계수 IX
Factor IX| F9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 식별자 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 에일리어스 | F9, F9 p22, FIX, HEMB, P19, PTC, TPH8, 응고인자 IX, 혈액응고인자 IX, 크리스마스인자 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 외부 ID | OMIM: 300746 MGI: 88384 HomoloGene: 106 GenCard: F9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 위키데이터 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
인자 IX(또는 크리스마스 인자)(EC 3.4.21.22)는 응고 시스템의 세린 단백질 분해효소 중 하나로, 펩티드가수분해효소 계열 S1에 속한다.이 단백질의 결핍은 혈우병 B를 일으킨다.그것은 1952년 스티븐 크리스마스라는 이름의 어린 소년이 [5]혈우병으로 이어지면서 이 요소가 부족하다는 것이 밝혀진 후 발견되었다.
응고인자 IX는 세계보건기구의 필수 [6]의약품 목록에 있다.
생리학
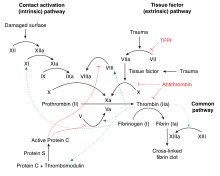
인자 IX는 불활성 전구체인 자이모겐으로 생성된다.시그널 펩타이드를 제거하고 글리코실화한 후 인자 XIa(접촉 경로의) 또는 인자 VIIa(조직 인자 경로의)에 의해 분해되어 사슬이 이황화물 [7][8]브릿지에 의해 결합되는 2-사슬 형태를 생성하기 위해 처리된다.인자 IXa로 활성화되면 Ca, 막인지질 및 인자 VIII의 존재2+ 하에서 인자 X에서 하나의 아르기닌-이소류신 결합을 가수분해하여 인자 Xa를 형성한다.
제9인자의 발현은 사람과 생쥐의 연령에 따라 증가한다.마우스 모델에서 인자 IX의 프로모터 영역 내 돌연변이는 연령 의존적 표현형을 [9]가진다.
도메인 아키텍처
인자 VII, IX 및 X는 모두 혈액 응고에 중요한 역할을 하며 공통 도메인 [10]아키텍처를 공유합니다.인자 IX 단백질은 Gla 도메인, EGF 도메인의 2개의 탠덤 복사본 및 촉매 분열을 수행하는 C 말단 트립신 유사 펩티다아제 도메인 등 4개의 단백질 도메인으로 구성됩니다.
N 말단 EGF 도메인은 적어도 부분적으로 조직 [10]인자와 결합하는 것으로 나타났다.윌킨슨 외 연구진은 두 번째 EGF 도메인의 잔류물 88~109가 혈소판 및 인자 X 활성화 [11]복합체에 대한 결합을 매개한다고 결론지었다.
4개 도메인의 구조는 모두 해결되었다.돼지 [12]단백질에 대해 2개의 EGF 도메인과 트립신 유사 도메인의 구조가 결정되었다.Ca(II) 의존성 인지질 결합을 담당하는 Gla 도메인의 구조도 NMR에 [13]의해 결정되었다.
응고 캐스케이드 내 다른 단백질에 의한 인자 IX 활성화의 성질을 밝히는 '슈퍼 액티브' 돌연변이들의 몇몇 구조가 [14]해결되었다.
유전학
인자 IX의 유전자는 X염색체(Xq27.1-q27.2)에 위치하므로 X연관 열성이다: 이 유전자의 돌연변이는 여성보다 남성에게 훨씬 더 자주 영향을 미친다.이 유전자에서 질병을 일으키는 변이가 적어도 534개 발견되었다.[15]F9 유전자는 1982년 코토쿠 쿠라치와 얼 데이비에 [16]의해 처음 복제됐다.
폴리는 1997년 [17]로슬린 연구소의 이안 윌머트 박사가 생산한 폴 도셋 양의 유전자 변형 복제품이다.
질병에서의 역할
인자 IX의 결핍은 크리스마스 질병(혈우병 B)[5]을 일으킨다.3000개 이상의 인자 IX 변형이 설명되었으며,[18] 461개 잔류물의 73%에 영향을 미쳤다. 일부는 증상을 유발하지 않지만, 대부분은 심각한 출혈 장애로 이어진다.원래 크리스마스 질병 돌연변이는 크리스마스의 DNA 염기서열을 분석함으로써 밝혀졌으며, 시스테인을 세린으로 [19]바꾼 돌연변이를 밝혀냈다.재조합인자 IX는 크리스마스 병을 치료하는데 사용된다.제제에는 다음이 포함됩니다.
- nonacog alfa(브랜드명 Benefix)[20]
- albutrepenacog alfa (브랜드명 Idelvion)[21]
- eftrenonacog alfa(브랜드명 Alprolix)[22]
- nonacog 베타 페골(브랜드명 Refixia)[23]
인자 IX의 일부 희귀한 돌연변이는 응고 활성을 증가시키고, 심정맥 혈전증과 같은 응고 질환을 일으킬 수 있다.이러한 기능 돌연변이의 증가는 단백질을 기능 과잉으로 만들고 가족성 혈전증 [24]초기 혈전증과 관련이 있다.
IX인자 결핍은 복제를 통해 생성된 정제인자 IX를 다양한 동물 또는 동물세포 벡터에 주입하여 치료한다.트라넥삼산은 출혈의 [25]주술적 위험을 줄이기 위해 인자 IX 결핍을 유전받은 수술 중인 환자에게 가치가 있을 수 있다.
인자 IX의 모든 돌연변이의 리스트는 EAHAD에 [26]의해 컴파일 및 유지된다.
응고인자 IX는 세계보건기구의 필수 [6]의약품 목록에 있다.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSG00000101981 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSMUSG000031138 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b Biggs R, Douglas AS, Macfarlane RG, Dacie JV, Pitney WR (Dec 1952). "Christmas disease: a condition previously mistaken for haemophilia". British Medical Journal. 2 (4799): 1378–82. doi:10.1136/bmj.2.4799.1378. PMC 2022306. PMID 12997790.
- ^ a b World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ a b Di Scipio RG, Kurachi K, Davie EW (Jun 1978). "Activation of human factor IX (Christmas factor)". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 61 (6): 1528–38. doi:10.1172/JCI109073. PMC 372679. PMID 659613.
- ^ Taran LD (Jul 1997). "Factor IX of the blood coagulation system: a review". Biochemistry. Biokhimiia. 62 (7): 685–93. PMID 9331959.
- ^ Boland EJ, Liu YC, Walter CA, Herbert DC, Weaker FJ, Odom MW, Jagadeeswaran P (Sep 1995). "Age-specific regulation of clotting factor IX gene expression in normal and transgenic mice". Blood. 86 (6): 2198–205. doi:10.1182/blood.V86.6.2198.bloodjournal8662198. PMID 7662969.
- ^ a b Zhong D, Bajaj MS, Schmidt AE, Bajaj SP (Feb 2002). "The N-terminal epidermal growth factor-like domain in factor IX and factor X represents an important recognition motif for binding to tissue factor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (5): 3622–31. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111202200. PMID 11723140.
- ^ Wilkinson FH, Ahmad SS, Walsh PN (Feb 2002). "The factor IXa second epidermal growth factor (EGF2) domain mediates platelet binding and assembly of the factor X activating complex". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (8): 5734–41. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107753200. PMID 11714704.
- ^ Brandstetter H, Bauer M, Huber R, Lollar P, Bode W (Oct 1995). "X-ray structure of clotting factor IXa: active site and module structure related to Xase activity and hemophilia B". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 92 (21): 9796–800. Bibcode:1995PNAS...92.9796B. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.21.9796. PMC 40889. PMID 7568220.
- ^ Freedman SJ, Furie BC, Furie B, Baleja JD (Sep 1995). "Structure of the calcium ion-bound gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-rich domain of factor IX". Biochemistry. 34 (38): 12126–37. doi:10.1021/bi00038a005. PMID 7547952.
- ^ Zögg T, Brandstetter H (Dec 2009). "Structural basis of the cofactor- and substrate-assisted activation of human coagulation factor IXa". Structure. 17 (12): 1669–78. doi:10.1016/j.str.2009.10.011. PMID 20004170.
- ^ Šimčíková D, Heneberg P (December 2019). "Refinement of evolutionary medicine predictions based on clinical evidence for the manifestations of Mendelian diseases". Scientific Reports. 9 (1): 18577. Bibcode:2019NatSR...918577S. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-54976-4. PMC 6901466. PMID 31819097.
- ^ Kurachi K, Davie EW (Nov 1982). "Isolation and characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor IX". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 79 (21): 6461–4. Bibcode:1982PNAS...79.6461K. doi:10.1073/pnas.79.21.6461. PMC 347146. PMID 6959130.
- ^ Nicholl D. (2002). An Introduction to Genetic Engineering Second Edition. Cambridge University Press. p. 257.
- ^ Goodeve, A. C. (2015). "Hemophilia B: Molecular pathogenesis and mutation analysis". Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 13 (7): 1184–1195. doi:10.1111/jth.12958. PMC 4496316. PMID 25851415.
- ^ Taylor SA, Duffin J, Cameron C, Teitel J, Garvey B, Lillicrap DP (Jan 1992). "Characterization of the original Christmas disease mutation (cysteine 206----serine): from clinical recognition to molecular pathogenesis". Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 67 (1): 63–5. doi:10.1055/s-0038-1648381. PMID 1615485.
- ^ "BeneFIX EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- ^ "Idelvion EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- ^ "Alprolix EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- ^ "Refixia EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Retrieved 17 June 2020.
- ^ Simioni P, Tormene D, Tognin G, Gavasso S, Bulato C, Iacobelli NP, Finn JD, Spiezia L, Radu C, Arruda VR (Oct 2009). "X-linked thrombophilia with a mutant factor IX (factor IX Padua)". The New England Journal of Medicine. 361 (17): 1671–5. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0904377. PMID 19846852.
- ^ Rossi M, Jayaram R, Sayeed R (Sep 2011). "Do patients with haemophilia undergoing cardiac surgery have good surgical outcomes?". Interactive Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery. 13 (3): 320–31. doi:10.1510/icvts.2011.272401. PMID 21712351.
- ^ "Home: EAHAD Factor 9 Gene Variant Database".
추가 정보
- Davie EW, Fujikawa K (1975). "Basic mechanisms in blood coagulation". Annual Review of Biochemistry. 44: 799–829. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004055. PMID 237463.
- Sommer SS (Jul 1992). "Assessing the underlying pattern of human germline mutations: lessons from the factor IX gene". FASEB Journal. 6 (10): 2767–74. doi:10.1096/fasebj.6.10.1634040. PMID 1634040. S2CID 15211597.
- Lenting PJ, van Mourik JA, Mertens K (Dec 1998). "The life cycle of coagulation factor VIII in view of its structure and function". Blood. 92 (11): 3983–96. doi:10.1182/blood.V92.11.3983. PMID 9834200.
- Lowe GD (Dec 2001). "Factor IX and thrombosis" (PDF). British Journal of Haematology. 115 (3): 507–13. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.03186.x. PMID 11736930. S2CID 44650866.
- O'Connell NM (Jun 2003). "Factor XI deficiency--from molecular genetics to clinical management". Blood Coagulation & Fibrinolysis. 14 Suppl 1: S59-64. doi:10.1097/00001721-200306001-00014. PMID 14567539.
- Du X (May 2007). "Signaling and regulation of the platelet glycoprotein Ib-IX-V complex". Current Opinion in Hematology. 14 (3): 262–9. doi:10.1097/MOH.0b013e3280dce51a. PMID 17414217. S2CID 39904506.
외부 링크
- "Coagulation Factor IX (Recombinant), Fc Fusion Protein". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Eftrenonacog alfa". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Nonacog alfa". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Albutrepenonacog alfa". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Nonacog beta pegol". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- PDB for UniProt: P00740(응고 계수 IX)에서 PDBe-KB에 있는 모든 구조 정보의 개요.
- 혈우병 B에 대한 Gene Reviews/NCBI/NIH/UW 엔트리
- 펩티드가수분해효소 및 그 억제제에 대한 MEROPS 온라인 데이터베이스: S01.214