라는 주로 시계열이 정지해[7] 있고 연속적일 때 작용한다.[8] 따라서 매우 중요한 사전 처리 단계는 시계열 내에서 자동 상관성, 추세 및 계절성을 확인하는 것이다.
시계열은 자동 상관 관계인 경우 변수 집합 간에 존재하지 않는 의존성을 생성하여 잘못된 코풀라 의존 구조를 초래할 수 있다.[9]
프레셰-후프딩 코풀라 경계
The Fréchet–Hoeffding Theorem (after Maurice René Fréchet and Wassily Hoeffding[10]) states that for any Copula and any the following bounds hold:
함수 W는 하부 프레셰트-회프딩 바운드라고 하며 다음과 같이 정의된다.
함수 M은 상부 프래쳇-회프딩 바운드라고 하며 다음과 같이 정의된다.
상한은 날카롭다: M은 항상 코풀라, 코모노톤 랜덤 변수에 해당한다.
하한은 포인트로 날카로우며, 고정 의 경우 C~과 C ~ {\}{\이) 있다는 점에서, 하한은 포인트로 날카롭다. 그러나 W는 2차원에 불과한 코풀라로, 이 경우 부표론적 무작위 변수에 해당한다.
2차원에서, 즉 이바리테의 경우, 프레셰트-회프딩 정리(Fréchet-Heffding Organization)는 다음과 같이 기술하고 있다.
- {+ - , (, v ) { , {\\}\v)\\{
코풀라 가문
코풀라 몇 가문이 설명되어 있다.
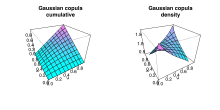
가우스 코풀라
가우스 코풀라(Gaussian copula)는 단위 하이퍼큐브 d 에 걸친 분포로 확률 적분 변환을 사용하여 에 대한 다변량 정규 분포로 구성된다.
주어진 상관 행렬 [- , d 에 대해 파라미터 R R을(를) 가진 가우스 코풀라(Gausian copula)를 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있다
여기서 - 는 표준 정규의 역 누적 분포 함수이고 R 은 상관 행렬 과 동일한 평균 벡터 0과 공분산 행렬을 가진 다변량 정규 분포의 합동 누적 분포 함수다. 코풀라 함수에 대한 간단한 분석 공식인 C ) 상한 또는 하한이 될 수 있으며, 숫자 통합을 사용하여 근사치를 구할 수 있다.[11][12] 밀도는 다음과[13] 같이 기록할 수 있다.
서 I 은는) ID 행렬이다.
아르키메데스 코플라스
아르키메데스 코플라는 연관성 있는 코플라의 부류다. 대부분의 일반적인 아르키메데스 코풀라들은 가우스 코풀라에게는 불가능한, 명시적인 공식을 인정한다. 실제로 아르키메데스 코플라는 하나의 매개 변수만으로 임의로 높은 차원으로 모델 의존도를 조절할 수 있어 인기가 높다.
코풀라 C는 대표성을[14] 인정하면 아르키메데스라고 불린다.
where is a continuous, strictly decreasing and convex function such that , is a parameter within some parameter space , \ \}은는) 소위 제너레이터 기능이며 [ - ]{\\ ^ 은(는) 정의한 유사 생성 기능이다.
또한 위의 C 공식은 - }가[ ,)[15] 에 d-monotone인 경우에만 를 산출한다. , d- 배 차이가 있고 파생상품이 충족되는 경우
for all and and is nonincreasing and convex.
가장 중요한 아르키메데스 코플라스
다음 표는 해당 발전기와 함께 가장 두드러진 바이바리산 아르키메데스 코플라를 강조한다. 이들 모두가 완전히 단조로운 것은 아니다. 즉, N 에 대한 d-모노톤이거나 특정 ∈ 에만 해당하는 d-모노톤은 아니다.
| 코풀라의 이름 | Bivariate copula (, ) | 변수 | 생성기 ( ) displaystyle \,\ | 제너레이터 역 - ( t) }^{- |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ali–Mikhail–Haq[16] | ||||
| Clayton[17] | ||||
| Frank | ||||
| Gumbel | ||||
| Independence | ||||
| Joe |
Expectation for copula models and Monte Carlo integration
In statistical applications, many problems can be formulated in the following way. One is interested in the expectation of a response function applied to some random vector .[18] If we denote the cdf of this random vector with , the quantity of interest can thus be written as
에 의해 H {\ H이(가 제공된 경우, 즉,
이 기대는 다음과 같이 다시 쓰여질 수 있다.
copula C가 절대적으로 연속적인 경우, 즉 C가 밀도 c를 갖는 경우, 이 방정식은 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있다.
그리고 각 한계 분포가 f 를 갖는 경우, 이 값을 더 유지한다.
코풀라와 마진이 알려진 경우(또는 추정된 경우) 이 기대치는 다음과 같은 몬테카를로 알고리즘을 통해 대략적으로 추정할 수 있다.
- 코풀라 C에서 n 크기의 표본 ,… , k)~ (= ,…, ) C를 그리십시오.
- By applying the inverse marginal cdf's, produce a sample of by setting
- 대략적인 E [ (X ,… , ) 을(를) 경험적 값으로 계산한다.
경험적 코플라스
다변량 데이터를 연구할 때, 기초 코풀라 조사를 원할 수 있다. 관측치가 있다고 가정합시다.
연속 여백을 갖는 임의 벡터 , 2,… , ) 에서. 그에 상응하는 "진정한" 코풀라 관찰은
그러나 한계 i 는 일반적으로 알려져 있지 않다. 따라서 경험적 분포 함수를 사용하여 유사 코풀라 관측치를 구성할 수 있다.
대신에 그 다음, 의사 코풀라 관측을 다음과 같이 정의한다.
이에 상응하는 경험적 코풀라를 다음과 같이 정의한다.
The components of the pseudo copula samples can also be written as , where is the rank of the observation :
따라서 경험적 코풀라는 순위 변환 데이터의 경험적 분포로 볼 수 있다.
스피어맨 rho의 샘플 버전:
적용들
양적금융
일반적인 재무 애플리케이션:
|
정량적 재무상태에서 위험관리, 포트폴리오 관리 및 최적화, 파생상품가격결정 등에 적용되고 있다.
전자에 대해 코플라는 극단적인 하방 사건이 발생할 수 있는 "하향/위기/패닉 정권" 동안 특히 중요한 스트레스 테스트와 건전성 검사를 수행하는 데 사용된다(예: 2007–2008년 글로벌 금융위기). 이 공식은 또한 금융 시장에 맞게 수정되었고 대출이나 채권 풀의 손실 확률 분포를 추정하는 데 사용되었다.
하방체제 동안 주식이나 부동산과 같은 위험자산에서 자리를 잡은 다수의 투자자들은 현금이나 채권과 같은 '안전한' 투자에 피신할 수 있다. 이는 또한 비행-품질 효과로도 알려져 있으며 투자자들은 단기간에 위험자산에서 대거 이탈하는 경향이 있다. 결과적으로, 하방 체제 동안, 주식들 간의 상관관계는 상승과 반대로 하락에서 더 크고 이것은 경제에 재앙적인 영향을 미칠 수 있다.[22][23] 예를 들어, 일화적으로, 우리는 종종 하루 만에 증권 거래소에서 수억 달러의 손실을 보고 있는 금융 뉴스 헤드라인을 읽는다. 그러나 우리는 같은 규모와 같은 짧은 기간 동안 주식 시장의 긍정적인 이득에 대한 보도를 거의 읽지 않는다.
코플라는 다변량 확률 모델의 여백과 의존 구조를 별도로 모델링할 수 있도록 하여 하방 체계의 영향을 분석하는 데 도움이 된다. 예를 들어, 증권거래소를 수익 극대화를 위해 각각의 전략을 가지고 영업하는 다수의 거래자로 구성된 시장으로 간주한다. 각 무역업자의 개인주의적 행동은 이윤을 모델링하는 것으로 설명할 수 있다. 그러나 모든 무역업자가 같은 거래소에서 영업하기 때문에 각 무역업자의 행동은 다른 무역업자와 상호 작용하는 효과가 있다. 이러한 상호작용 효과는 의존 구조를 모델링하여 설명할 수 있다. 따라서 코플라는 투자자들이 그들의 거래 행태와 의사결정을 무리지어 하는 경향이 있기 때문에 하방체제에 특히 관심이 있는 상호작용 효과를 분석할 수 있게 해준다. (다양한 시장 참여자들의 상호 작용으로 인해 가격이 새로운 현상으로 취급되는 에이전트 기반의 계산경제학도 참조) 또는 에이전트)
단순 버전이 그 목적에 적합하지 않다고 인정받았음에도 불구하고 단순 코풀링을 계속 사용하는 '평가문화'를 만들어 이용자들이 비판을 받아왔다.[24][25] 따라서 이전에 대규모 차원에 대한 확장 가능한 코풀라 모델은 상방 또는 하방 체계에 상관관계가 다른 상관관계 비대칭성을 허용하지 않는 타원형 의존구조(즉, 가우스와 학생-t 코풀라)의 모델링만 허용했다. 그러나 최근 덩굴 코플라스[26](일명 쌍코플라스)가 개발됨에 따라 대형차원의 포트폴리오에 대한 의존 구조를 유연하게 모델링할 수 있게 되었다.[27] 클레이튼 정식 포도 코풀라(Clayton conpical bine copula)는 극단적인 하방 사건의 발생을 가능하게 하며, 포트폴리오 최적화 및 리스크 관리 애플리케이션에 성공적으로 적용되었다. 이 모델은 극단적 하방 상관관계의 영향을 줄일 수 있으며 가우스와 학생-t 코풀라 같은 확장 가능한 타원 의존성 코풀라에 비해 향상된 통계 및 경제적 성능을 산출한다.[28]
위험관리 애플리케이션을 위해 개발된 다른 모델들은 패닉 코풀라로서, 패닉 체계가 포트폴리오 손익 분배에 미치는 영향을 분석하기 위해 한계 분포의 시장 추정치를 붙인다. 패닉 코플라는 몬테카를로 시뮬레이션에 의해 생성되며, 각 시나리오의 확률에 대한 재가중과 혼합된다.[29]
파생상품 가격 결정과 관련하여, 코풀라 함수를 사용한 의존성 모델링은 예를 들어 담보부 채무(CDO)의 가격 결정과 같은 재무위험 평가 및 보험수리적 분석의 적용에 널리 사용된다.[30] 일부에서는 가우스 코풀라를 신용파생상품에 적용하는 방법론이 2008~2009년 글로벌 금융위기의 원인 중 하나라고 믿고 있다.[31][32][33] Li § CDOs and Gaussian copula.
이러한 인식에도 불구하고, 가우스 코풀라와 코풀라 기능의 한계를 보다 일반적으로, 특히 의존 역학성의 결여를 다루기 위해, 위기 이전에 일어난 금융 산업 내에서는 문서화된 시도가 있다. 가우스 코풀라는 타원 의존 구조만 허용하기 때문에, 의존성은 분산-공분산 행렬만을 사용하여 모델링되기 때문에 부족하다.[28] 이 방법론은 금융시장이 비대칭 의존성을 보이므로 의존성이 진화하는 것을 허용하지 않기 때문에 제한적이며, 이는 상승에 비해 침체기에 자산 간 상관관계가 크게 증가한다. 따라서 가우스 코풀라를 사용한 모델링 접근방식은 극단적 사건들의 서투른 표현을 보여준다.[28][34] 코풀라 제한을 일부 수정하는 모델을 제안하려는 시도가 있었다.[34][35][36]
CDO 외에도, 코플라는 다중자산 파생상품 분석의 유연한 도구로서 다른 자산 분류에 적용되었다. 첫 번째 외부신용 적용은 바구니 구성요소의 변동성 미소를 고려하여 [37]바스켓 암시적 변동성 표면을 구성하기 위해 코풀라를 사용하는 것이었다. 그 이후 코플라는 주식, 외환 및 고정 수익 파생상품의 변동성 미소와 함께 다중 자산에 대한 옵션의 가격 책정 및 위험 관리에서[38] 인기를 얻었다.
토목공학
최근에는 고속도로 교량의 신뢰성 분석을 위한 데이터베이스 제형과 토목공학의 다양한 다변량 시뮬레이션 연구,[39] 풍력·지진공학의 신뢰성,[40] 기계·해양공학 등에 코풀라 기능이 성공적으로 적용되고 있다.[41] 연구자들은 또한 교통 흐름을 형성하는 개별 운전자들의 행동 사이의 상호작용을 이해하기 위해 교통 분야에서 이러한 기능들을 시도하고 있다.
신뢰성 공학
코플라는 경쟁적 고장 모드가 있는 기계 부품의 복잡한 시스템의 신뢰성 분석에 사용되고 있다. [42]
보증자료분석
꼬리 의존도를 분석하는 보증 데이터 분석에 코풀라 사용
난류 연소
코플라는 실제 연소 물질에서 흔히 발생하는 난류 부분 사전 혼합 연소를 모델링하는 데 사용된다. [44] [45]
약
코풀로는 예를 들어 의학 분야에 응용이 많다.
- 코풀로스는 예를 들어 자기공명영상(MRI) 분야에서, 영상을 분할하는 데,[46] 조현병 연구에서 영상유전학의 그래픽 모델의 빈자리를 메우고,[47] 정상환자와 알츠하이머환자를 구분하는 데 사용되어 왔다.[48]
- Copulæ 뇌 연구 범위를 뇌파 신호에 기초한에서는, 예를 들어, 낮 nap,[49]동안 순간 동등한 대역 폭의 변화를 추적하여 졸음을 발견할 수 있는 알츠하이머 disease,[51]진동 활동에 뇌파 channels,[52]고로 사이에 의존의 특징을 나타내는 것의 조기 진단용 동기화를 유도하기 위해(IEBWs)[50] 왔다.sess은 reliabi시간 변동 봉투를 사용하여 EEG 채널 쌍 간의 의존성을 포착하기 위한 방법 사용 능력.[53] 코풀라 함수는 신경 과학에서 신경 의존성과[54] 급증하는 카운트의 분석에 성공적으로 적용되었다.[55]
- 코풀라 모델은 종양학 분야에서 개발되었으며, 예를 들어 유전자형, 표현형, 세포 네트워크를 재구성하는 경로를 공동으로 모델링하여 특정 표현형과 다분자 특성 사이의 상호작용을 식별한다(예: 돌연변이와 유전자 발현 변화). 바오 [56]외 NCI60 암세포 라인 데이터를 사용하여 임상 표현형의 예측 변수로서 공동으로 수행하는 분자 형상의 여러 하위 집합을 식별했다. 제안된 코풀라는 암 치료에서부터 질병 예방에 이르는 생물 의학 연구에 영향을 미칠 수 있다. 코풀라는 대장내시경 영상에서 대장내막 병변의 조직학적 진단을 예측하고,[57] 암 아형을 분류하는 데도 이용되어 왔다.[58]
지오디
SSA와 코풀라 기반 방법의 조합은 EOP 예측을 위한 새로운 확률 도구로서 최초로 적용되었다.[59][60]
수문학 연구
코플라는 수경화 데이터의 이론적 분석과 응용적 분석에 모두 사용되어 왔다. 이론적 연구는 예를 들어 세계 여러 지역에서 온도와 강수량의 의존 구조를 더 잘 이해하기 위해 코풀라 기반 방법론을 채택했다.[9][61][62] 적용 연구는 코풀라 기반 방법론을 채택하여 예를 들어 농업 가뭄이나 극한 온도 및 강수량의 공동 효과가 식물의 성장에 미치는지를 조사했다.[64]
기후 및 기상 연구
코플라는 기후와 날씨와 관련된 연구에 광범위하게 사용되어 왔다.[65][66]
일조 강도 변동성
코플라는 공간 네트워크의 일조 강도 가변성을 추정하기 위해 사용되었고, 단일 위치에 대해 일시적으로 사용되어 왔다. [67] [68]
랜덤 벡터 생성
벡터와 고정 시계열의 대형 합성 흔적은 소형 데이터셋의 전체 의존 구조를 보존하면서 경험적 코풀라를 사용하여 생성될 수 있다.[69] 이러한 경험적 추적은 다양한 시뮬레이션 기반 성능 연구에 유용하다.[70]
전기 모터의 순위
코플라는 전자 정류된 모터의 제조에서 품질 순위에 사용되어 왔다.[71]
신호처리
코플라는 한계 분포를 사용하지 않고 의존 구조를 나타내기 때문에 중요하다. 코플라는 금융 분야에서 널리 사용되어 왔지만, 신호 처리에 사용되는 것은 비교적 새로운 것이다. 무선 통신 분야에서는 레이더 신호 분류, 원격 감지 응용 분야에서의 변화 감지, 의학 분야에서의 EEG 신호 처리 등이 채용되었다. 이 절에서는 코풀라 밀도 함수를 얻기 위한 짧은 수학적 도출에 이어 관련 신호 처리 애플리케이션과 함께 코풀라 밀도 함수의 목록을 제공하는 표를 제시한다.
코풀라 밀도함수의 수학적 유도
임의의 두 랜덤 변수 X와 Y에 대해 연속적인 관절 확률 분포 함수는 다음과 같이 기록할 수 있다.
where and 는 각각 랜덤 변수 X와 Y의 한계 누적 분포 함수다.
그러면 코풀라 분포함수 , v) 는 다음과 같이 Sclar의 정리를 사용하여[72][73] 정의할 수 있다.
C
where and are marginal distribution functions, joint and .
우리는 먼저 관절 확률밀도함수(PDF)와 관절 누적분포함수(CDF)와 그것의 부분파생상품 사이의 관계를 이용한다.
여기서 ( , ) c은(는) 코풀라 밀도함수이고 ( x) {\xf(는 각각 X와 Y의 한계 확률 밀도함수다. 이 방정식에는 네 가지 원소가 있다는 것을 이해하는 것이 중요하며, 세 가지 원소가 조금이라도 알려지면 네 번째 원소를 계산할 수 있다. 예를 들어, 사용될 수 있다.
- when joint probability density function between two random variables is known, the copula density function is known, and one of the two marginal functions are known, then, the other marginal function can be calculated, or
- when the two marginal functions and the copula density function are known, then the joint probability density function between the two random variables can be calculated, or
- when the two marginal functions and the joint probability density function between the two random variables are known, then the copula density function can be calculated.
List of copula density functions and applications
Various bivariate copula density functions are important in the area of signal processing. and are marginal distributions functions and and are marginal density functions. Extension and generalization of copulas for statistical signal processing have been shown to construct new bivariate copulas for exponential, Weibull, and Rician distributions.[74] Zeng et al.[75] presented algorithms, simulation, optimal selection, and practical applications of these copulas in signal processing.
| Copula density: c(u, v) | Use | |
|---|---|---|
| Gaussian | supervised classification of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images,[76] validating biometric authentication,[77] modeling stochastic dependence in large-scale integration of wind power,[78] unsupervised classification of radar signals[79] | |
| Exponential | queuing system with infinitely many servers[80] | |
| Rayleigh | bivariate exponential, Rayleigh, and Weibull copulas have been proved to be equivalent[81][82][83] | change detection from SAR images[84] |
| Weibull | bivariate exponential, Rayleigh, and Weibull copulas have been proved to be equivalent[81][82][83] | digital communication over fading channels[85] |
| Log-normal | bivariate log-normal copula and Gaussian copula are equivalent[83][82] | shadow fading along with multipath effect in wireless channel[86][87] |
| Farlie–Gumbel–Morgenstern (FGM) | information processing of uncertainty in knowledge-based systems[88] | |
| Clayton | location estimation of random signal source and hypothesis testing using heterogeneous data[89][90] | |
| Frank | change detection in remote sensing applications[91] | |
| Student's t | supervised SAR image classification,[84] fusion of correlated sensor decisions[92] | |
| Nakagami-m | ||
| Rician |
See also
References
- ^ Thorsten Schmidt (2006) "Coping with Copulas", https://web.archive.org/web/20100705040514/http://www.tu-chemnitz.de/mathematik/fima/publikationen/TSchmidt_Copulas.pdf
- ^ a b Low, R.K.Y.; Alcock, J.; Faff, R.; Brailsford, T. (2013). "Canonical vine copulas in the context of modern portfolio management: Are they worth it?". Journal of Banking & Finance. 37 (8): 3085–3099. doi:10.1016/j.jbankfin.2013.02.036. S2CID 154138333.
- ^ a b Low, R.K.Y.; Faff, R.; Aas, K. (2016). "Enhancing mean–variance portfolio selection by modeling distributional asymmetries" (PDF). Journal of Economics and Business. 85: 49–72. doi:10.1016/j.jeconbus.2016.01.003.
- ^ Nelsen, Roger B. (1999), An Introduction to Copulas, New York: Springer, ISBN 978-0-387-98623-4
- ^ Sklar, A. (1959), "Fonctions de répartition à n dimensions et leurs marges", Publ. Inst. Statist. Univ. Paris, 8: 229–231
- ^ Durante, Fabrizio; Fernández-Sánchez, Juan; Sempi, Carlo (2013), "A Topological Proof of Sklar's Theorem", Applied Mathematics Letters, 26 (9): 945–948, doi:10.1016/j.aml.2013.04.005
- ^ Sadegh, Mojtaba; Ragno, Elisa; AghaKouchak, Amir (2017). "Multivariate Copula Analysis Toolbox (MvCAT): Describing dependence and underlying uncertainty using a Bayesian framework". Water Resources Research. 53 (6): 5166–5183. Bibcode:2017WRR....53.5166S. doi:10.1002/2016WR020242. ISSN 1944-7973.
- ^ AghaKouchak, Amir; Bárdossy, András; Habib, Emad (2010). "Copula-based uncertainty modelling: application to multisensor precipitation estimates". Hydrological Processes. 24 (15): 2111–2124. doi:10.1002/hyp.7632. ISSN 1099-1085.
- ^ a b Tootoonchi, Faranak; Haerter, Jan Olaf; Räty, Olle; Grabs, Thomas; Sadegh, Mojtaba; Teutschbein, Claudia (2020-07-21). "Copulas for hydroclimatic applications – A practical note on common misconceptions and pitfalls". Hydrology and Earth System Sciences Discussions: 1–31. doi:10.5194/hess-2020-306. ISSN 1027-5606.
- ^ J. J. O'Connor and E. F. Robertson (March 2011). "Biography of Wassily Hoeffding". School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews, Scotland. Retrieved 14 February 2019.
- ^ Botev, Z. I. (2016). "The normal law under linear restrictions: simulation and estimation via minimax tilting". Journal of the Royal Statistical Society, Series B. 79: 125–148. arXiv:1603.04166. Bibcode:2016arXiv160304166B. doi:10.1111/rssb.12162. S2CID 88515228.
- ^ Botev, Zdravko I. (10 November 2015). "TruncatedNormal: Truncated Multivariate Normal" – via R-Packages.
- ^ Arbenz, Philipp (2013). "Bayesian Copulae Distributions, with Application to Operational Risk Management—Some Comments". Methodology and Computing in Applied Probability. 15 (1): 105–108. doi:10.1007/s11009-011-9224-0. hdl:20.500.11850/64244. S2CID 121861059.
- ^ a b Nelsen, R. B. (2006). An Introduction to Copulas (Second ed.). New York: Springer. ISBN 978-1-4419-2109-3.
- ^ McNeil, A. J.; Nešlehová, J. (2009). "Multivariate Archimedean copulas, d-monotone functions and 1-norm symmetric distributions". Annals of Statistics. 37 (5b): 3059–3097. arXiv:0908.3750. doi:10.1214/07-AOS556. S2CID 9858856.
- ^ Ali, M. M.; Mikhail, N. N.; Haq, M. S. (1978), "A class of bivariate distributions including the bivariate logistic", J. Multivariate Anal., 8 (3): 405–412, doi:10.1016/0047-259X(78)90063-5
- ^ Clayton, David G. (1978). "A model for association in bivariate life tables and its application in epidemiological studies of familial tendency in chronic disease incidence". Biometrika. 65 (1): 141–151. doi:10.1093/biomet/65.1.141. JSTOR 2335289.
- ^ Alexander J. McNeil, Rudiger Frey and Paul Embrechts (2005) "Quantitative Risk Management: Concepts, Techniques, and Tools", Princeton Series in Finance
- ^ Nelsen, Roger B. (2006). An introduction to copulas (2nd ed.). New York: Springer. p. 220. ISBN 978-0-387-28678-5.
- ^ a b Low, Rand (2017-05-11). "Vine copulas: modelling systemic risk and enhancing higher-moment portfolio optimisation". Accounting & Finance. 58: 423–463. doi:10.1111/acfi.12274.
- ^ Rad, Hossein; Low, Rand Kwong Yew; Faff, Robert (2016-04-27). "The profitability of pairs trading strategies: distance, cointegration and copula methods". Quantitative Finance. 16 (10): 1541–1558. doi:10.1080/14697688.2016.1164337. S2CID 219717488.
- ^ Longin, F; Solnik, B (2001), "Extreme correlation of international equity markets", Journal of Finance, 56 (2): 649–676, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.321.4899, doi:10.1111/0022-1082.00340, S2CID 6143150
- ^ Ang, A; Chen, J (2002), "Asymmetric correlations of equity portfolios", Journal of Financial Economics, 63 (3): 443–494, doi:10.1016/s0304-405x(02)00068-5
- ^ Felix Salmon. "Recipe for Disaster: The Formula That Killed Wall Street" Wired Magazine, Feb 2m 2009, https://www.wired.com/2009/02/wp-quant/
- ^ Donald Mackenzie and Taylor Spears. 'The formula that killed Wall Street': The Gaussian copula and modelling practices in investment banking. Social Studies of Science Vol. 44, No. 3 (June 2014), pp. 393-417. https://www.jstor.org/stable/43284238
- ^ Cooke, R.M.; Joe, H.; Aas, K. (January 2011). Kurowicka, D.; Joe, H. (eds.). Dependence Modeling Vine Copula Handbook (PDF). World Scientific. pp. 37–72. ISBN 978-981-4299-87-9.
- ^ Aas, K; Czado, C; Bakken, H (2009), "Pair-copula constructions of multiple dependence", Insurance: Mathematics and Economics, 44 (2): 182–198, CiteSeerX 10.1.1.61.3984, doi:10.1016/j.insmatheco.2007.02.001
- ^ a b c Low, R; Alcock, J; Brailsford, T; Faff, R (2013), "Canonical vine copulas in the context of modern portfolio management: Are they worth it?", Journal of Banking and Finance, 37 (8): 3085–3099, doi:10.1016/j.jbankfin.2013.02.036, S2CID 154138333
- ^ Meucci, Attilio (2011), "A New Breed of Copulas for Risk and Portfolio Management", Risk, 24 (9): 122–126
- ^ Meneguzzo, David; Vecchiato, Walter (Nov 2003), "Copula sensitivity in collateralized debt obligations and basket default swaps", Journal of Futures Markets, 24 (1): 37–70, doi:10.1002/fut.10110
- ^ Recipe for Disaster: The Formula That Killed Wall Street Wired, 2/23/2009
- ^ MacKenzie, Donald (2008), "End-of-the-World Trade", London Review of Books (published 2008-05-08), pp. 24–26, retrieved 2009-07-27
- ^ Jones, Sam (April 24, 2009), "The formula that felled Wall St", Financial Times
- ^ a b Lipton, Alexander; Rennie, Andrew (2008). Credit Correlation: Life After Copulas. World Scientific. ISBN 978-981-270-949-3.
- ^ Donnelly, C; Embrechts, P (2010). "The devil is in the tails: actuarial mathematics and the subprime mortgage crisis". ASTIN Bulletin 40(1), 1–33. Cite journal requires
journal=(help) - ^ Brigo, D; Pallavicini, A; Torresetti, R (2010). Credit Models and the Crisis: A Journey into CDOs, Copulas, Correlations and dynamic Models. Wiley and Sons.
- ^ Qu, Dong (2001). "Basket Implied Volatility Surface". Derivatives Week (4 June).
- ^ Qu, Dong (2005). "Pricing Basket Options With Skew". Wilmott Magazine (July).
- ^ Thompson, David; Kilgore, Roger (2011), "Estimating Joint Flow Probabilities at Stream Confluences using Copulas", Transportation Research Record, 2262: 200–206, doi:10.3141/2262-20, S2CID 17179491, retrieved 2012-02-21
- ^ Yang, S.C.; Liu, T.J.; Hong, H.P. (2017). "Reliability of Tower and Tower-Line Systems under Spatiotemporally Varying Wind or Earthquake Loads". Journal of Structural Engineering. 143 (10): 04017137. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0001835.
- ^ Zhang, Yi; Beer, Michael; Quek, Ser Tong (2015-07-01). "Long-term performance assessment and design of offshore structures". Computers & Structures. 154: 101–115. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2015.02.029.
- ^ Pham, Hong (2003), Handbook of Reliability Engineering, Springer, pp. 150–151
- ^ Wu, S. (2014), "Construction of asymmetric copulas and its application in two-dimensional reliability modelling" (PDF), European Journal of Operational Research, 238 (2): 476–485, doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2014.03.016, S2CID 22916401
- ^ Ruan, S.; Swaminathan, N; Darbyshire, O (2014), "Modelling of turbulent lifted jet flames using flamelets: a priori assessment and a posteriori validation", Combustion Theory and Modelling, 18 (2): 295–329, Bibcode:2014CTM....18..295R, doi:10.1080/13647830.2014.898409, S2CID 53641133
- ^ Darbyshire, O.R.; Swaminathan, N (2012), "A presumed joint pdf model for turbulent combustion with varying equivalence ratio", Combustion Science and Technology, 184 (12): 2036–2067, doi:10.1080/00102202.2012.696566, S2CID 98096093
- ^ Lapuyade-Lahorgue, Jerome; Xue, Jing-Hao; Ruan, Su (July 2017). "Segmenting Multi-Source Images Using Hidden Markov Fields With Copula-Based Multivariate Statistical Distributions". IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. 26 (7): 3187–3195. Bibcode:2017ITIP...26.3187L. doi:10.1109/tip.2017.2685345. ISSN 1057-7149. PMID 28333631. S2CID 11762408.
- ^ Zhang, Aiying; Fang, Jian; Calhoun, Vince D.; Wang, Yu-ping (April 2018). "High dimensional latent Gaussian copula model for mixed data in imaging genetics". 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2018). IEEE: 105–109. doi:10.1109/isbi.2018.8363533. ISBN 978-1-5386-3636-7. S2CID 44114562.
- ^ Bahrami, Mohsen; Hossein-Zadeh, Gholam-Ali (May 2015). "Assortativity changes in Alzheimer's disease: A resting-state FMRI study". 2015 23rd Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering. IEEE: 141–144. doi:10.1109/iraniancee.2015.7146198. ISBN 978-1-4799-1972-7. S2CID 20649428.
- ^ Qian, Dong; Wang, Bei; Qing, Xiangyun; Zhang, Tao; Zhang, Yu; Wang, Xingyu; Nakamura, Masatoshi (April 2017). "Drowsiness Detection by Bayesian-Copula Discriminant Classifier Based on EEG Signals During Daytime Short Nap". IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. 64 (4): 743–754. doi:10.1109/tbme.2016.2574812. ISSN 0018-9294. PMID 27254855. S2CID 24244444.
- ^ Yoshida, Hisashi; Kuramoto, Haruka; Sunada, Yusuke; Kikkawa, Sho (August 2007). "EEG Analysis in Wakefulness Maintenance State against Sleepiness by Instantaneous Equivalent Bandwidths". 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE. 2007: 19–22. doi:10.1109/iembs.2007.4352212. ISBN 978-1-4244-0787-3. PMID 18001878. S2CID 29527332.
- ^ Iyengar, Satish G.; Dauwels, Justin; Varshney, Pramod K.; Cichocki, Andrzej (2010). "Quantifying EEG synchrony using copulas". 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. IEEE: 505–508. doi:10.1109/icassp.2010.5495664. ISBN 978-1-4244-4295-9. S2CID 16476449.
- ^ Gao, Xu; Shen, Weining; Ting, Chee-Ming; Cramer, Steven C.; Srinivasan, Ramesh; Ombao, Hernando (April 2019). "Estimating Brain Connectivity Using Copula Gaussian Graphical Models". 2019 IEEE 16th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI 2019). IEEE: 108–112. doi:10.1109/isbi.2019.8759538. ISBN 978-1-5386-3641-1. S2CID 195881851.
- ^ Fadlallah, B. H.; Brockmeier, A. J.; Seth, S.; Lin Li; Keil, A.; Principe, J. C. (August 2012). "An Association Framework to Analyze Dependence Structure in Time Series". 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. IEEE. 2012: 6176–6179. doi:10.1109/embc.2012.6347404. ISBN 978-1-4577-1787-1. PMID 23367339. S2CID 9061806.
- ^ Eban, E; Rothschild, R; Mizrahi, A; Nelken, I; Elidan, G (2013), Carvalho, C; Ravikumar, P (eds.), "Dynamic Copula Networks for Modeling Real-valued Time Series" (PDF), Journal of Machine Learning Research, 31
- ^ Onken, A; Grünewälder, S; Munk, MH; Obermayer, K (2009), Aertsen, Ad (ed.), "Analyzing Short-Term Noise Dependencies of Spike-Counts in Macaque Prefrontal Cortex Using Copulas and the Flashlight Transformation", PLOS Computational Biology, 5 (11): e1000577, Bibcode:2009PLSCB...5E0577O, doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000577, PMC 2776173, PMID 19956759
- ^ Bao, Le; Zhu, Zhou; Ye, Jingjing (March 2009). "Modeling oncology gene pathways network with multiple genotypes and phenotypes via a copula method". 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology. IEEE: 237–246. doi:10.1109/cibcb.2009.4925734. ISBN 978-1-4244-2756-7. S2CID 16779505.
- ^ Kwitt, Roland; Uhl, Andreas; Hafner, Michael; Gangl, Alfred; Wrba, Friedrich; Vecsei, Andreas (June 2010). "Predicting the histology of colorectal lesions in a probabilistic framework". 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition - Workshops. IEEE: 103–110. doi:10.1109/cvprw.2010.5543146. ISBN 978-1-4244-7029-7. S2CID 14841548.
- ^ Kon, M. A.; Nikolaev, N. (December 2011). "Empirical Normalization for Quadratic Discriminant Analysis and Classifying Cancer Subtypes". 2011 10th International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications and Workshops. IEEE: 374–379. doi:10.1109/icmla.2011.160. hdl:2144/38445. ISBN 978-1-4577-2134-2. S2CID 346934.
- ^ Modiri, S.; Belda, S.; Heinkelmann, R.; Hoseini, M.; Ferrándiz, J.M.; Schuh, H. (2018). "Polar motion prediction using the combination of SSA and Copula-based analysis". Earth, Planets and Space. 70 (70): 115. Bibcode:2018EP&S...70..115M. doi:10.1186/s40623-018-0888-3. PMC 6434970. PMID 30996648.
- ^ Modiri, S.; Belda, S.; Hoseini, M.; Heinkelmann, R.; Ferrándiz, J.M.; Schuh, H. (2020). "A new hybrid method to improve the ultra-short-term prediction of LOD". Journal of Geodesy. 94 (23): 23. Bibcode:2020JGeod..94...23M. doi:10.1007/s00190-020-01354-y. PMC 7004433. PMID 32109976.
- ^ Lazoglou, Georgia; Anagnostopoulou, Christina (February 2019). "Joint distribution of temperature and precipitation in the Mediterranean, using the Copula method". Theoretical and Applied Climatology. 135 (3–4): 1399–1411. Bibcode:2019ThApC.135.1399L. doi:10.1007/s00704-018-2447-z. ISSN 0177-798X. S2CID 125268690.
- ^ Cong, Rong-Gang; Brady, Mark (2012). "The Interdependence between Rainfall and Temperature: Copula Analyses". The Scientific World Journal. 2012: 405675. doi:10.1100/2012/405675. ISSN 1537-744X. PMC 3504421. PMID 23213286.
- ^ Wang, Long; Yu, Hang; Yang, Maoling; Yang, Rui; Gao, Rui; Wang, Ying (April 2019). "A drought index: The standardized precipitation evapotranspiration runoff index". Journal of Hydrology. 571: 651–668. Bibcode:2019JHyd..571..651W. doi:10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.02.023.
- ^ Alidoost, Fakhereh; Su, Zhongbo; Stein, Alfred (December 2019). "Evaluating the effects of climate extremes on crop yield, production and price using multivariate distributions: A new copula application". Weather and Climate Extremes. 26: 100227. doi:10.1016/j.wace.2019.100227.
- ^ Schölzel, C.; Friederichs, P. (2008). "Multivariate non-normally distributed random variables in climate research – introduction to the copula approach". Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics. 15 (5): 761–772. Bibcode:2008NPGeo..15..761S. doi:10.5194/npg-15-761-2008.
- ^ Laux, P.; Vogl, S.; Qiu, W.; Knoche, H.R.; Kunstmann, H. (2011). "Copula-based statistical refinement of precipitation in RCM simulations over complex terrain". Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 15 (7): 2401–2419. Bibcode:2011HESS...15.2401L. doi:10.5194/hess-15-2401-2011.
- ^ Munkhammar, J.; Widén, J. (2017). "A copula method for simulating correlated instantaneous solar irradiance in spatial networks". Solar Energy. 143: 10–21. Bibcode:2017SoEn..143...10M. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2016.12.022.
- ^ Munkhammar, J.; Widén, J. (2017). "An autocorrelation-based copula model for generating realistic clear-sky index time-series". Solar Energy. 158: 9–19. Bibcode:2017SoEn..158....9M. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2017.09.028.
- ^ Strelen, Johann Christoph (2009). Tools for Dependent Simulation Input with Copulas. 2nd International ICST Conference on Simulation Tools and Techniques. doi:10.4108/icst.simutools2009.5596.
- ^ Bandara, H. M. N. D.; Jayasumana, A. P. (Dec 2011). On Characteristics and Modeling of P2P Resources with Correlated Static and Dynamic Attributes. IEEE Globecom. pp. 1–6. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.309.3975. doi:10.1109/GLOCOM.2011.6134288. ISBN 978-1-4244-9268-8. S2CID 7135860.
- ^ Mileva Boshkoska, Biljana; Bohanec, Marko; Boškoski, Pavle; Juričić, Ðani (2015-04-01). "Copula-based decision support system for quality ranking in the manufacturing of electronically commutated motors". Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing. 26 (2): 281–293. doi:10.1007/s10845-013-0781-7. ISSN 1572-8145. S2CID 982081.
- ^ Appell, Paul; Goursat, Edouard (1895). Théorie des fonctions algébriques et de leurs intégrales étude des fonctions analytiques sur une surface de Riemann / par Paul Appell, Édouard Goursat. Paris: Gauthier-Villars. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.18731.
- ^ Durante, Fabrizio; Fernández-Sánchez, Juan; Sempi, Carlo (2013). "A topological proof of Sklar's theorem". Applied Mathematics Letters. 26 (9): 945–948. doi:10.1016/j.aml.2013.04.005. ISSN 0893-9659.
- ^ Zeng, Xuexing; Ren, Jinchang; Wang, Zheng; Marshall, Stephen; Durrani, Tariq (January 2014). "Copulas for statistical signal processing (Part I): Extensions and generalization" (PDF). Signal Processing. 94: 691–702. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.07.009. ISSN 0165-1684.
- ^ Zeng, Xuexing; Ren, Jinchang; Sun, Meijun; Marshall, Stephen; Durrani, Tariq (January 2014). "Copulas for statistical signal processing (Part II): Simulation, optimal selection and practical applications" (PDF). Signal Processing. 94: 681–690. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.07.006. ISSN 0165-1684.
- ^ Storvik, B.; Storvik, G.; Fjortoft, R. (2009). "On the Combination of Multisensor Data Using Meta-Gaussian Distributions". IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. 47 (7): 2372–2379. Bibcode:2009ITGRS..47.2372S. doi:10.1109/tgrs.2009.2012699. ISSN 0196-2892. S2CID 371395.
- ^ Dass, S.C.; Yongfang Zhu; Jain, A.K. (2006). "Validating a Biometric Authentication System: Sample Size Requirements". IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. 28 (12): 1902–1319. doi:10.1109/tpami.2006.255. ISSN 0162-8828. PMID 17108366. S2CID 1272268.
- ^ Papaefthymiou, G.; Kurowicka, D. (2009). "Using Copulas for Modeling Stochastic Dependence in Power System Uncertainty Analysis". IEEE Transactions on Power Systems. 24 (1): 40–49. Bibcode:2009ITPSy..24...40P. doi:10.1109/tpwrs.2008.2004728. ISSN 0885-8950.
- ^ Brunel, N.J.-B.; Lapuyade-Lahorgue, J.; Pieczynski, W. (2010). "Modeling and Unsupervised Classification of Multivariate Hidden Markov Chains With Copulas". IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control. 55 (2): 338–349. doi:10.1109/tac.2009.2034929. ISSN 0018-9286. S2CID 941655.
- ^ Lai, Chin Diew; Balakrishnan, N. (2009). Continuous Bivariate Distributions. doi:10.1007/b101765. ISBN 978-0-387-09613-1.
- ^ a b Durrani, T.S.; Zeng, X. (2007). "Copulas for bivariate probability distributions". Electronics Letters. 43 (4): 248. Bibcode:2007ElL....43..248D. doi:10.1049/el:20073737. ISSN 0013-5194.
- ^ a b c Liu, X. (2010). "Copulas of bivariate Rayleigh and log-normal distributions". Electronics Letters. 46 (25): 1669. Bibcode:2010ElL....46.1669L. doi:10.1049/el.2010.2777. ISSN 0013-5194.
- ^ a b c Zeng, Xuexing; Ren, Jinchang; Wang, Zheng; Marshall, Stephen; Durrani, Tariq (2014). "Copulas for statistical signal processing (Part I): Extensions and generalization" (PDF). Signal Processing. 94: 691–702. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.07.009. ISSN 0165-1684.
- ^ a b Hachicha, S.; Chaabene, F. (2010). Frouin, Robert J; Yoo, Hong Rhyong; Won, Joong-Sun; Feng, Aiping (eds.). "SAR change detection using Rayleigh copula". Remote Sensing of the Coastal Ocean, Land, and Atmosphere Environment. SPIE. 7858: 78581F. Bibcode:2010SPIE.7858E..1FH. doi:10.1117/12.870023. S2CID 129437866.
- ^ "Coded Communication over Fading Channels", Digital Communication over Fading Channels, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., pp. 758–795, 2005, doi:10.1002/0471715220.ch13, ISBN 978-0-471-71522-1
- ^ Das, Saikat; Bhattacharya, Amitabha (2020). "Application of the Mixture of Lognormal Distribution to Represent the First-Order Statistics of Wireless Channels". IEEE Systems Journal. 14 (3): 4394–4401. Bibcode:2020ISysJ..14.4394D. doi:10.1109/JSYST.2020.2968409. ISSN 1932-8184. S2CID 213729677.
- ^ Alouini, M.-S.; Simon, M.K. (2002). "Dual diversity over correlated log-normal fading channels". IEEE Transactions on Communications. 50 (12): 1946–1959. doi:10.1109/TCOMM.2002.806552. ISSN 0090-6778.
- ^ Kolesárová, Anna; Mesiar, Radko; Saminger-Platz, Susanne (2018), Medina, Jesús; Ojeda-Aciego, Manuel; Verdegay, José Luis; Pelta, David A. (eds.), "Generalized Farlie-Gumbel-Morgenstern Copulas", Information Processing and Management of Uncertainty in Knowledge-Based Systems. Theory and Foundations, Springer International Publishing, 853, pp. 244–252, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-91473-2_21, ISBN 978-3-319-91472-5
- ^ Sundaresan, Ashok; Varshney, Pramod K. (2011). "Location Estimation of a Random Signal Source Based on Correlated Sensor Observations". IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing. 59 (2): 787–799. Bibcode:2011ITSP...59..787S. doi:10.1109/tsp.2010.2084084. ISSN 1053-587X. S2CID 5725233.
- ^ Iyengar, Satish G.; Varshney, Pramod K.; Damarla, Thyagaraju (2011). "A Parametric Copula-Based Framework for Hypothesis Testing Using Heterogeneous Data". IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing. 59 (5): 2308–2319. Bibcode:2011ITSP...59.2308I. doi:10.1109/tsp.2011.2105483. ISSN 1053-587X. S2CID 5549193.
- ^ Mercier, G.; Moser, G.; Serpico, S.B. (2008). "Conditional Copulas for Change Detection in Heterogeneous Remote Sensing Images". IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing. 46 (5): 1428–1441. Bibcode:2008ITGRS..46.1428M. doi:10.1109/tgrs.2008.916476. ISSN 0196-2892. S2CID 12208493.
- ^ Sundaresan, Ashok; Varshney, Pramod K.; Rao, Nageswara S. V. (2011). "Copula-Based Fusion of Correlated Decisions". IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems. 47 (1): 454–471. Bibcode:2011ITAES..47..454S. doi:10.1109/taes.2011.5705686. ISSN 0018-9251. S2CID 22562771.
Further reading
- The standard reference for an introduction to copulas. Covers all fundamental aspects, summarizes the most popular copula classes, and provides proofs for the important theorems related to copulas
- Roger B. Nelsen (1999), "An Introduction to Copulas", Springer. ISBN 978-0-387-98623-4
- A book covering current topics in mathematical research on copulas:
- Piotr Jaworski, Fabrizio Durante, Wolfgang Karl Härdle, Tomasz Rychlik (Editors): (2010): "Copula Theory and Its Applications" Lecture Notes in Statistics, Springer. ISBN 978-3-642-12464-8
- A reference for sampling applications and stochastic models related to copulas is
- Jan-Frederik Mai, Matthias Scherer (2012): Simulating Copulas (Stochastic Models, Sampling Algorithms and Applications). World Scientific. ISBN 978-1-84816-874-9
- A paper covering the historic development of copula theory, by the person associated with the "invention" of copulas, Abe Sklar.
- Abe Sklar (1997): "Random variables, distribution functions, and copulas – a personal look backward and forward" in Rüschendorf, L., Schweizer, B. und Taylor, M. (eds) Distributions With Fixed Marginals & Related Topics (Lecture Notes – Monograph Series Number 28). ISBN 978-0-940600-40-9
- The standard reference for multivariate models and copula theory in the context of financial and insurance models
- Alexander J. McNeil, Rudiger Frey and Paul Embrechts (2005) "Quantitative Risk Management: Concepts, Techniques, and Tools", Princeton Series in Finance. ISBN 978-0-691-12255-7
External links
- "Copula", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press, 2001 [1994]
- Copula Wiki: community portal for researchers with interest in copulas
- A collection of Copula simulation and estimation codes
- Copulas & Correlation using Excel Simulation Articles
- Chapter 1 of Jan-Frederik Mai, Matthias Scherer (2012) "Simulating Copulas: Stochastic Models, Sampling Algorithms, and Applications"

![{\displaystyle F_{i}(x)=\Pr[X_{i}\leq x]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2980e5dcb25467ed9d2238ba1990c9aff7ca8b5c)


![{\displaystyle C(u_{1},u_{2},\dots ,u_{d})=\Pr[U_{1}\leq u_{1},U_{2}\leq u_{2},\dots ,U_{d}\leq u_{d}].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9a94a2eeb84fc83baad8a1e819ff4f8b46b9fd07)




![{\displaystyle C(u_{1},u_{2},\dots ,u_{d})=\Pr[X_{1}\leq F_{1}^{-1}(u_{1}),X_{2}\leq F_{2}^{-1}(u_{2}),\dots ,X_{d}\leq F_{d}^{-1}(u_{d})].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/01a3e0330faabf83d10247540cabac352edd1f5a)
![[0,1]^{d}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e13ae4917276744b214714a20b3cb8ee305e309d)
![C:[0,1]^{d}\rightarrow [0,1]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/40af55f356a2e5d65a93019852c1c5e0cbf07625) .
.

![B=\prod _{i=1}^{d}[x_{i},y_{i}]\subseteq [0,1]^{d}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/351f96aa29a3d1851e3bbc80c6348449ffe0746c)


![{\displaystyle C:[0,1]\times [0,1]\rightarrow [0,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f271c6025d698ce8ebf1078044d193b1a5587a94)







![{\displaystyle H(x_{1},\dots ,x_{d})=\Pr[X_{1}\leq x_{1},\dots ,X_{d}\leq x_{d}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2b6e179e9bd5d86f303c58ae8fef0e67155ddbce)
![{\displaystyle F_{i}(x_{i})=\Pr[X_{i}\leq x_{i}]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/787d08554a01e4fc5b4100e85eb73e3137cf5cf1)




 코풀라의 밀도다.
코풀라의 밀도다. 




![(u_{1},\dots ,u_{d})\in [0,1]^{d}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f357cb50ea6b8e6f47f4f470b5436fa090f658c6)







![{\displaystyle R\in [-1,1]^{d\times d}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1a071e34a31e85adcd94121469d8f270035b2eaf)






![{\displaystyle C(u_{1},\dots ,u_{d};\theta )=\psi ^{[-1]}\left(\psi (u_{1};\theta )+\cdots +\psi (u_{d};\theta );\theta \right)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e14136d227b55fcd8527f288eeb736d0279e2d85)
![\psi \!:[0,1]\times \Theta \rightarrow [0,\infty )](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/72604f5871b27926c148bace5587ddf8d8c16946)




![\psi ^{[-1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6f5a9a83275e37dfa551138b6420eadcb18e7917) (는) 정의한 유사 생성 기능이다.
(는) 정의한 유사 생성 기능이다. ![{\displaystyle \psi ^{[-1]}(t;\theta )=\left\{{\begin{array}{ll}\psi ^{-1}(t;\theta )&{\mbox{if }}0\leq t\leq \psi (0;\theta )\\0&{\mbox{if }}\psi (0;\theta )\leq t\leq \infty .\end{array}}\right.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a1f44a5e0acb87f721756ccfa4172e461dc039a9)








 해당하는 d-모노톤은 아니다.
해당하는 d-모노톤은 아니다. 
![{\displaystyle \theta \in [-1,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5fcef395b022543b8655b81eaf82ecf028550abb)
![\log \!\left[{\frac {1-\theta (1-t)}{t}}\right]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4cd29ebc997de95a338f66163136f5513152e4e3)

![\left[\max \left\{u^{-\theta }+v^{-\theta }-1;0\right\}\right]^{-1/\theta }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7266b1df307368fd625b261caee57a2136bcd521)



![-{\frac {1}{\theta }}\log \!\left[1+{\frac {(\exp(-\theta u)-1)(\exp(-\theta v)-1)}{\exp(-\theta )-1}}\right]](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/594e71d78f84f97fa19a76d57940d15fe68f998e)



![{\textstyle \exp \!\left[-\left((-\log(u))^{\theta }+(-\log(v))^{\theta }\right)^{1/\theta }\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/739c3170ca7ea51fe7489b2e6248e8fe26768720)






![{\textstyle {1-\left[(1-u)^{\theta }+(1-v)^{\theta }-(1-u)^{\theta }(1-v)^{\theta }\right]^{1/\theta }}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c30e67e928a1c0940b7b030587d29affda291fc4)




![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} \left[g(X_{1},\dots ,X_{d})\right]=\int _{\mathbb {R} ^{d}}g(x_{1},\dots ,x_{d})\,\mathrm {d} H(x_{1},\dots ,x_{d}).}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d3b79232a4f8caba8f38d321679233824256d4d3)

![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} \left[g(X_{1},\dots ,X_{d})\right]=\int _{[0,1]^{d}}g(F_{1}^{-1}(u_{1}),\dots ,F_{d}^{-1}(u_{d}))\,\mathrm {d} C(u_{1},\dots ,u_{d}).}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/926f937f6b5cdce4c11e058b18cf41ac585a0324)
![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} \left[g(X_{1},\dots ,X_{d})\right]=\int _{[0,1]^{d}}g(F_{1}^{-1}(u_{1}),\dots ,F_{d}^{-1}(u_{d}))\cdot c(u_{1},\dots ,u_{d})\,du_{1}\cdots \mathrm {d} u_{d},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/7e63d57530cb81f73691e124bbe7ef057a65b29e)

![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} \left[g(X_{1},\dots ,X_{d})\right]=\int _{\mathbb {R} ^{d}}g(x_{1},\dots x_{d})\cdot c(F_{1}(x_{1}),\dots ,F_{d}(x_{d}))\cdot f_{1}(x_{1})\cdots f_{d}(x_{d})\,\mathrm {d} x_{1}\cdots \mathrm {d} x_{d}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/cea4d38bc3f0acf3b8a35a0db2922da06bd02fa9)

![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} \left[g(X_{1},\dots ,X_{d})\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/ba4b7e451d1c2f65485ec3b5f1469324bafacb52)
![{\displaystyle \operatorname {E} \left[g(X_{1},\dots ,X_{d})\right]\approx {\frac {1}{n}}\sum _{k=1}^{n}g(X_{1}^{k},\dots ,X_{d}^{k})}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6f1c7564cfbe956cd4fe9d987b4a185270bb4914)









![{\displaystyle r={\frac {12}{n^{2}-1}}\sum _{i=1}^{n}\sum _{i=1}^{n}\left[C^{n}\left({\frac {i}{n}},{\frac {j}{n}}\right)-{\frac {i}{n}}\cdot {\frac {j}{n}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c22466afa5ac0291f10092b9bb5db3c8baacf375)



 각각 랜덤 변수 X와 Y의 한계 누적 분포 함수다.
각각 랜덤 변수 X와 Y의 한계 누적 분포 함수다. 






 (는) 코풀라 밀도함수이고
(는) 코풀라 밀도함수이고



![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}={}&1+\theta (1-2u)(1-2v)\\&{\text{where }}\theta \in [-1,1]\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/b30181c64bf603461998b09871a4969e8f86cad8)






