Mdm2
Mdm2E3 유비퀴틴-단백질 연결효소 Mdm2로도 알려진 마우스 더블미닛2 호몰로그(MDM2)는 사람에게서 MDM2 [5][6]유전자에 의해 암호화되는 단백질이다.Mdm2는 p53 종양 억제제의 중요한 음성 조절기입니다.Mdm2 단백질은 p53 종양억제제의 N말단 트랜스활성화 도메인(TAD)을 인식하는 E3 유비퀴틴 연결효소 및 p53 전사활성화 억제제로서 기능한다.
종양세포의 발견과 발현
Mdm2 단백질을 코드하는 뮤린 더블미닛(mdm2) 종양유전자는 원래 변형된 마우스 세포주 3T3-DM의 두 개의 다른 유전자(mdm1과 mdm3)와 함께 복제되었다. Mdm2 과잉발현은 발암성 Ras와 협력하여 1차 설치류 섬유아세포의 형성과 mdm2의 누드발현을 촉진한다.얼음. 이 단백질의 인간 상동성은 나중에 확인되었고 때때로 Hdm2라고 불린다.종양유전자로서의 mdm2의 역할을 더욱 뒷받침하기 위해, 유방종양뿐만 아니라 연조직육종, 골육종 등을 포함한 몇몇 인간종양에서 Mdm2의 수치가 증가한 것으로 나타났다.MDM2 온코프로틴은 p53을 유비쿼터스화 및 길항하지만 p53의존성 기능을 수행할 수도 있다.MDM2는 p53에 의존하지 않고 혈통 고유의 유전자에 대한 폴리콤 매개 억제를 지원합니다.p53이 없는 상태에서 MDM2 고갈은 인간 간엽 줄기세포의 분화를 촉진하고 암세포의 클로노제닉 생존을 감소시켰다.MDM2 제어 유전자의 대부분은 폴리콤 억제 복합체 2(PRC2)와 그 촉매 성분 EZH2의 불활성화에도 반응했다.염색질에서 EZH2와 물리적으로 관련된 MDM2는 리신27(H3K27me3)에서의 히스톤3의 트리메틸화와 그 표적유전자에서의 리신119(H2AK119)에서의 히스톤2A의 유비쿼티화를 촉진한다.H2AK119 E3 리가아제 링1B/RNF2와 동시에 MDM2를 제거함으로써 이들 유전자를 더욱 유도하여 세포의 [7]증식을 합성적으로 억제하였다.
추가 Mdm2 패밀리멤버 Mdm4(MdmX라고도 불립니다)가 검출되어 p53의 중요한 네거티브 레귤레이터이기도 합니다.
MDM2는 또한 저항하지 않는 p53 활성화가 p53 과활성화 의존성 세포사망으로 이어지기 때문에 장기발달과 조직의 항상성을 위해 필요하다.포도자멸증은 카스파아제 비의존적이며 따라서 아포토시스와는 다르다.MDM2의 승모원적 역할은 조직 손상 시 상처 치유에도 필요하며, MDM2 억제는 상피 손상 시 재상피화를 손상시킨다.또한 MDM2는 핵인자 카파 베타(NFκB) 활성화에서 p53-비의존성 전사인자 유사효과를 가진다.따라서 MDM2는 조직 염증을 촉진하고 MDM2 억제는 조직 손상에 강력한 항염증 효과가 있다.따라서 MDM2 차단은 전신성 홍반성 낭창이나 초승달성 사구체신염과 [8]같은 특정 암이나 림프증식성 자가면역과 같은 염증성 및 과증식성 질환에 부가적인 치료 효과가 있을 수 있는 항염증 및 항유도 효과가 대부분이었다.
유비쿼티네이션 대상: p53
Mdm2의 주요 표적은 p53 종양 억제제이다.Mdm2는 p53 전사 활성을 억제하는 p53 상호작용 단백질로 확인되었다.Mdm2는 p53의 N 터미널 트랜스 액티베이션도메인에 바인드 및 블로킹함으로써 이 억제를 실현합니다.Mdm2는 p53 응답성 유전자입니다.즉, 그 전사는 p53에 의해 활성화 될 수 있습니다.따라서 p53이 안정화되면 Mdm2의 전사가 유도되어 Mdm2 단백질 수치가 높아진다.
E3 리가아제 활성
E3 유비퀴틴 연결효소 MDM2는 p53 종양 억제 단백질의 음성 조절제입니다.MDM2는 p53을 바인드 및 편재시켜 열화를 촉진합니다.p53은 MDM2의 전사를 유도하여 네거티브 피드백 [9]루프를 생성합니다.Mdm2는 또한 E3 유비퀴틴 연결효소로 작용하여 프로테아솜에 의한 분해에 대해 자신과 p53을 모두 목표로 한다(유비퀴틴 참조).p53 C 말단의 여러 리신 잔기가 유비퀴티네이션 부위로 확인되었으며, 프로테아솜 의존적인 방식으로 Mdm2에 의해 p53 단백질 수치가 하향 조절되는 것으로 나타났다.Mdm2는 자가 폴리유비퀴티네이션이 가능하며, p300과 복합체에서는 E3 유비퀴틴 결합효소인 p53이 폴리유비퀴티네이션이 가능하다.이와 같이 Mdm2 및 p53은 p53 안정화 신호가 없을 때 p53 레벨을 낮게 유지하는 네거티브 피드백 제어 루프의 멤버입니다.이 루프는 DNA 손상을 포함한 p53 활성화 신호가 높을 때 키나아제 및 p14arf와 같은 유전자에 의해 간섭될 수 있습니다.
구조 및 기능
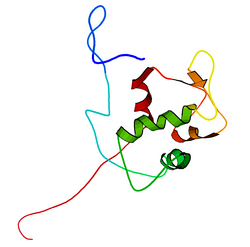
mdm2 유전자의 전장 전사물은 예측 분자량 56kDa의 491개의 아미노산 단백질을 암호화한다.이 단백질은 N-말단 p53 상호작용 도메인을 포함한 여러 보존된 구조 도메인을 포함하고 있으며, 그 구조는 X선 결정학을 사용하여 해결되었다.Mdm2 단백질은 또한 중심 산성 도메인(잔류 230-300)을 포함합니다.이 영역 내 잔류물의 인산화 작용은 Mdm2 기능의 조절에 중요한 것으로 보인다.또한 이 지역은 Mdm2의 적절한 핵 세포질 밀매에 필수적인 핵 수출입 신호를 포함하고 있다.Mdm2 단백질 내에서 보존된 또 다른 도메인은 아연 핑거 도메인으로, 그 기능은 잘 알려져 있지 않다.
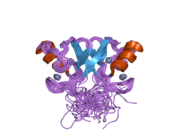
Mdm2는 또한 아연의 두 이온을 조정하는 Cis3-His2-Cis3 컨센서스를 포함하는 C-말단 RING 도메인(아미노산 잔류물 430-480)을 포함한다.이러한 잔류물은 아연 결합에 필요하며, 이는 RING 도메인의 적절한 접힘에 필수적이다.Mdm2의 RING 도메인은 E3 유비퀴틴 리가아제 활성을 부여하며, Mdm2 RING 자동 결합에서 E3 리가아제 활성을 부여하기에 충분하다.Mdm2의 RING 도메인은 뉴클레오티드 결합 단백질의 보존된 워커 A 또는 P-루프 모티브와 핵소자 국재 시퀀스를 통합한다는 점에서 독특하다.RING 도메인은 또한 RNA에 특이적으로 결합하지만, 이것의 기능은 잘 알려져 있지 않습니다.
규정
Mdm2의 조절에는 몇 가지 알려진 메커니즘이 있습니다.이러한 메커니즘 중 하나는 Mdm2 단백질의 인산화이다.Mdm2는 세포의 여러 부위에서 인산화된다.DNA 손상에 이어 Mdm2의 인산화도 단백질 기능의 변화와 p53의 안정화를 이끈다.또한 Mdm2의 중심산성 영역 내의 특정 잔류물에서의 인산화도 p53을 분해 대상으로 하는 능력을 자극할 수 있다.HIPK2는 이런 식으로 Mdm2를 조절하는 단백질이다.p16INK4a 궤적의 대체 판독 프레임 산물인 p14arf 단백질의 유도도 p53-Mdm2 상호작용을 부정적으로 조절하는 메커니즘입니다.p14arf는 Mdm2와 직접 상호작용하여 p53 전사 응답의 상향 조절로 이어집니다.ARF는 적절한 p53 분해에 핵 수출이 필수적이기 때문에 핵물질의 수출 억제와 p53의 활성화를 초래하는 Mdm2를 핵물질에 격납한다.
MDM2-p53 상호작용의 억제제는 시스이미다졸린 아날로그 [10]너틀린을 포함한다.
Mdm2의 수준과 안정성 또한 유비쿼티라이제이션에 의해 조절된다.Mdm2는 프로테아솜에 의해 분해될 수 있는 자동 유비쿼티레이트입니다.Mdm2는 또한 유비퀴틴 특이 단백질 효소인 USP7과 상호작용하여 Mdm2-유비퀴틸화를 역전시키고 프로테아솜에 의해 분해되는 것을 방지할 수 있다.또한 USP7은 Mdm2의 주요 타깃인 p53 단백질의 분해로부터 보호합니다.따라서 Mdm2와 USP7은 복잡한 회로를 형성하여 p53의 안정성과 액티비티를 미세하게 조절합니다.p53의 레벨은 기능에 매우 중요합니다.
상호 작용

Mdm2는 다음 제품과 상호 작용하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
- ABL1,[11]
- ARB1,[12][13]
- ARB2,[12][13][14]
- CCNG1,[15]
- CTBP1,[16]
- CTBP2,[16]
- DAXX,[17]
- DHFR,[18]
- EP300,[19]
- ERICH3,[20]
- FKBP3,[21]
- FOXO4,[22]
- GNL3,[23]
- HDAC1,[24]
- HIF1A,[25][26]
- HTATIP,[27]
- IGF1R,[28]
- MDM4,[29][30][31][32]
- 무감각하다[33][34]
- P16,[17][35][36][37][38]
- P53,[39][40]
- P73,[41][42]
- PCAF,[43]
- PSMD10,[44]
- PSME3,[45]
- RPL5,[23][35][46]
- RPL11,[23][35]
- PML,[47][48][49][50]
- RPL26,[51]
- RRM2B,[52]
- RYBP,[53]
- TBP [54][55]및
- UBC.[17][56][57]
Mdm2 p53에 의존하지 않는 역할
Mdm2 과발현은 P53과는 무관하고 Mdm2와 Nbs1 사이의 새롭고 직접적인 상호작용을 통해 매개되는 DNA 이중 가닥 단절을 억제하는 것으로 나타났다.p53 상태에 관계없이 Mdm2의 수치가 증가했지만 Nbs1 결합 도메인이 없는 Mdm2는 증가하지 않아 DNA 파괴 복구 지연, 염색체 이상 및 게놈 불안정성을 초래했다.이러한 데이터는 Mdm2 유도 게놈 불안정성을 Mdm2:Nbs1 상호작용을 통해 매개할 수 있으며 p53과의 연관성과는 무관하다는 것을 보여주었다.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSG00000135679 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSMUSG000020184 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Oliner JD, Kinzler KW, Meltzer PS, George DL, Vogelstein B (July 1992). "Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas". Nature. 358 (6381): 80–3. Bibcode:1992Natur.358...80O. doi:10.1038/358080a0. hdl:2027.42/62637. PMID 1614537. S2CID 1056405.
- ^ Wade M, Wong ET, Tang M, Stommel JM, Wahl GM (November 2006). "Hdmx modulates the outcome of p53 activation in human tumor cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (44): 33036–44. doi:10.1074/jbc.M605405200. PMID 16905769. S2CID 16619596.
- ^ Wienken M, Dickmanns A, Nemajerova A, Kramer D, Najafova Z, Weiss M, Karpiuk O, Kassem M, Zhang Y, Lozano G, Johnsen SA, Moll UM, Zhang X, Dobbelstein M (January 2016). "MDM2 Associates with Polycomb Repressor Complex 2 and Enhances Stemness-Promoting Chromatin Modifications Independent of p53". Molecular Cell. 61 (1): 68–83. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.12.008. PMC 6284523. PMID 26748827.
- ^ Ebrahim M, Mulay SR, Anders HJ, Thomasova D (November 2015). "MDM2 beyond cancer: podoptosis, development, inflammation, and tissue regeneration". Histology and Histopathology. 30 (11): 1271–82. doi:10.14670/HH-11-636. PMID 26062755.
- ^ Huun J, Gansmo LB, Mannsåker B, Iversen GT, Sommerfelt-Pettersen J, Øvrebø JI, Lønning PE, Knappskog S (October 2017). "The Functional Roles of the MDM2 Splice Variants P2-MDM2-10 and MDM2-∆5 in Breast Cancer Cells". Translational Oncology. 10 (5): 806–817. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2017.07.006. PMC 5576977. PMID 28844019.
- ^ Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, Kong N, Kammlott U, Lukacs C, Klein C, Fotouhi N, Liu EA (February 2004). "In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2". Science. 303 (5659): 844–8. Bibcode:2004Sci...303..844V. doi:10.1126/science.1092472. PMID 14704432. S2CID 16132757.
- ^ Goldberg Z, Vogt Sionov R, Berger M, Zwang Y, Perets R, Van Etten RA, Oren M, Taya Y, Haupt Y (July 2002). "Tyrosine phosphorylation of Mdm2 by c-Abl: implications for p53 regulation". The EMBO Journal. 21 (14): 3715–27. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf384. PMC 125401. PMID 12110584.
- ^ a b Wang P, Wu Y, Ge X, Ma L, Pei G (March 2003). "Subcellular localization of beta-arrestins is determined by their intact N domain and the nuclear export signal at the C terminus". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (13): 11648–53. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208109200. PMID 12538596. S2CID 8453277.
- ^ a b Shenoy SK, Xiao K, Venkataramanan V, Snyder PM, Freedman NJ, Weissman AM (August 2008). "Nedd4 mediates agonist-dependent ubiquitination, lysosomal targeting, and degradation of the beta2-adrenergic receptor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 283 (32): 22166–76. doi:10.1074/jbc.M709668200. PMC 2494938. PMID 18544533.
- ^ Wang P, Gao H, Ni Y, Wang B, Wu Y, Ji L, Qin L, Ma L, Pei G (February 2003). "Beta-arrestin 2 functions as a G-protein-coupled receptor-activated regulator of oncoprotein Mdm2". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (8): 6363–70. doi:10.1074/jbc.M210350200. PMID 12488444. S2CID 28251970.
- ^ Zhao L, Samuels T, Winckler S, Korgaonkar C, Tompkins V, Horne MC, Quelle DE (January 2003). "Cyclin G1 has growth inhibitory activity linked to the ARF-Mdm2-p53 and pRb tumor suppressor pathways". Molecular Cancer Research. 1 (3): 195–206. PMID 12556559.
- ^ a b Mirnezami AH, Campbell SJ, Darley M, Primrose JN, Johnson PW, Blaydes JP (July 2003). "Hdm2 recruits a hypoxia-sensitive corepressor to negatively regulate p53-dependent transcription" (PDF). Current Biology. 13 (14): 1234–9. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(03)00454-8. PMID 12867035. S2CID 2451241.
- ^ a b c Ivanchuk SM, Mondal S, Rutka JT (June 2008). "p14ARF interacts with DAXX: effects on HDM2 and p53". Cell Cycle. 7 (12): 1836–50. doi:10.4161/cc.7.12.6025. PMID 18583933. S2CID 13168647.
- ^ Maguire M, Nield PC, Devling T, Jenkins RE, Park BK, Polański R, Vlatković N, Boyd MT (May 2008). "MDM2 regulates dihydrofolate reductase activity through monoubiquitination". Cancer Research. 68 (9): 3232–42. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-5271. PMC 3536468. PMID 18451149.
- ^ Grossman SR, Perez M, Kung AL, Joseph M, Mansur C, Xiao ZX, Kumar S, Howley PM, Livingston DM (October 1998). "p300/MDM2 complexes participate in MDM2-mediated p53 degradation". Molecular Cell. 2 (4): 405–15. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80140-9. PMID 9809062.
- ^ Miyamoto-Sato E, Fujimori S, Ishizaka M, Hirai N, Masuoka K, Saito R, Ozawa Y, Hino K, Washio T, Tomita M, Yamashita T, Oshikubo T, Akasaka H, Sugiyama J, Matsumoto Y, Yanagawa H (Feb 2010). "A comprehensive resource of interacting protein regions for refining human transcription factor networks". PLOS ONE. 5 (2): e9289. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...5.9289M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009289. PMC 2827538. PMID 20195357.
- ^ Ochocka AM, Kampanis P, Nicol S, Allende-Vega N, Cox M, Marcar L, Milne D, Fuller-Pace F, Meek D (February 2009). "FKBP25, a novel regulator of the p53 pathway, induces the degradation of MDM2 and activation of p53". FEBS Letters. 583 (4): 621–6. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2009.01.009. PMID 19166840. S2CID 6110.
- ^ Brenkman AB, de Keizer PL, van den Broek NJ, Jochemsen AG, Burgering BM (2008). "Mdm2 induces mono-ubiquitination of FOXO4". PLOS ONE. 3 (7): e2819. Bibcode:2008PLoSO...3.2819B. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002819. PMC 2475507. PMID 18665269.
- ^ a b c Dai MS, Sun XX, Lu H (July 2008). "Aberrant expression of nucleostemin activates p53 and induces cell cycle arrest via inhibition of MDM2". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 28 (13): 4365–76. doi:10.1128/MCB.01662-07. PMC 2447154. PMID 18426907.
- ^ Ito A, Kawaguchi Y, Lai CH, Kovacs JJ, Higashimoto Y, Appella E, Yao TP (November 2002). "MDM2-HDAC1-mediated deacetylation of p53 is required for its degradation". The EMBO Journal. 21 (22): 6236–45. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf616. PMC 137207. PMID 12426395.
- ^ Chen D, Li M, Luo J, Gu W (April 2003). "Direct interactions between HIF-1 alpha and Mdm2 modulate p53 function". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (16): 13595–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.C200694200. PMID 12606552. S2CID 85351036.
- ^ Ravi R, Mookerjee B, Bhujwalla ZM, Sutter CH, Artemov D, Zeng Q, Dillehay LE, Madan A, Semenza GL, Bedi A (January 2000). "Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by p53-induced degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha". Genes & Development. 14 (1): 34–44. doi:10.1101/gad.14.1.34. PMC 316350. PMID 10640274.
- ^ Legube G, Linares LK, Lemercier C, Scheffner M, Khochbin S, Trouche D (April 2002). "Tip60 is targeted to proteasome-mediated degradation by Mdm2 and accumulates after UV irradiation". The EMBO Journal. 21 (7): 1704–12. doi:10.1093/emboj/21.7.1704. PMC 125958. PMID 11927554.
- ^ Sehat B, Andersson S, Girnita L, Larsson O (July 2008). "Identification of c-Cbl as a new ligase for insulin-like growth factor-I receptor with distinct roles from Mdm2 in receptor ubiquitination and endocytosis". Cancer Research. 68 (14): 5669–77. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6364. PMID 18632619.
- ^ Kadakia M, Brown TL, McGorry MM, Berberich SJ (December 2002). "MdmX inhibits Smad transactivation". Oncogene. 21 (57): 8776–85. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205993. PMID 12483531. S2CID 38919290.
- ^ Tanimura S, Ohtsuka S, Mitsui K, Shirouzu K, Yoshimura A, Ohtsubo M (March 1999). "MDM2 interacts with MDMX through their RING finger domains". FEBS Letters. 447 (1): 5–9. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(99)00254-9. PMID 10218570. S2CID 20021952.
- ^ Badciong JC, Haas AL (December 2002). "MdmX is a RING finger ubiquitin ligase capable of synergistically enhancing Mdm2 ubiquitination". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (51): 49668–75. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208593200. PMID 12393902. S2CID 21036861.
- ^ Linke K, Mace PD, Smith CA, Vaux DL, Silke J, Day CL (May 2008). "Structure of the MDM2/MDMX RING domain heterodimer reveals dimerization is required for their ubiquitylation in trans". Cell Death and Differentiation. 15 (5): 841–8. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4402309. PMID 18219319. S2CID 24048476.
- ^ Yogosawa S, Miyauchi Y, Honda R, Tanaka H, Yasuda H (March 2003). "Mammalian Numb is a target protein of Mdm2, ubiquitin ligase". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 302 (4): 869–72. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00282-1. PMID 12646252.
- ^ Colaluca IN, Tosoni D, Nuciforo P, Senic-Matuglia F, Galimberti V, Viale G, Pece S, Di Fiore PP (January 2008). "NUMB controls p53 tumour suppressor activity". Nature. 451 (7174): 76–80. Bibcode:2008Natur.451...76C. doi:10.1038/nature06412. PMID 18172499. S2CID 4431258.
- ^ a b c Zhang Y, Wolf GW, Bhat K, Jin A, Allio T, Burkhart WA, Xiong Y (December 2003). "Ribosomal protein L11 negatively regulates oncoprotein MDM2 and mediates a p53-dependent ribosomal-stress checkpoint pathway". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 23 (23): 8902–12. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.23.8902-8912.2003. PMC 262682. PMID 14612427.
- ^ Zhang Y, Xiong Y, Yarbrough WG (March 1998). "ARF promotes MDM2 degradation and stabilizes p53: ARF-INK4a locus deletion impairs both the Rb and p53 tumor suppression pathways". Cell. 92 (6): 725–34. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81401-4. PMID 9529249. S2CID 334187.
- ^ Clark PA, Llanos S, Peters G (July 2002). "Multiple interacting domains contribute to p14ARF mediated inhibition of MDM2". Oncogene. 21 (29): 4498–507. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205558. PMID 12085228. S2CID 5636220.
- ^ Pomerantz J, Schreiber-Agus N, Liégeois NJ, Silverman A, Alland L, Chin L, Potes J, Chen K, Orlow I, Lee HW, Cordon-Cardo C, DePinho RA (March 1998). "The Ink4a tumor suppressor gene product, p19Arf, interacts with MDM2 and neutralizes MDM2's inhibition of p53". Cell. 92 (6): 713–23. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81400-2. PMID 9529248. S2CID 17190271.
- ^ Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A, Oren M (May 1997). "Mdm2 promotes the rapid degradation of p53". Nature. 387 (6630): 296–9. Bibcode:1997Natur.387..296H. doi:10.1038/387296a0. PMID 9153395. S2CID 4336620.
- ^ Honda R, Tanaka H, Yasuda H (December 1997). "Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase E3 for tumor suppressor p53". FEBS Letters. 420 (1): 25–7. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01480-4. PMID 9450543. S2CID 29014813.
- ^ Bálint E, Bates S, Vousden KH (July 1999). "Mdm2 binds p73 alpha without targeting degradation". Oncogene. 18 (27): 3923–9. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202781. PMID 10435614. S2CID 36277590.
- ^ Zeng X, Chen L, Jost CA, Maya R, Keller D, Wang X, Kaelin WG, Oren M, Chen J, Lu H (May 1999). "MDM2 suppresses p73 function without promoting p73 degradation". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 19 (5): 3257–66. doi:10.1128/mcb.19.5.3257. PMC 84120. PMID 10207051.
- ^ Jin Y, Zeng SX, Dai MS, Yang XJ, Lu H (August 2002). "MDM2 inhibits PCAF (p300/CREB-binding protein-associated factor)-mediated p53 acetylation". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (34): 30838–43. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204078200. PMID 12068014. S2CID 45597631.
- ^ Qiu W, Wu J, Walsh EM, Zhang Y, Chen CY, Fujita J, Xiao ZX (July 2008). "Retinoblastoma protein modulates gankyrin-MDM2 in regulation of p53 stability and chemosensitivity in cancer cells". Oncogene. 27 (29): 4034–43. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.43. PMID 18332869. S2CID 7815368.
- ^ Zhang Z, Zhang R (March 2008). "Proteasome activator PA28 gamma regulates p53 by enhancing its MDM2-mediated degradation". The EMBO Journal. 27 (6): 852–64. doi:10.1038/emboj.2008.25. PMC 2265109. PMID 18309296.
- ^ Marechal V, Elenbaas B, Piette J, Nicolas JC, Levine AJ (November 1994). "The ribosomal L5 protein is associated with mdm-2 and mdm-2-p53 complexes". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 14 (11): 7414–20. doi:10.1128/mcb.14.11.7414. PMC 359276. PMID 7935455.
- ^ Bernardi R, Scaglioni PP, Bergmann S, Horn HF, Vousden KH, Pandolfi PP (July 2004). "PML regulates p53 stability by sequestering Mdm2 to the nucleolus". Nature Cell Biology. 6 (7): 665–72. doi:10.1038/ncb1147. PMID 15195100. S2CID 26281860.
- ^ Zhu H, Wu L, Maki CG (December 2003). "MDM2 and promyelocytic leukemia antagonize each other through their direct interaction with p53". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (49): 49286–92. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308302200. PMID 14507915. S2CID 21775225.
- ^ Kurki S, Latonen L, Laiho M (October 2003). "Cellular stress and DNA damage invoke temporally distinct Mdm2, p53 and PML complexes and damage-specific nuclear relocalization". Journal of Cell Science. 116 (Pt 19): 3917–25. doi:10.1242/jcs.00714. PMID 12915590. S2CID 10448090.
- ^ Wei X, Yu ZK, Ramalingam A, Grossman SR, Yu JH, Bloch DB, Maki CG (August 2003). "Physical and functional interactions between PML and MDM2". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (31): 29288–97. doi:10.1074/jbc.M212215200. PMID 12759344. S2CID 27707203.
- ^ Ofir-Rosenfeld Y, Boggs K, Michael D, Kastan MB, Oren M (October 2008). "Mdm2 regulates p53 mRNA translation through inhibitory interactions with ribosomal protein L26". Molecular Cell. 32 (2): 180–9. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2008.08.031. PMC 2587494. PMID 18951086.
- ^ Chang L, Zhou B, Hu S, Guo R, Liu X, Jones SN, Yen Y (November 2008). "ATM-mediated serine 72 phosphorylation stabilizes ribonucleotide reductase small subunit p53R2 protein against MDM2 to DNA damage". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 105 (47): 18519–24. Bibcode:2008PNAS..10518519C. doi:10.1073/pnas.0803313105. PMC 2587585. PMID 19015526.
- ^ Chen D, Zhang J, Li M, Rayburn ER, Wang H, Zhang R (February 2009). "RYBP stabilizes p53 by modulating MDM2". EMBO Reports. 10 (2): 166–72. doi:10.1038/embor.2008.231. PMC 2637313. PMID 19098711.
- ^ Léveillard T, Wasylyk B (December 1997). "The MDM2 C-terminal region binds to TAFII250 and is required for MDM2 regulation of the cyclin A promoter". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (49): 30651–61. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.49.30651. PMID 9388200. S2CID 8983914.
- ^ Thut CJ, Goodrich JA, Tjian R (August 1997). "Repression of p53-mediated transcription by MDM2: a dual mechanism". Genes & Development. 11 (15): 1974–86. doi:10.1101/gad.11.15.1974. PMC 316412. PMID 9271120.
- ^ Song MS, Song SJ, Kim SY, Oh HJ, Lim DS (July 2008). "The tumour suppressor RASSF1A promotes MDM2 self-ubiquitination by disrupting the MDM2-DAXX-HAUSP complex". The EMBO Journal. 27 (13): 1863–74. doi:10.1038/emboj.2008.115. PMC 2486425. PMID 18566590.
- ^ Yang W, Dicker DT, Chen J, El-Deiry WS (March 2008). "CARPs enhance p53 turnover by degrading 14-3-3sigma and stabilizing MDM2". Cell Cycle. 7 (5): 670–82. doi:10.4161/cc.7.5.5701. PMID 18382127. S2CID 83606690.
추가 정보
- Cahilly-Snyder L, Yang-Feng T, Francke U, George DL (May 1987). "Molecular analysis and chromosomal mapping of amplified genes isolated from a transformed mouse 3T3 cell line". Somatic Cell and Molecular Genetics. 13 (3): 235–44. doi:10.1007/BF01535205. PMID 3474784. S2CID 27300300.
- Chen J, Lin J, Levine AJ (January 1995). "Regulation of transcription functions of the p53 tumor suppressor by the mdm-2 oncogene". Molecular Medicine. 1 (2): 142–52. doi:10.1007/BF03401562. PMC 2229942. PMID 8529093.
- Fang S, Jensen JP, Ludwig RL, Vousden KH, Weissman AM (March 2000). "Mdm2 is a RING finger-dependent ubiquitin protein ligase for itself and p53". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (12): 8945–51. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.12.8945. PMID 10722742. S2CID 25630836.
- Freedman DA, Wu L, Levine AJ (January 1999). "Functions of the MDM2 oncoprotein". Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 55 (1): 96–107. doi:10.1007/s000180050273. PMID 10065155. S2CID 20034406.
- Hay TJ, Meek DW (July 2000). "Multiple sites of in vivo phosphorylation in the MDM2 oncoprotein cluster within two important functional domains". FEBS Letters. 478 (1–2): 183–6. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01850-0. PMID 10922493. S2CID 40688636.
- Honda R, Tanaka H, Yasuda H (December 1997). "Oncoprotein MDM2 is a ubiquitin ligase E3 for tumor suppressor p53". FEBS Letters. 420 (1): 25–7. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(97)01480-4. PMID 9450543. S2CID 29014813.
- Honda R, Yasuda H (March 2000). "Activity of MDM2, a ubiquitin ligase, toward p53 or itself is dependent on the RING finger domain of the ligase". Oncogene. 19 (11): 1473–6. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203464. PMID 10723139. S2CID 8734229.
- Kubbutat MH, Jones SN, Vousden KH (May 1997). "Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2". Nature. 387 (6630): 299–303. Bibcode:1997Natur.387..299K. doi:10.1038/387299a0. PMID 9153396. S2CID 4329670.
- Kussie PH, Gorina S, Marechal V, Elenbaas B, Moreau J, Levine AJ, Pavletich NP (November 1996). "Structure of the MDM2 oncoprotein bound to the p53 tumor suppressor transactivation domain". Science. 274 (5289): 948–53. Bibcode:1996Sci...274..948K. doi:10.1126/science.274.5289.948. PMID 8875929. S2CID 33081920.
- Meek DW, Knippschild U (December 2003). "Posttranslational modification of MDM2". Molecular Cancer Research. 1 (14): 1017–26. PMID 14707285.
- Midgley CA, Desterro JM, Saville MK, Howard S, Sparks A, Hay RT, Lane DP (May 2000). "An N-terminal p14ARF peptide blocks Mdm2-dependent ubiquitination in vitro and can activate p53 in vivo". Oncogene. 19 (19): 2312–23. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203593. PMID 10822382. S2CID 24814361.
- Momand J, Wu HH, Dasgupta G (January 2000). "MDM2--master regulator of the p53 tumor suppressor protein". Gene. 242 (1–2): 15–29. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00487-4. PMID 10721693.
- Momand J, Zambetti GP, Olson DC, George D, Levine AJ (June 1992). "The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation". Cell. 69 (7): 1237–45. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-R. PMID 1535557. S2CID 22594319.
- Shieh SY, Ikeda M, Taya Y, Prives C (October 1997). "DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53 alleviates inhibition by MDM2". Cell. 91 (3): 325–34. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80416-X. PMID 9363941. S2CID 11328296.
- Tao W, Levine AJ (June 1999). "P19(ARF) stabilizes p53 by blocking nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of Mdm2". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (12): 6937–41. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.6937T. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.12.6937. PMC 22020. PMID 10359817.
- Tao W, Levine AJ (March 1999). "Nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of oncoprotein Hdm2 is required for Hdm2-mediated degradation of p53". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (6): 3077–80. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.3077T. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.6.3077. PMC 15897. PMID 10077639.