아포콜라네르
Afoxolaner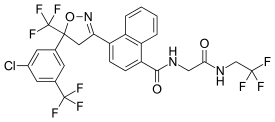 | |
| 임상자료 | |
|---|---|
| 발음 | /eɪˌfɒksoʊˈlænər/ Ay-FOK-soh-LAN-lan-lan-lan-lan-lan- |
| 상명 | 넥스가드, 프런트프로 |
| 기타 이름 | 4-[(5RS)-5-(5-Chloro-α,α,α-trifluoro-m-tolyl)-4,5-dihydro-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-oxazol-3-yl]-N-[2-oxo-2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethylamino)ethyl]naphthalene-1-carboxamide |
| 라이센스 데이터 | |
| 경로: 행정 | 입으로(치즈) |
| ATCvet 코드 | |
| 법적현황 | |
| 법적현황 | |
| 약동학 데이터 | |
| 생체이용가능성 | 74%(Tmax = 2~4시간)[1] |
| 제거 반감기 | 14시간[1] |
| 배설 | 담즙관(주요경로) |
| 식별자 | |
| |
| CAS 번호 | |
| 펍켐 CID | |
| 드러그뱅크 | |
| 켐스파이더 | |
| 유니 | |
| 케그 | |
| 켐벨 | |
| CompTox 대시보드 (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.267.822 |
| 화학 및 물리적 데이터 | |
| 공식 | C26H17CLF9N3O3 |
| 어금질량 | 625.88 g·migration−1 |
| 3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| 치랄리티 | 인종 혼합물 |
| |
| |
아포콜라네르(INN)[2]는 이소카졸린 화학 화합물 그룹에 속하는 살충제·아카리아제다.
특히 신경전달물질 감마-아미노부티르산(GABA-receptors)에 의해 게이트된 염화 리간드 채널에서 길항제 역할을 한다. 이소사졸린은 염화 채널 변조기 중 곤충 GABA-gated solidate channel 내의 독특하고 독특한 표적지에 결합하여 세포막을 가로질러 염화 이온의 사전 및 사후 시냅스 전달을 차단한다. 아포콜라네르 유도 과대확산술은 중추신경계의 통제되지 않은 활동과 곤충과 아카린의 죽음을 초래한다.[3]
마케팅
아포콜라너는 수의약품인 넥스가드(혼자), 프런트프로(혼자), 넥스가드 스펙트럼(밀배미신 옥소임과 결합)의 활성원리다.[4][5][6] 벼룩의 치료와 예방, 개와 강아지(생후 8주 이상, 몸무게 4파운드(약 1.8kg) 이상)의 진드기 충혈 치료와 통제를 위해 1개월간 처방된다.[7] 이 제품들은 일단 먹이를 주기 시작하면 구강으로 투여되고 독성 플라이가 먹이를 먹기 시작한다.
2014년 2월 유럽 의약품청(European Medicine Agency, European Medicine Agency), 넥스가드 스펙트럼(NexGard Spectrum)에 대해 CVMP([10]Committee for Phariatic Products for Pharious Use, CVMP)에서 실시한 품질, 안전성 및 유효성 평가 결과 14개월에[8][9] 그쳐졌다. 따라서 장기적인 효과는 알 수 없다.
입원 환자 목록
NexGard[11] 및 NexGard 스펙트럼의 경우:[3]
- 메이즈 전분
- 콩단백질과태료
- 쇠고기 조림 향미
- 포비돈(E1201)
- 마크로골 400(명백한 설사제)
- 마크로골 4000(명백한 설사제)
- 마크로골 15 히드록시스테아레이트(명백한 설사제)
- 글리세롤(E422)
- 트리글리세리드, 중간 체인
추가적으로 NexGard 스펙트럼:
안전
복용량
아포콜라너는 개의 몸무게 2.7~7mg/kg으로 투여하는 것이 좋다.[11]
포유류 독성
사전 마케팅을 수행한 임상 연구에 따르면:
- 아포콜라너의 경구 독성 프로파일은 이뇨 효과(랫드만 해당), 식품 소비 감소에 부수적인 효과(쥐와 토끼만 해당), 높은 경구 투여 후 가끔 구토 및/또는 설사(개, 120mg/kg 체중(bw))로 구성된다. 구토 또는 설사에 대한 치료 관련 영향은 중추적 대상 동물 안전 연구 또는 EU 현장 시험에서 최대 31.5mg/kg bw의 경구 투여 후 파악되지 않았다.[9]
- 가벼운 위장 효과(소변, 설사, 설사), 프리루션, 무기력, 거식증, 신경학적 증상(소변, 아탁시아, 근육 떨림)이 치료받은 동물 1만 마리 중 0.1% 미만에서 보고되었으며, 격리된 보고, 대부분의 부작용은 자가 치료되고 짧은 기간 동안 보고되었다.[11]
- (밀베미신소독과 결합): 구토, 설사, 무기력, 거식증, 그리고 프리리투스가 치료된 동물 1만 마리 중 0.2~1%에서 관찰되었고 일반적으로 자가 치료되고 짧은 기간 동안 지속되었다.[3]
- 시험관내 연구에서는 아포콜라네르가 도파민 및 노르에피네프린 세포전달수용체 시스템과 CB1 수용체에 결합할 수 있다고 보고하였다; 이러한 카테콜아민제 시스템과 CB1 수용체에서의 특정 유형의 경쟁적 결합을 억제하면 이뇨의 약동학적 효과, 식품소비 감소, 체중 감소 등을 매개할 수 있다. 동물들[9]
시판 후 안전 경험에 따라:
- (밀베미신 옥소극과 함께): 홍반과 신경학적 증상(뇌졸중, 아탁시아, 근육 떨림)은 격리된 보고를 포함하여 치료받은 동물 10,000마리 중 0.1% 미만에서 보고되었다.[3]
- 미국 FDA는 아포칼라네르를 포함한 이 등급의 일부 약품(이소산사졸린)은 근육 떨림, 아탁시아, 발작 등 일부 개에게 신경학적 악영향을 미칠 수 있다고[12] 보고하고 있다.
- 애완용 돼지에서 아포콜라네어의 외부 사용은 어떠한 부작용도 없이 설명되어 왔다.[13] 상업용 돼지에 실험적으로 사용해도 부작용이 없었다.[14]
포유류보다 곤충의 선택성
아포콜라나제(foxolaner-derivative) 약품을 생산하는 회사인 MERIAL이 제공한 생체내 연구(실험용 동물의 반복 독성학, 표적 동물 안전성, 현장 연구)는 포유류에서 GABA 매개 동요를 암시하는 신경학적 또는 행동적 효과의 증거를 보여주지 않았다. 따라서 수의약물위원회(CVMP)는 개, 랫드 또는 인간 GABA 수용체에 대한 결합이 아포콜라너에 대해 낮을 것으로 예상된다고 결론지었다.[9]
포유류 GABA 수용체보다 곤충에 대한 선택성은 다른 이소사졸린에 대해 입증되었다.[15] 선택성은 곤충과 척추동물의 GABA 게이트 염화물 통로 사이에 존재하는 약리학적 차이 수로 설명될 수 있다.[16]
참고 항목
참조
- ^ a b c "Frontline NexGard (afoxolaner) for the Treatment and Prophylaxis of Ectoparasitic Diseases in Dogs. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF) (in Russian). Sanofi Russia. Retrieved 14 November 2016.
- ^ "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names: List 70" (PDF). World Health Organization. pp. 276–7. Retrieved 14 November 2016.
- ^ a b c d "NexGard Spectra product information - Annex I "Summary of product characteristics"" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. Retrieved 13 November 2019.
- ^ Shoop WL, Hartline EJ, Gould BR, Waddell ME, McDowell RG, Kinney JB, et al. (April 2014). "Discovery and mode of action of afoxolaner, a new isoxazoline parasiticide for dogs". Veterinary Parasitology. 201 (3–4): 179–89. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.02.020. PMID 24631502.
- ^ Beugnet F, deVos C, Liebenberg J, Halos L, Fourie J (25 August 2014). "Afoxolaner against fleas: immediate efficacy and resultant mortality after short exposure on dogs". Parasite. 21: 42. doi:10.1051/parasite/2014045. PMC 4141545. PMID 25148564.
- ^ Beugnet F, Crafford D, de Vos C, Kok D, Larsen D, Fourie J (August 2016). "Evaluation of the efficacy of monthly oral administration of afoxolaner plus milbemycin oxime (NexGard Spectra, Merial) in the prevention of adult Spirocerca lupi establishment in experimentally infected dogs". Veterinary Parasitology. 226: 150–61. doi:10.1016/j.vetpar.2016.07.002. PMID 27514901.
- ^ "Boehringer-Ingelheim companion-animals-product NexGard (afoxolaner)". Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH. Retrieved 13 November 2019.
- ^ "CVMP Assessment Report for NEXGARD SPECTRA(EMEA/V/C/003842/0000)" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. Retrieved 14 November 2019.
- ^ a b c d "CVMP assessment report for NexGard (EMEA/V/C/002729/0000)" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. Retrieved 14 November 2019.
- ^ "Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP) - Section "Role of the CVMP"". European Medicines Agency. Retrieved 14 November 2019.
- ^ a b c "NexGard product information - Annex I "Summary of product characteristics"" (PDF). European Medicines Angency. Retrieved 14 November 2019.
- ^ Medicine, Center for Veterinary. "CVM Updates - Animal Drug Safety Communication: FDA Alerts Pet Owners and Veterinarians About Potential for Neurologic Adverse Events Associated with Certain Flea and Tick Products". www.fda.gov. Retrieved 2018-09-22.
- ^ Smith, Joe S.; Berger, Darren J.; Hoff, Sarah E.; Jesudoss Chelladurai, Jeba R. J.; Martin, Katy A.; Brewer, Matthew T. (2020). "Afoxolaner as a Treatment for a Novel Sarcoptes scabiei Infestation in a Juvenile Potbelly Pig". Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 7: 473. doi:10.3389/fvets.2020.00473. PMC 7505946. PMID 33102538.
- ^ Bernigaud, C.; Fang, F.; Fischer, K.; Lespine, A.; Aho, L. S.; Mullins, A. J.; Tecle, B.; Kelly, A.; Sutra, J. F.; Moreau, F.; Lilin, T.; Beugnet, F.; Botterel, F.; Chosidow, O.; Guillot, J. (2018). "Efficacy and Pharmacokinetics Evaluation of a Single Oral Dose of Afoxolaner against Sarcoptes scabiei in the Porcine Scabies Model for Human Infestation". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 62 (9). doi:10.1128/AAC.02334-17. PMC 6125498. PMID 29914951.
- ^ Casida JE (April 2015). "Golden age of RyR and GABA-R diamide and isoxazoline insecticides: common genesis, serendipity, surprises, selectivity, and safety". Chemical Research in Toxicology. 28 (4): 560–6. doi:10.1021/tx500520w. PMID 25688713.
- ^ Hosie AM, Aronstein K, Sattelle DB, ffrench-Constant RH (December 1997). "Molecular biology of insect neuronal GABA receptors". Trends in Neurosciences. 20 (12): 578–83. doi:10.1016/S0166-2236(97)01127-2. PMID 9416671. S2CID 5028039.

