EIF6
EIF6| EIF6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 식별자 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 에일리어스 | EIF6, CAB, EIF3A, ITGB4BP, b(2)gcn, eIF-6, p27(BBP), p27BP, 진핵생물 번역 개시인자 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 외부 ID | OMIM: 602912 MGI: 1196288 HomoloGene: 7135 GenCards: EIF6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 위키데이터 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
인테그린 베타 4 결합 단백질(ITGB4BP)로도 알려진 진핵생물 번역 개시 인자 6(EIF6)은 인간 [5]유전자이다.
헤미데스모솜은 기저 적층체와 중간 필라멘트 세포골격을 연결하는 구조이다.헤미데스모솜의 중요한 기능성 성분은 2개의 피브로넥틴 타입 III 도메인을 포함하는 단백질인 인테그린 베타-4 서브유닛(ITGB4)이다.이 유전자에 의해 암호화된 단백질은 ITGB4의 피브로넥틴 타입 III 도메인에 결합하고 ITGB4를 중간 필라멘트 세포골격에 연결하는 데 도움을 줄 수 있다.핵과 세포질에서 모두 발견되는 불용성 단백질은 번역 개시 인자로 기능할 수 있으며 GTP에 결합된 eIF5와 함께 40S 및 60S 리보솜 서브유닛의 연결을 촉매한다.이 [5]유전자에 대해 몇 가지 다른 동질 형태를 코드하는 다중 전사 변형이 발견되었다.
EIF6는 진핵생물 80S 리보솜 형성, 세포 성장 및 유전자 발현에 중요한 역할을 한다.80S 리보솜은 40S 서브유닛과 60S 서브유닛으로 나눌 수 있습니다.EIF6는 성숙한 60s 서브유닛을 보호하는 데 도움이 되며 EIF6는 60s 서브유닛과 연관성을 해제하여 40s 서브유닛에 결합하여 리보솜을 형성할 수 있습니다.EIF6의 균형을 유지하는 것은 신체에 필수적입니다. EIF6는 거의 정상적인 리보솜 합성에 도움이 되지 않으며, EIF6 억제된 많은 양의 60s 서브유닛은 40s [6]서브유닛에 결합합니다.
기능.
EIF6는 핵과 세포질 모두에 존재한다.진핵핵핵생물에서 성숙한 리보솜 합성에 관여하는 60S 프리리보솜 복합체와 분리된 90S 프리리보솜 복합체와 40S 프리리보솜 복합체.EIF6는 60S 서브유닛 생물 형성에 필수적이며 EIF6의 결실은 치명적인 영향을 미친다.eIF6의 부분 결실은 자유 60S 리보솜 서브유닛의 감소를 초래하며, 이는 40S/60S 서브유닛 비율을 균형을 잃고 단백질 합성의 속도를 제한한다는 것을 의미한다.60S 서브유닛이 40S 서브유닛에 결합할 수 있도록 핵에서 세포질로 가는 eIF6 셔틀과 관련된 60S 프리리보솜 복합체, 그리고 60S 프리유닛과 관련된 eIF6은 60S 프리리보솜 복합체.EIF6는 환율제한 트랜슬레이션 개시계수로 기능할 수 있으며 그 표현수준이 트랜슬레이션환율에 영향을 줍니다.eIF6 중 적은 수의 eIF6가 단백질 번역을 가속화하지만, 큰 eIF6는 [7]리보솜 생성을 억제하여 번역 과정을 방해합니다.또한 eIF6의 활성은 mRNA의 번역 제어에 [8]의해 당분해와 지방산 합성을 유발한다.
표현
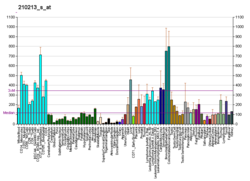
EIF6는 조직과 세포에 따라 발현 수준이 다릅니다.EIF6는 줄기세포와 순환세포에서 높은 수준의 발현을 보이는 반면 후유두세포에서는 그렇지 않다; 뇌와 상피에서는 높은 수준의 발현을 보이는 반면 [9]근육에서는 낮은 수치를 보인다.
상호 작용
EIF6는 FHL2,[10] ITGB4[11], GNB2L1과 [12]상호작용하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
EIF6는 80S 리보솜 형성, 세포 성장 및 유전자 [13]발현에 중요한 역할을 한다.
「 」를 참조해 주세요.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSG00000242372 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSMUSG000027613 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: ITGB4BP integrin beta 4 binding protein".
- ^ Brina D, Grosso S, Miluzio A, Biffo S (October 2011). "Translational control by 80S formation and 60S availability: the central role of eIF6, a rate limiting factor in cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis". Cell Cycle. 10 (20): 3441–6. doi:10.4161/cc.10.20.17796. PMID 22031223.
- ^ Brina D, Miluzio A, Ricciardi S, Biffo S (July 2015). "eIF6 anti-association activity is required for ribosome biogenesis, translational control and tumor progression". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms. 1849 (7): 830–5. doi:10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.09.010. PMID 25252159.
- ^ Biffo S, Manfrini N, Ricciardi S (February 2018). "Crosstalks between translation and metabolism in cancer". Current Opinion in Genetics & Development. 48: 75–81. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2017.10.011. PMID 29153483.
- ^ Miluzio A, Beugnet A, Volta V, Biffo S (May 2009). "Eukaryotic initiation factor 6 mediates a continuum between 60S ribosome biogenesis and translation". EMBO Reports. 10 (5): 459–65. doi:10.1038/embor.2009.70. PMC 2680881. PMID 19373251.
- ^ Wixler V, Geerts D, Laplantine E, Westhoff D, Smyth N, Aumailley M, Sonnenberg A, Paulsson M (October 2000). "The LIM-only protein DRAL/FHL2 binds to the cytoplasmic domain of several alpha and beta integrin chains and is recruited to adhesion complexes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (43): 33669–78. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002519200. PMID 10906324.
- ^ Biffo S, Sanvito F, Costa S, Preve L, Pignatelli R, Spinardi L, Marchisio PC (November 1997). "Isolation of a novel beta4 integrin-binding protein (p27(BBP)) highly expressed in epithelial cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (48): 30314–21. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.48.30314. PMID 9374518.
- ^ Ceci M, Gaviraghi C, Gorrini C, Sala LA, Offenhäuser N, Marchisio PC, Biffo S (December 2003). "Release of eIF6 (p27BBP) from the 60S subunit allows 80S ribosome assembly". Nature. 426 (6966): 579–84. doi:10.1038/nature02160. PMID 14654845. S2CID 2431706.
- ^ Brina D, Grosso S, Miluzio A, Biffo S (October 2011). "Translational control by 80S formation and 60S availability: the central role of eIF6, a rate limiting factor in cell cycle progression and tumorigenesis". Cell Cycle. 10 (20): 3441–6. doi:10.4161/cc.10.20.17796. PMID 22031223.
추가 정보
- Biffo S, Sanvito F, Costa S, Preve L, Pignatelli R, Spinardi L, Marchisio PC (November 1997). "Isolation of a novel beta4 integrin-binding protein (p27(BBP)) highly expressed in epithelial cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (48): 30314–21. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.48.30314. PMID 9374518.
- Si K, Chaudhuri J, Chevesich J, Maitra U (December 1997). "Molecular cloning and functional expression of a human cDNA encoding translation initiation factor 6". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 94 (26): 14285–90. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.26.14285. PMC 24943. PMID 9405604.
- Mao M, Fu G, Wu JS, Zhang QH, Zhou J, Kan LX, Huang QH, He KL, Gu BW, Han ZG, Shen Y, Gu J, Yu YP, Xu SH, Wang YX, Chen SJ, Chen Z (July 1998). "Identification of genes expressed in human CD34(+) hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells by expressed sequence tags and efficient full-length cDNA cloning". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (14): 8175–80. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.14.8175. PMC 20949. PMID 9653160.
- Sanvito F, Arrigo G, Zuffardi O, Agnelli M, Marchisio PC, Biffo S (August 1998). "Localization of p27 beta4 binding protein gene (ITGB4BP) to human chromosome region 20q11.2". Genomics. 52 (1): 111–2. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5403. PMID 9740680.
- Sanvito F, Piatti S, Villa A, Bossi M, Lucchini G, Marchisio PC, Biffo S (March 1999). "The beta4 integrin interactor p27(BBP/eIF6) is an essential nuclear matrix protein involved in 60S ribosomal subunit assembly". The Journal of Cell Biology. 144 (5): 823–37. doi:10.1083/jcb.144.5.823. PMC 2148184. PMID 10085284.
- Wixler V, Geerts D, Laplantine E, Westhoff D, Smyth N, Aumailley M, Sonnenberg A, Paulsson M (October 2000). "The LIM-only protein DRAL/FHL2 binds to the cytoplasmic domain of several alpha and beta integrin chains and is recruited to adhesion complexes". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (43): 33669–78. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002519200. PMID 10906324.
- Zhang QH, Ye M, Wu XY, Ren SX, Zhao M, Zhao CJ, Fu G, Shen Y, Fan HY, Lu G, Zhong M, Xu XR, Han ZG, Zhang JW, Tao J, Huang QH, Zhou J, Hu GX, Gu J, Chen SJ, Chen Z (October 2000). "Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells". Genome Research. 10 (10): 1546–60. doi:10.1101/gr.140200. PMC 310934. PMID 11042152.
- Donadini A, Giodini A, Sanvito F, Marchisio PC, Biffo S (March 2001). "The human ITGB4BP gene is constitutively expressed in vitro, but highly modulated in vivo". Gene. 266 (1–2): 35–43. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(01)00370-5. PMID 11290417.
- Andersen JS, Lyon CE, Fox AH, Leung AK, Lam YW, Steen H, Mann M, Lamond AI (January 2002). "Directed proteomic analysis of the human nucleolus". Current Biology. 12 (1): 1–11. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(01)00650-9. PMID 11790298. S2CID 14132033.
- Basu U, Si K, Deng H, Maitra U (September 2003). "Phosphorylation of mammalian eukaryotic translation initiation factor 6 and its Saccharomyces cerevisiae homologue Tif6p: evidence that phosphorylation of Tif6p regulates its nucleocytoplasmic distribution and is required for yeast cell growth". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 23 (17): 6187–99. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.17.6187-6199.2003. PMC 180954. PMID 12917340.
- Ceci M, Gaviraghi C, Gorrini C, Sala LA, Offenhäuser N, Marchisio PC, Biffo S (December 2003). "Release of eIF6 (p27BBP) from the 60S subunit allows 80S ribosome assembly". Nature. 426 (6966): 579–84. doi:10.1038/nature02160. PMID 14654845. S2CID 2431706.
- Rosso P, Cortesina G, Sanvito F, Donadini A, Di Benedetto B, Biffo S, Marchisio PC (May 2004). "Overexpression of p27BBP in head and neck carcinomas and their lymph node metastases". Head & Neck. 26 (5): 408–17. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.503.9652. doi:10.1002/hed.10401. PMID 15122657. S2CID 39531947.
- Lehner B, Sanderson CM (July 2004). "A protein interaction framework for human mRNA degradation". Genome Research. 14 (7): 1315–23. doi:10.1101/gr.2122004. PMC 442147. PMID 15231747.
- Rush J, Moritz A, Lee KA, Guo A, Goss VL, Spek EJ, Zhang H, Zha XM, Polakiewicz RD, Comb MJ (January 2005). "Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells". Nature Biotechnology. 23 (1): 94–101. doi:10.1038/nbt1046. PMID 15592455. S2CID 7200157.
- Andersen JS, Lam YW, Leung AK, Ong SE, Lyon CE, Lamond AI, Mann M (January 2005). "Nucleolar proteome dynamics". Nature. 433 (7021): 77–83. doi:10.1038/nature03207. PMID 15635413. S2CID 4344740.
- Stelzl U, Worm U, Lalowski M, Haenig C, Brembeck FH, Goehler H, Stroedicke M, Zenkner M, Schoenherr A, Koeppen S, Timm J, Mintzlaff S, Abraham C, Bock N, Kietzmann S, Goedde A, Toksöz E, Droege A, Krobitsch S, Korn B, Birchmeier W, Lehrach H, Wanker EE (September 2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell. 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0010-8592-0. PMID 16169070. S2CID 8235923.