메타 티라미네
meta-Tyramine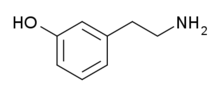 | |
 | |
| 이름 | |
|---|---|
| 선호 IUPAC 이름 3-(2-아미노에틸)페놀 | |
| 기타 이름 m-Tyramine; 3-Tyramine; 3-히드록시페닐틸아민 | |
| 식별자 | |
3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| 체비 | |
| 켐스파이더 | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.197.155 |
펍켐 CID | |
| 유니 | |
CompTox 대시보드 (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| 특성. | |
| C8H11NO | |
| 어금질량 | 137.1987 g·190−1 |
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하고, 표준 상태(25°C [77°F], 100 kPa)의 재료에 대한 데이터가 제공된다. | |
| Infobox 참조 자료 | |
m-tyramine과 3-tyramine으로도 알려진 메타-Tyramine은 내생적인 미량 아민 신경계통체로서 페네틸아민의 구조적인 아날로그물이다.[1][2][3] 그것은 파라티라마인의 위치 이성질체로서, 그것과 유사하게 아드레날린과 도파민계통에 영향을 미친다.[4][5]
메타 티라미인은 방향족 아미노산 데카복실라제 매개 메타티로신 대사를 통해 인간에서 생성되며,[6] 메타 티라미인은 인간 내 말초나 뇌 CYP2D6 효소를 통해 도파민으로 대사될 수 있다.[7]
참고 항목
참조
- ^ Boulton AA, Huebert ND (November 1981). "Biosynthesis of some urinary trace amines in the rat and the human". Research Communications in Chemical Pathology and Pharmacology. 34 (2): 295–310. PMID 7335956.
- ^ Dyck LE, Juorio AV, Boulton AA (June 1982). "The in vitro release of endogenous m-tyramine, p-tyramine and dopamine from rat striatum". Neurochemical Research. 7 (6): 705–16. doi:10.1007/bf00965523. PMID 7121718. S2CID 20758261.
- ^ Sardar A, Juorio AV, Boulton AA (June 1987). "The concentration of p- and m-tyramine in the rat mesolimbic system: its regional distribution and effect of monoamine oxidase inhibition". Brain Research. 412 (2): 370–4. doi:10.1016/0006-8993(87)91145-0. PMID 3607473. S2CID 34094088.
- ^ Dyck LE, Kazakoff CW, Dourish CT (October 1982). "The role of catecholamines, 5-hydroxytryptamine and m-tyramine in the behavioural effects of m-tyrosine in the rat". European Journal of Pharmacology. 84 (3–4): 139–49. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(82)90196-0. PMID 7173317.
- ^ McQuade PS, Wood PL (1984). "The effects of administration of meta-tyramine and para-tyramine on dopamine and its metabolites in the rat striatum". Progress in Neuro-psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry. 8 (4–6): 705–9. doi:10.1016/0278-5846(84)90042-3. PMID 6531442. S2CID 24889205.
- ^ "EC 4.1.1.28 – Aromatic-L-amino-acid decarboxylase (Homo sapiens)". BRENDA. Technische Universität Braunschweig. July 2016. Retrieved 7 October 2016.
Substrate: m-tyrosine
Product: m-tyramine + CO2
Organism: Homo sapiens
반응도 - ^ Wang X, Li J, Dong G, Yue J (February 2014). "The endogenous substrates of brain CYP2D". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 724: 211–218. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.12.025. PMID 24374199.
The highest level of brain CYP2D activity was found in the substantia nigra ... The in vitro and in vivo studies have shown the contribution of the alternative CYP2D-mediated dopamine synthesis to the concentration of this neurotransmitter although the classic biosynthetic route to dopamine from tyrosine is active. ... Tyramine levels are especially high in the basal ganglia and limbic system, which are thought to be related to individual behavior and emotion (Yu et al., 2003c). ... Rat CYP2D isoforms (2D2/2D4/2D18) are less efficient than human CYP2D6 for the generation of dopamine from p-tyramine. The Km values of the CYP2D isoforms are as follows: CYP2D6 (87–121 μm) ≈ CYP2D2 ≈ CYP2D18 > CYP2D4 (256 μm) for m-tyramine and CYP2D4 (433 μm) > CYP2D2 ≈ CYP2D6 > CYP2D18 (688 μm) for p-tyramine


