멀린(단백질)
Merlin (protein)멀린(Neurofibromin 2 또는 슈완노민이라고도 함)은 세포골격계 단백질이다.인간의 경우 신경섬유화증 타입 II에 관여하는 종양 억제 단백질이다.[5][6]시퀀스 데이터는 ERM 단백질 제품군과 유사함을 보여준다.
merlin이라는 이름은 "Moesin-Ezrin-Radixin-Like 단백질"의 약자다.
유전자
인간 멀린은 22번 염색체의 NF2 유전자에 의해 코딩된다.생쥐 멀린 유전자는 11번[7] 염색체에, 쥐 멀린 유전자는 17번 염색체에 있다.과일파리머린유전자(심볼메르)는 1번 염색체에 위치하며 인간의 호몰로게이션과 58%의 유사성을 공유한다.다른 멀린과 같은 유전자는 광범위한 동물로부터 알려져 있으며 멀린의 유래는 초기 메타조아에 있는 것으로 생각된다.멀린은 에즈린, 모신, 라딕신 등 ERM 단백질 계열로 단백질 4.1 슈퍼패밀리에 속한다.멀린은 또한 슈완노민(shwannomin)으로도 알려져 있는데, NF2 환자 표현형인 슈완노마(schwannoma)에서 가장 흔한 형태의 종양에서 유래한 이름이다.
구조
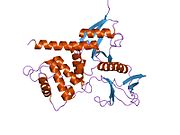
척추동물 멀린은 70 kDa 단백질이다.인간 멀린 분자의 알려진 등소 형태는 10가지가 있다(전체 분자는 길이가 595개 아미노산이다).이 중 가장 흔한 두 가지는 마우스에서도 발견되며 타입 1과 타입 2라고 불리며 각각 exon 16이나 17의 부재나 존재에 따라 다르다.알려진 모든 품종은 보존된 N-단자 부분을 가지고 있는데, FERM 도메인(대부분의 세포골격계-기억단백질 조직에서 발견되는 영역)을 포함하고 있다.FERM 도메인은 알파헬리컬 도메인과 친수성 꼬리가 뒤따른다.[8][9]Merlin은 스스로 조광할 수 있고 다른 ERM 계열 단백질로 이질화할 수 있다.
함수
Merlin은 막-사이토스켈레톤 비계 단백질로, 즉 액틴 필라멘트를 세포막이나 막 당단백질에 연결하는 것이다.[10]인간 멀린은 주로 신경 조직에서 발견되지만, 다른 몇몇 태아 조직에서도 발견되며, 주로 부속물 접합부에 위치한다.[11]종양 억제기 특성은 아마도 접촉 매개 성장 억제와 관련이 있을 것이다.드로소필라 멀린은 배아 힌드굿, 침샘, 상상디스크 등으로 표현되며 척추동물과는 역할이 약간 다르다.[12]
세린 518의 인산화 작용은 멀린의 기능 상태를 변화시키는 것으로 알려져 있다.[13]멀린의 신호 경로에는 eIF3c, CD44, 단백질키나아제 A, p21 활성키나제 등 몇몇 두드러진 세포 성장 제어 분자가 포함되도록 제안된다.
드로소필라에서의 연구는 멀린이 포유동물들에게 보존되어 있는 기능인 히포종양 억제기 경로의 상류 조절기로 확인되었다.[14][15]히포 경로는 세포 증식과 사멸을 조절하는 잘 보존된 신호 전달 경로다.[16]
NF2 유전자의 돌연변이는 신경섬유화증 타입 2라고 불리는 인간의 자가우월성 질환을 유발한다.가장 흔히 양쪽 전정맥 슈완노마(음극신경종이라고도 함)의 하나인 신경계의 종양이 발달한 것이 특징이다.NF2는 종양 억제기 유전자에 속한다.[17]
상호작용
멀린(단백질)은 다음과 상호작용하는 것으로 나타났다.
참조
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리스 89: ENSG00000186575 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리스 89: ENSMUSG00000009073 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Rouleau GA, Merel P, Lutchman M, Sanson M, Zucman J, Marineau C, Hoang-Xuan K, Demczuk S, Desmaze C, Plougastel B (1993). "Alteration in a new gene encoding a putative membrane-organizing protein causes neuro-fibromatosis type 2". Nature. 363 (6429): 515–21. Bibcode:1993Natur.363..515R. doi:10.1038/363515a0. PMID 8379998.
- ^ Golovnina K, Blinov A, Akhmametyeva EM, Omelyanchuk LV, Chang LS (2005). "Evolution and origin of merlin, the product of the Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) tumor-suppressor gene". BMC Evol. Biol. 5: 69. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-5-69. PMC 1315344. PMID 16324214.
- ^ Haase VH, Trofatter JA, MacCollin M, Tarttelin E, Gusella JF, Ramesh V (1994). "The murine NF2 homologue encodes a highly conserved merlin protein with alternative forms". Hum. Mol. Genet. 3 (3): 407–11. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.3.407. PMID 8012352.
- ^ Shimizu T, Seto A, Maita N, Hamada K, Tsukita S, Tsukita S, Hakoshima T (2002). "Structural basis for neurofibromatosis type 2. Crystal structure of the merlin FERM domain". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (12): 10332–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109979200. PMID 11756419.
- ^ Ali Khajeh, J; Ju, JH; Atchiba, M (2014). "Molecular conformation of the full-length tumor suppressor NF2/Merlin--a small-angle neutron scattering study". Journal of Molecular Biology. 426 (15): 2755–68. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2014.05.011. PMC 4407695. PMID 24882693.
- ^ McClatchey AI, Giovannini M (2005). "Membrane organization and tumorigenesis--the NF2 tumor suppressor, Merlin". Genes Dev. 19 (19): 2265–77. doi:10.1101/gad.1335605. PMID 16204178.
- ^ den Bakker MA, Vissers KJ, Molijn AC, Kros JM, Zwarthoff EC, van der Kwast TH (1999). "Expression of the neurofibromatosis type 2 gene in human tissues". J. Histochem. Cytochem. 47 (11): 1471–80. doi:10.1177/002215549904701113. PMID 10544220. Archived from the original on 2008-05-18.
- ^ LaJeunesse DR, McCartney BM, Fehon RG (1998). "Structural Analysis of Drosophila Merlin Reveals Functional Domains Important for Growth Control and Subcellular Localization". J. Cell Biol. 141 (7): 1589–99. doi:10.1083/jcb.141.7.1589. PMC 2133006. PMID 9647651.
- ^ Alfthan K, Heiska L, Grönholm M, Renkema GH, Carpén O (2004). "Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates merlin at serine 518 independently of p21-activated kinase and promotes merlin-ezrin heterodimerization". J. Biol. Chem. 279 (18): 18559–66. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313916200. PMID 14981079.
- ^ Hamaratoglu F, Willecke M, Kango-Singh M, et al. (2006). "The tumour-suppressor genes NF2/Merlin and Expanded act through Hippo signalling to regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis". Nature Cell Biology. 8 (1): 27–36. doi:10.1038/ncb1339. PMID 16341207.
- ^ Zhang N, Bai H, David KK, Dong J, Zheng Y, Cai J, Giovannini M, Liu P, Anders RA, Pan D (2010). "The Merlin/NF2 tumor suppressor functions through the YAP oncoprotein to regulate tissue homeostasis in mammals". Developmental Cell. 19 (1): 27–38. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2010.06.015. PMC 2925178. PMID 20643348.
- ^ Pan D (October 2010). "The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer". Developmental Cell. 19 (4): 491–505. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2010.09.011. PMC 3124840. PMID 20951342.
- ^ Scoles DR, Yong WH, Qin Y, Wawrowsky K, Pulst SM (2006). "Schwannomin inhibits tumorigenesis through direct interaction with the eukaryotic initiation factor subunit c (eIF3c)". Hum. Mol. Genet. 15 (7): 1059–70. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddl021. PMID 16497727.
- ^ a b c d Huang J, Chen J (July 2008). "VprBP targets Merlin to the Roc1-Cul4A-DDB1 E3 ligase complex for degradation". Oncogene. 27 (29): 4056–64. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.44. PMID 18332868.
- ^ Grönholm M, Sainio M, Zhao F, Heiska L, Vaheri A, Carpén O (March 1999). "Homotypic and heterotypic interaction of the neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor protein merlin and the ERM protein ezrin". J. Cell Sci. 112 (6): 895–904. PMID 10036239.
- ^ Gutmann DH, Haipek CA, Burke SP, Sun CX, Scoles DR, Pulst SM (April 2001). "The NF2 interactor, hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (HRS), associates with merlin in the "open" conformation and suppresses cell growth and motility". Hum. Mol. Genet. 10 (8): 825–34. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.8.825. PMID 11285248.
- ^ Scoles DR, Huynh DP, Chen MS, Burke SP, Gutmann DH, Pulst SM (July 2000). "The neurofibromatosis 2 tumor suppressor protein interacts with hepatocyte growth factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate". Hum. Mol. Genet. 9 (11): 1567–74. doi:10.1093/hmg/9.11.1567. PMID 10861283.
- ^ Wiederhold T, Lee MF, James M, Neujahr R, Smith N, Murthy A, Hartwig J, Gusella JF, Ramesh V (November 2004). "Magicin, a novel cytoskeletal protein associates with the NF2 tumor suppressor merlin and Grb2". Oncogene. 23 (54): 8815–25. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208110. PMID 15467741.
- ^ Jannatipour M, Dion P, Khan S, Jindal H, Fan X, Laganière J, Chishti AH, Rouleau GA (August 2001). "Schwannomin isoform-1 interacts with syntenin via PDZ domains". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (35): 33093–100. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105792200. PMID 11432873.
- ^ Neill GW, Crompton MR (September 2001). "Binding of the merlin-I product of the neurofibromatosis type 2 tumour suppressor gene to a novel site in beta-fodrin is regulated by association between merlin domains". Biochem. J. 358 (Pt 3): 727–35. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3580727. PMC 1222106. PMID 11535133.