ACTG2 식별자 별칭 ACTG2 외부 ID OMIM : 102545 MGI : 104589 HomoloGene : 123845 GeneCard : ACTG2 직교체 종 인간 마우스 엔트레스 앙상블 유니프로트 RefSeq(mRNA) RefSeq(단백질) 위치(UCSC) Chr 2: 73.89 – 73.92Mb Chr 6: 83.51 – 83.54Mb PubMed 검색[3] [4] 위키다타
액틴, 감마-엔터틱 매끄러운 근육 은 인간에게 있어 ACTG2 유전자 에 의해 암호화 된 단백질이다.[5] [6] [7]
액틴은 세포 운동성과 세포골격의 유지에 관여하는 보존도가 높은 단백질이다. 척추동물의 경우 액틴 등소형, 알파, 베타, 감마형의 세 가지 주요 그룹이 확인되었다. 알파 액틴은 근육 조직에서 발견되며 수축기구의 주요 성분이다. 베타 액틴과 감마액틴은 사이토스켈레톤 구성 요소로서 그리고 내부 세포 운동성의 매개체로 대부분의 세포 유형에서 공존한다. 액틴, 감마 2는 이 유전자에 의해 부호화되어 장 조직에서 발견되는 부드러운 근육액틴이다.[7]
상호작용 ACTG2는 에메린 과 상호작용 하는 것으로 나타났다.[8]
참조 ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리스 89: ENSG00000163017 - 앙상블 , 2017년 5월^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리스 89: ENSMUSG000059430 - 앙상블 , 2017년 5월^ "Human PubMed Reference:" . National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine .^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:" . National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine .^ Miwa T, Manabe Y, Kurokawa K, Kamada S, Kanda N, Bruns G, Ueyama H, Kakunaga T (July 1991). "Structure, chromosome location, and expression of the human smooth muscle (enteric type) gamma-actin gene: evolution of six human actin genes" . Mol Cell Biol . 11 (6): 3296–306. doi :10.1128/mcb.11.6.3296 . PMC 360182 PMID 1710027 . ^ Ueyama H (May 1991). "A HindIII DNA polymorphism in the human enteric type smooth muscle actin gene (ACTSG)" . Nucleic Acids Res . 19 (2): 411. doi :10.1093/nar/19.2.411 . PMC 333620 PMID 1673027 . ^ a b "Entrez Gene: ACTG2 actin, gamma 2, smooth muscle, enteric" .^ Lattanzi, Giovanna; Cenni Vittoria; Marmiroli Sandra; Capanni Cristina; Mattioli Elisabetta; Merlini Luciano; Squarzoni Stefano; Maraldi Nadir Mario (April 2003). "Association of emerin with nuclear and cytoplasmic actin is regulated in differentiating myoblasts". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun . United States. 303 (3): 764–70. doi :10.1016/S0006-291X(03)00415-7 . ISSN 0006-291X . PMID 12670476 .
외부 링크 추가 읽기 Snásel J, Pichová I (1997). "The cleavage of host cell proteins by HIV-1 protease". Folia Biol. (Praha) . 42 (5): 227–30. doi :10.1007/BF02818986 . PMID 8997639 . S2CID 7617882 . Adams LD, Tomasselli AG, Robbins P, et al. (1992). "HIV-1 protease cleaves actin during acute infection of human T-lymphocytes" . AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses . 8 (2): 291–5. doi :10.1089/aid.1992.8.291 . PMID 1540415 . Tomasselli AG, Hui JO, Adams L, et al. (1991). "Actin, troponin C, Alzheimer amyloid precursor protein and pro-interleukin 1 beta as substrates of the protease from human immunodeficiency virus" . J. Biol. Chem . 266 (22): 14548–53. doi :10.1016/S0021-9258(18)98721-1 PMID 1907279 . Shoeman RL, Kesselmier C, Mothes E, et al. (1991). "Non-viral cellular substrates for human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease" . FEBS Lett . 278 (2): 199–203. doi :10.1016/0014-5793(91)80116-K PMID 1991513 . S2CID 37002682 . Miwa T, Kamada S (1990). "The nucleotide sequence of a human smooth muscle (enteric type) gamma-actin cDNA" . Nucleic Acids Res . 18 (14): 4263. doi :10.1093/nar/18.14.4263 . PMC 331204 PMID 2377475 . Ueyama H, Inazawa J, Nishino H, et al. (1995). "Chromosomal mapping of the human smooth muscle actin gene (enteric type, ACTA3) to 2p13.1 and molecular nature of the hindIII polymorphism". Genomics . 25 (3): 720–3. doi :10.1016/0888-7543(95)80016-F . PMID 7759108 . Szucsik JC, Lessard JL (1996). "Cloning and sequence analysis of the mouse smooth muscle gamma-enteric actin gene". Genomics . 28 (2): 154–62. doi :10.1006/geno.1995.1126 . PMID 8530021 . Bukrinskaya A, Brichacek B, Mann A, Stevenson M (1999). "Establishment of a Functional Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) Reverse Transcription Complex Involves the Cytoskeleton" . J. Exp. Med . 188 (11): 2113–25. doi :10.1084/jem.188.11.2113 . PMC 2212381 PMID 9841925 . Zhang H, Wang L, Kao S, et al. (1999). "Functional interaction between the cytoplasmic leucine-zipper domain of HIV-1 gp41 and p115-RhoGEF" . Curr. Biol . 9 (21): 1271–4. doi :10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80511-9 . PMC 4513661 PMID 10556093 . Kohnen G, Campbell S, Jeffers MD, Cameron IT (2000). "Spatially regulated differentiation of endometrial vascular smooth muscle cells" . Hum. Reprod . 15 (2): 284–92. doi :10.1093/humrep/15.2.284 PMID 10655297 . Filmore RA, Dean DA, Zimmer WE (2003). "The smooth muscle gamma-actin gene is androgen responsive in prostate epithelia" . Gene Expr . 10 (5–6): 201–11. doi :10.3727/000000002783992424 . PMC 5977519 PMID 12450213 . Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences" . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A . 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode :2002PNAS...9916899M . doi :10.1073/pnas.242603899 PMC 139241 PMID 12477932 . Cheng C, Sharp PA (2003). "RNA Polymerase II Accumulation in the Promoter-Proximal Region of the Dihydrofolate Reductase and γ-Actin Genes" . Mol. Cell. Biol . 23 (6): 1961–7. doi :10.1128/MCB.23.6.1961-1967.2003 . PMC 149466 PMID 12612070 . Wu RF, Gu Y, Xu YC, et al. (2004). "Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Tat Regulates Endothelial Cell Actin Cytoskeletal Dynamics through PAK1 Activation and Oxidant Production" . J. Virol . 78 (2): 779–89. doi :10.1128/JVI.78.2.779-789.2004 . PMC 368750 PMID 14694110 . Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al. (2004). "Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length human cDNAs" . Nat. Genet . 36 (1): 40–5. doi :10.1038/ng1285 PMID 14702039 . Gerhard DS, Wagner L, Feingold EA, et al. (2004). "The Status, Quality, and Expansion of the NIH Full-Length cDNA Project: The Mammalian Gene Collection (MGC)" . Genome Res . 14 (10B): 2121–7. doi :10.1101/gr.2596504 . PMC 528928 PMID 15489334 . Hillier LW, Graves TA, Fulton RS, et al. (2005). "Generation and annotation of the DNA sequences of human chromosomes 2 and 4" . Nature . 434 (7034): 724–31. Bibcode :2005Natur.434..724H . doi :10.1038/nature03466 PMID 15815621 .
PDB 갤러리
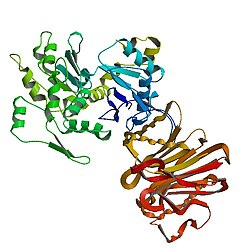
1atn : 액틴의 원자 구조:DNASE I 복합체
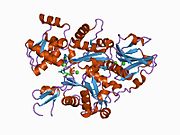
1c0f : 겔솔린 세그먼트 1 복합체에서 딕티요스텔리움 CAATP-actin의 결정구조
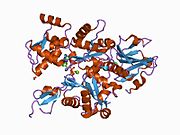
1c0g : 겔솔린 세그먼트 1과 지시요스텔리움/테트라히메나 치메라 액틴(Mutant 228: Q228K/T229A/A230Y/E360H) 사이의 1:1 복합 크리스털 구조
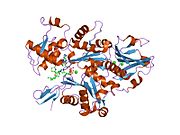
1d4x : Elegans Mg-ATP Actin Complex with Human Gelsolin Segment 1의 분해능 1.75.
1dej : CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF A DICTYOSTELIUM/TETRAHYMENA CHIMERA ACTIN (MUTANT 646: Q228K/T229A/A230Y/A231K/S232E/E360H) IN COMPLEX WITH HUMAN GELSOLIN SEGMENT 1
1eqy : RABB 사이의 복잡함IT 근육 알파 액틴: 인간 겔솔린 도메인 1
1esv : 라트런쿨린 A 사이의 복잡함:토끼 근육 알파 액틴: 인간 겔솔린 도메인 1
1h1v : GELSOLIN G4-G6/ACTIN 복합체
1hlu : 액틴 결합 ATP 인산염 용제가 접근 가능한 소 베타 액틴 프로필린 복합체의 구조
1ijj : RABB 사이의 콤플렉스의 X-Ray 결정분해능 2.85에서 IT 골격근 작용 및 래트런쿨린 A
1kxp : 골격 작용이 있는 복합체 내 비타민D 결합 단백질의 결정구조
1lcu : Polylysine이 필라멘트 조립체를 핵으로 만드는 항타렐 액틴 디머를 유도한다: 3.5A 해상도의 결정구조
1lot : 비타민D 결합 단백질을 포함한 액틴 복합체의 결정구조
1m8q : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomograms에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모델
1ma9 : 인간 비타민D 결합 단백질과 토끼 근육 액틴 복합체의 결정 구조
1mdu : 인간 겔솔린 세그먼트 1로 복잡한 치킨 액틴 트리머의 결정 구조(GS-1)
1mvw : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomograms(토모그램)에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모델
1nlv : Ca ATP와 휴먼겔솔린 세그먼트 1로 복합된 디스코스텔리움 액틴의 결정구조
1nm1 : D의 결정구조. 분해능 1.8A에서 겔솔린 세그먼트 1과 Mg ATP로 복잡한 Dicsoideum Actin
1nmd : D의 결정구조. 리튬 ATP가 존재하는 디스코이덤 액틴겔솔린 세그먼트 1 복합체 결정화
1nwk : ATP 상태에서 모노메릭 액틴의 결정구조
1o18 : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomogram(토모그램)에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모델
1o19 : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomogram(토모그램)에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모형
1o1a : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomogram(토모그램)에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모델
1o1b : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomogram(토모그램)에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모델
1o1c : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomogram(토모그램)에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모델
1o1d : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomogram(토모그램)에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모델
1o1e : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomogram(토모그램)에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모델
1o1f : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomogram(토모그램)에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모델
1o1g : 곤충 비행 근육의 Tomogram(토모그램)에서 얻은 평균 경직 교차 교량의 분자 모델
1p8z : 토끼 근육 알파-액틴 사이의 복잡함: 인간겔솔린 잔류물 Val26-Glu156
1qz5 : 카비라마이드 C와 복합된 토끼 액틴의 구조
1qz6 : 자스피사미드 A와 복합된 토끼 액틴의 구조
1w : Actin Crystal Dynamics: Anti-parallel Dimmer에 의해 매개된 F-actin 핵화, 중합화 및 분지에 대한 구조적 의미
1rfq : Actin Crystal Dynamics: Anti-parallel Dimmer에 의해 매개된 F-actin 핵화, 중합화 및 분지에 대한 구조적 의미
1rgi : 작용하는 겔솔린 도메인 G1-G3의 결정구조
1제곱 : 골격 액틴이 있는 복합체 내 시불롯의 결정구조
1t44 : 티모신-B4에 의한 액틴 격리 구조기준: arp2/3 활성화에 대한 의미
1wua : Aplyronine A-actin 복합체의 구조
1y64 : ATP-actin으로 복잡한 Bni1p Formin Homology 2 도메인
1yync : swinholide A와 함께 복합된 액틴의 결정구조
2a3z : Actin-DNAse I를 사용하는 WASP의 WH2 도메인의 테르나리 복합체
2a40 : Actin-DNAse I이 있는 WAVE의 WH2 도메인의 테너리 복합체
2a41 : Actin-DNAse I을 포함한 WIP의 WH2 도메인의 테너리 복합체
2asm : 레이디스폰기올라이드를 이용한 복합 토끼액틴의 구조 A
2아소 : 스핑크솔라이드 B와 함께 복합된 토끼 액틴의 구조
2asp : Reidisponiolide C를 사용한 복합 토끼 액틴의 구조
2d1k : Actin-dnase I과 밈의 WH2 도메인의 테르나리 콤플렉스
2ff3 : 겔솔린 도메인 1:N 와스프 V2 모티브 하이브리드(actin)의 크리스털 구조
2ff6 : 액틴과 콤플렉스의 젤솔린 도메인 1:시불롯 도메인 2 하이브리드 결정구조
2fxu : 1.35 A 해상도에서 비스트라마이드 A-액틴 복합체의 X선 구조
2gwj : SpvB ADP-리보실화 액틴: 육각 결정 형태
2gwk : SpvB ADP-리보실화 액틴: Orthorhombic crystal form
2hf3 : ADP 바운드 상태의 모노메릭 액틴 결정구조
2hf4 : ATP 바인딩 상태에서 모노메릭 액틴의 결정 구조
2hmp : 프로테아제 ECP32로 분해된 복잡하지 않은 액틴
2Q1n : Actin Dimer Cross-Linked Betters 41과 374
2Q31 : Actin Dimmer Cross-Linked Betters 41과 374, 그리고 잔류물 47과 48 사이에서 아중분리신(subtilisin)에 의해 단백질 분해된다.
2q36 : Actin Dimer Cross-linked with Kabiramide C.