부포르민
Buformin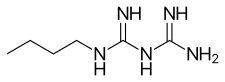 | |
| 임상자료 | |
|---|---|
| 경로: 행정 | 구강 |
| ATC 코드 | |
| 약동학 데이터 | |
| 배설 | 레날 |
| 식별자 | |
| CAS 번호 | |
| 펍켐 CID | |
| 드러그뱅크 | |
| 켐스파이더 | |
| 유니 | |
| 케그 | |
| 체비 | |
| 켐벨 | |
| PDB 리간드 | |
| CompTox 대시보드 (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.662 |
| 화학 및 물리적 데이터 | |
| 공식 | C6H15N5 |
| 어금질량 | 157.17 g·190−1 |
| 3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
부포르민(1-butyl biguanide)은 비구아나이드계급의 경구용 당뇨병 치료제로, 메트포민, 펜포민 등과 화학적으로 관련이 있다.부포르민은 독일 제약회사 그뤼넨탈에 의해 실루빈으로 시판되었다.
화학 및 동물 독성학
부포민 염산염은 희고, 희고 약간 노랗고, 결정적이고, 냄새 없는 가루로, 약한 산성의 쓴맛을 가지고 있다.녹는점은 174~177 °C로 기초가 튼튼하며 물과 메탄올, 에탄올 등에 자유롭게 용해되지만 클로로포름과 에테르에서는 용해되지 않는다.[1][2]독성: 기니피그 LD50 피하 18mg/kg; 쥐 LD50 복강 내 140mg/kg, 300mg/kg 경구.[3]로그 옥탄올-물 분할계수(로그 P)는 -1.20E+00이며, 용해도는 25 °C에서 7.46E+05 mg/l이다.증기압은 25°C(EST)에서 1.64E-04mm Hg이며, 헨리의 법칙 상수는 25°C(EST)에서 8.14E-16 atm-m3/mole이다.대기 -OH 속도 상수는 25°C에서 1.60E-10 cm3/molecule-sec이다.[4]
작용기전
부포민은 위장관으로부터 포도당 흡수를 지연시키고 인슐린 민감성과 포도당 흡수율을 높여 세포로 흡수하며 간에 의한 포도당 합성을 억제한다.Buformin과 다른 biguanides는 저혈당이 아니라 오히려 항혈당제다.그들은 저혈당증을 일으키지 않는다; 대신에 당뇨병 환자들의 기저귀와 후기 고혈당을 감소시킨다.[5]비구아니드는 글루카곤의 작용에 반감을 일으켜 단식 포도당 수치를 감소시킬 수 있다.[6]
약동학
자원봉사자에게 부포민 50mg을 경구 투여한 결과 소변에서 거의 90%가 회수됐으며, 소변 제거율 상수는 시간당 0.38로 나타났다.부포민은 강한 염기(pKa = 11.3)로 위장에 흡수되지 않는다.약 1mg/kg 부포민-14-C의 정맥주사 후 초기 혈청 농도는 0.2-0.4µg/ml이다.혈청 수준과 비뇨기 제거율은 선형적으로 상관관계가 있다.[7]남성의 경우 50mg 14-C-부포민 경구 투여 후 혈청 최대 농도는 0.26-0.41µg/ml이었다.부포민은 평균 반감기가 2시간인 상태에서 제거되었다. 투여된 투여량의 약 84%가 소변에서 변하지 않고 배설된 것으로 나타났다.[8]부포민은 사람에게서 대사되지 않는다.구강 부포르민 및 기타 비구아니아이드의 생체이용률은 40%~60%이다.혈장 단백질에 대한 결합은 없거나 매우 낮다.[9][10][11]
복용량
부포민의 하루 복용량은 입으로 150~300mg이다.[12]부포르민 또한 루마니아에서 판매되고 있는 지속적인 출시 준비물인 Silubin Relatin에서도 판매되고 있다.
부작용 및 금기
마주치는 부작용은 거식증, 메스꺼움, 설사, 금속성 맛, 체중 감소 등이다.그것의 사용은 당뇨병성 혼수상태, 케토아시데스증, 심각한 감염, 외상, 부포민이 고혈당증, 신장 또는 간 장애, 심부전, 최근의 심근경색, 탈수, 알코올 중독, 그리고 젖산증을 일으킬 가능성이 있는 조건들에 억제된다.
독성
부포르민은 젖산증을 유발할 위험이 높아져 많은 국가에서 시장에서 철수했다(미국은 아니지만 팔리지 않은 곳).부포르민은 여전히 사용 가능하고 루마니아(시간대 출시 시실루빈 리텐더는 젠티바에서 판매), 헝가리,[13][14][15][16] 대만[17], 일본(니치이코제약이 각각 50mg의 부포르민 염산염을 함유한 'DIBETOS' 태블릿으로 판매)에서 처방하고 있다.[18]젖산증은 부포민 혈장 수치가 0.60µg/ml 이상인 환자에서만 발생했으며 정상적인 신장 기능을 가진 환자에서는 드물었다.[19][20][21]
한 보고서에서 독성 경구 투여량은 부포민에서 젖산증이 발생한 24명의 환자 중 하루 329 ± 30mg/day이었다.258 ± 25 mg/일 24명의 또 다른 환자군은 부포민에서 젖산증이 발병하지 않았다.[22]
항암 특성
부포르민은 펜포민, 메트포민 등과 함께 암의 성장과 발달을 억제한다.[23][24][25][26][27]이들 약물의 항암 특성은 워버그 효과를 교란시키고 암세포의 세포질 글리콜리시스 특성을 미토콘드리아에 의한 피루브산염의 정상 산화로 되돌리는 능력 때문이다.[28]메트포민(Metformin)은 당뇨병 환자의 간 포도당 생성을 감소시키고 암의 워버그 효과를 AMPK 활성화와 mTor 경로의 억제에 의해 교란시킨다.[29]부포민은 화학적으로 유도된 쥐 유방암에서 암 발병률, 다중성, 부담을 줄인 반면 메트포민과 펜포민은 대조군에 비해 발암성 과정에 통계적으로 유의미한 영향을 미치지 않았다.[30]부포민 역시 자궁내막암세포,[31] 폐암세포[32], 자궁경부암세포 등에서 항응생 및 항침습작용을 보인다.[33]
항바이러스 속성
비구아니데스는 1940년대에 처음으로 인플루엔자에 대항하여 활동한 것으로 알려져 있다.[34]더 많은 연구들이 그들의 항바이러스 활동을 체외에서 확인했다.[35]특히 부포르민은 백신과 인플루엔자에 대한 강력한 항바이러스제였다.[36][37][38]부포민은 인플루엔자, 중동호흡기증후군 관련 코로나바이러스 등이 사용하는 mTOR 경로를 억제하는 대사 항바이러스다.[40]
역사
부포민은 1957년에 구강항당제로 합성되었다.[41]
합성
부포르민은 부틸아민(Butylamine)과 2-시아노구아니아니딘(Cyanoguanidine)의 반응으로 얻어진다.
참조
- ^ Jacker HJ (1964). "New Pharmacologic Products. 2. Buformin For Oral Therapy Of Diabetes". Pharm Prax. 10: 247–9. PMID 14328846.
- ^ Clarke EG, Berle J (1974). Isolation and identification of drugs in pharmaceuticals, body fluids and post-mortem material. Vol. 1. Pharmaceutical Press, Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain. Dept. of Pharmaceutical Sciences. p. 226.
- ^ Shroff JR, Bandurco V, Desai R, Kobrin S, Cervoni P (December 1981). "Chemistry and hypoglycemic activity of benzimidoylpyrazoles". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 24 (12): 1521–5. doi:10.1021/jm00144a031. PMID 7310831.
- ^ 미국 국립 의학 박물관LDplus 고급 데이터베이스
- ^ Ravina E, Kubinyi H (2011). The Evolution of Drug Discovery: From Traditional Medicines to Modern Drugs. Wiley. p. 215.
- ^ Miller RA, Chu Q, Xie J, Foretz M, Viollet B, Birnbaum MJ (February 2013). "Biguanides suppress hepatic glucagon signalling by decreasing production of cyclic AMP". Nature. 494 (7436): 256–60. Bibcode:2013Natur.494..256M. doi:10.1038/nature11808. PMC 3573218. PMID 23292513.
- ^ Beckmann R (March 1968). "The fate of biguanides in man". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 148 (3): 820–32. Bibcode:1968NYASA.148..820B. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb27755.x. PMID 5241479.
- ^ Beckmann R, Lintz W, Schmidt-Böthelt E (September 1971). "Evaluation of a sustained release form of the oral antidiabetic butylbiguanide (Silubin retard)". European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 3 (4): 221–8. doi:10.1007/bf00565010. PMID 5151304.
- ^ Marchetti P, Giannarelli R, di Carlo A, Navalesi R (October 1991). "Pharmacokinetic optimisation of oral hypoglycaemic therapy". Clinical Pharmacokinetics. 21 (4): 308–17. doi:10.2165/00003088-199121040-00006. PMID 1760902. S2CID 11701663.
- ^ Gutsche H, Blumenbach L, Losert W, Wiemann H (1976). "[Concentration of 14C-1-butylbiguanide in plasma of diabetic patients and its elimination after administration of a new Galenical formulation (author's transl)]". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 26 (6): 1227–9. PMID 989423.
- ^ Ritzl F, Feinendegen LE, Lintz W, Tisljar U (1978). "[Distribution and excretion of 14c-butylbiguanide in man (author's transl)]". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 28 (7): 1184–6. PMID 582707.
- ^ 구스타프 쿠스키, 하인츠 뤼만약리학 교과서.학술신문 p 225, 1973
- ^ Hankó B, Tukarcs E, Kumli P, Vincze Z (June 2005). "Antidiabetic drug utilization in hungary". Pharmacy World & Science. 27 (3): 263–5. doi:10.1007/s11096-004-5804-1. PMID 16096899. S2CID 9083315.
- ^ 한코 BZ, 레제기 CA, 금리 P, 빈체 Z. [헝가리에서의 당뇨병 치료법 연습]Acta 제약 Hung. 2005;75(2):77-86.
- ^ 게일 리서치 주식회사 제리 L. Schlesser.해외에서 구할 수 있는 약.Derwent Publications, Ltd - 1990 p28
- ^ Verdonck LF, Sangster B, van Heijst AN, de Groot G, Maes RA (1981). "Buformin concentrations in a case of fatal lactic acidosis". Diabetologia. 20 (1): 45–6. doi:10.1007/BF01789112. PMID 7202882.
- ^ Chou CH, Cheng CL, Huang CC (May 2004). "A validated HPLC method with ultraviolet detection for the determination of buformin in plasma". Biomedical Chromatography. 18 (4): 254–8. doi:10.1002/bmc.312. PMID 15162388.
- ^ 아민 우리타, 하세가와 쿠타로, 노자와 히데키, 야마가시 이타루, 미나카타 가요코, 와타나베 가나코, 스즈키 오사무.QuECHERS 추출법을 사용한 액체 크로마토그래피-탄뎀 질량 분석법을 사용한 부검 사례에서 체액 및 고형 조직에서 부포민의 사후에 분포/재분포.법의학 과학 2020년 6월 20일;314:110376. 도이: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2020.110376
- ^ 비트만 P, 하슬벡 M, 바흐만 W, 메흐너트 H. [비구아니아이드에 대한 당뇨병 환자의 락트산증(저자의 번역)]도이체 메디치니스체 보첸쉬리프트 102(1):5-10, 1977
- ^ Berger W, Mehnert-Aner S, Mülly K, Heierli C, Ritz R (December 1976). "[10 cases of lactic acidosis during biguanide therapy (buformin and phenformin)]". Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift. 106 (50): 1830–4. PMID 1013709.
- ^ Deppermann D, Heidland A, Ritz E, Hörl W (September 1978). "[Lactic acidosis--a possible complication in buformin-treated diabetics (author's transl)]". Klinische Wochenschrift. 56 (17): 843–53. doi:10.1007/BF01479834. PMID 713413. S2CID 39728557.
- ^ Luft D, Schmülling RM, Eggstein M (February 1978). "Lactic acidosis in biguanide-treated diabetics: a review of 330 cases". Diabetologia. 14 (2): 75–87. doi:10.1007/bf01263444. PMID 344119.
- ^ Saito S, Furuno A, Sakurai J, Sakamoto A, Park HR, Shin-Ya K, et al. (May 2009). "Chemical genomics identifies the unfolded protein response as a target for selective cancer cell killing during glucose deprivation". Cancer Research. 69 (10): 4225–34. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-2689. PMID 19435925.
- ^ Anisimov VN (October 2003). "Insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway driving aging and cancer as a target for pharmacological intervention". Experimental Gerontology. 38 (10): 1041–9. doi:10.1016/s0531-5565(03)00169-4. PMID 14580857.
- ^ Alexandrov VA, Anisimov VN, Belous NM, Vasilyeva IA, Mazon VB (1980). "The inhibition of the transplacental blastomogenic effect of nitrosomethylurea by postnatal administration of buformin to rats". Carcinogenesis. 1 (12): 975–8. doi:10.1093/carcin/1.12.975. PMID 11272113.
- ^ Anisimov VN, Ostroumova MN, Dil'man VM (1980). "Inhibition of the blastomogenic effect of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene in female rats by buformin, diphenin, a polypeptide pineal extract and L-DOPA". Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine. 89 (6): 819–822. doi:10.1007/bf00836263. PMID 6772259.
- ^ Anisimov VN, Berstein LM, Popovich IG, Zabezhinski MA, Egormin PA, Tyndyk ML, et al. (December 2005). "Central and peripheral effects of insulin/IGF-1 signaling in aging and cancer: antidiabetic drugs as geroprotectors and anticarcinogens". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1057 (1): 220–34. Bibcode:2005NYASA1057..220A. doi:10.1196/annals.1356.017. PMID 16399897.
- ^ Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB (May 2009). "Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation". Science. 324 (5930): 1029–33. Bibcode:2009Sci...324.1029V. doi:10.1126/science.1160809. PMC 2849637. PMID 19460998.
- ^ Shaw RJ, Lamia KA, Vasquez D, Koo SH, Bardeesy N, Depinho RA, et al. (December 2005). "The kinase LKB1 mediates glucose homeostasis in liver and therapeutic effects of metformin". Science. 310 (5754): 1642–6. Bibcode:2005Sci...310.1642S. doi:10.1126/science.1120781. PMC 3074427. PMID 16308421.
- ^ Zhu Z, Jiang W, Thompson MD, Echeverria D, McGinley JN, Thompson HJ (June 2015). "Effects of metformin, buformin, and phenformin on the post-initiation stage of chemically induced mammary carcinogenesis in the rat". Cancer Prevention Research. 8 (6): 518–27. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-14-0121. PMC 4452421. PMID 25804611.
- ^ Kilgore J, Jackson AL, Clark LH, Guo H, Zhang L, Jones HM, et al. (2016). "Buformin exhibits anti-proliferative and anti-invasive effects in endometrial cancer cells". American Journal of Translational Research. 8 (6): 2705–15. PMC 4931164. PMID 27398153.
- ^ Yakisich JS, Azad N, Kaushik V, Iyer AK (2019). "The Biguanides Metformin and Buformin in Combination with 2-Deoxy-glucose or WZB-117 Inhibit the Viability of Highly Resistant Human Lung Cancer Cells". Stem Cells International. 2019: 6254269. doi:10.1155/2019/6254269. PMC 6409035. PMID 30918522.
- ^ Li J, Chen L, Liu Q, Tang M, Wang Y, Yu J (June 2018). "Buformin suppresses proliferation and invasion via AMPK/S6 pathway in cervical cancer and synergizes with paclitaxel". Cancer Biology & Therapy. 19 (6): 507–517. doi:10.1080/15384047.2018.1433504. PMC 5927663. PMID 29400636.
- ^ Bailey CJ (September 2017). "Metformin: historical overview". Diabetologia. 60 (9): 1566–1576. doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4318-z. PMID 28776081. S2CID 2088719.
- ^ Weinberg ED (March 1968). "Antimicrobial activities of biguanides". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 148 (3): 587–600. Bibcode:1968NYASA.148..587W. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1968.tb27733.x. PMID 4872309.
- ^ Fara GM, Lugaro G, Galli MG, Giannattasio G (April 1974). "Antiviral activity of selected biguanide derivatives". Pharmacological Research Communications. 6 (2): 117–26. doi:10.1016/s0031-6989(74)80019-6. PMID 4373765.
- ^ Denys A, Bocian J (March 1970). "[Effect of Silubin-retard (1-butyl-biguanide hydrochloride) on the course of influenza-virus infection in mice]". Polski Tygodnik Lekarski (Warsaw, Poland : 1960) (in Polish). 25 (9): 332–4. PMID 5447272.
- ^ Babiński S, Giermaziak H (November 1973). "[Influenza epidemic in 1971 in diabetics treated with 1-butyl-biguanidine hydrochloride (Silubin retard) and 1-phenylethyl-biguanidine hydrochloride (Phenformin)]". Polski Tygodnik Lekarski (Warsaw, Poland : 1960) (in Polish). 28 (46): 1815–7. PMID 4771858.
- ^ Lehrer S (May 2020). "Inhaled biguanides and mTOR inhibition for influenza and coronavirus (Review)". World Academy of Sciences Journal. 2 (3). doi:10.3892/wasj.2020.42. PMC 7170270. PMID 32313883.
- ^ Kindrachuk J, Ork B, Hart BJ, Mazur S, Holbrook MR, Frieman MB, Traynor D, Johnson RF, Dyall J, Kuhn JH, Olinger GG, Hensley LE, Jahrling PB (February 2015). "Antiviral potential of ERK/MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling modulation for Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection as identified by temporal kinome analysis". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 59 (2): 1088–99. doi:10.1128/AAC.03659-14. PMC 4335870. PMID 25487801.
- ^ US 2961377, 샤피로 SL 외, 1960년 발행된 "N-아밀비구아나이드 팔츠"
- ^ Shapiro SL, Parrino VA, Freedman L (1959). "Hypoglycemic Agents. III.1—3N1-Alkyl- and Aralkylbiguanides". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 81 (14): 3728–3736. doi:10.1021/ja01523a060.




