데옥시우리딘단인산염
Deoxyuridine monophosphate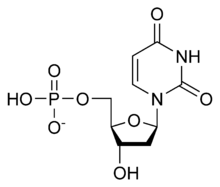 | |
 | |
| 이름 | |
|---|---|
| 선호 IUPAC 이름 [(2R,3S,5R)-5-(2,4-Dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-3-hydroxyoxolan-2-yl)methyl dihydrogen phosphate. | |
| 기타 이름 덤프 | |
| 식별자 | |
3D 모델(JSmol) | |
| 켐벨 | |
| 켐스파이더 | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.012.290 |
| 메슈 | 우리딘-4'-몬인산염 |
펍켐 CID | |
| 유니 | |
CompTox 대시보드 (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| 특성. | |
| C9H13N2O8P | |
| 어금질량 | 308.182 |
달리 명시된 경우를 제외하고, 표준 상태(25°C [77°F], 100 kPa)의 재료에 대한 데이터가 제공된다. | |
| Infobox 참조 자료 | |
디옥시우리딘모노인산(dUMP)은 각각 그것의 결합산과 결합기원형에서 디옥시우리딜산 또는 디옥시리딜산이라고도 알려져 있으며 디옥시뉴클레오타이드다.
그것은 디옥시리보뉴클레오티드 신진대사의 중간이다.
생합성
디옥시우리딘모노인산염(dump)은 우리딘모노인산염(UMP)의 디옥시미딘모노인산염(dooxythymidine monophosphate, dTMP)의 전구체로 DNA 뉴클레오티드 생합성의 성분이다.[1]리보스의 2' 탄소에 있는 히드록실 그룹을 수소로 대체함으로써 UMP는 덤프로 탈산화된다.
디옥시우리딘모노인산염(dUMP) 합성은 피리미딘생합성의 산물인 우리딘모노인산염(UMP)으로 시작하는 다단계 공정이다.[2]nucleoside monophosphate kinase 효소는 UMP와 ATP를 uridine diphosphate(UDP)와 ADP로 변환한다.
과잉 ATP가 있는 경우 리보뉴클레오티드 환원효소는 UDP와 연쇄반응을 일으켜 디옥시우리딘 디포스포산염(dUDP)의 형성을 촉진하고, 디옥시우리딘 트리인산염(dUTP)으로 변환한 다음 인산염 그룹의 첨가 또는 제거를 통해 디옥시우리딘 모노인산염(dUMP)을 만든다.[3]
대화형 경로 지도
각 기사에 연결하려면 아래의 유전자, 단백질, 대사물을 클릭하십시오.[§ 1]
Fluorouracil(5-FU) 활동 편집
- ^ 대화형 경로 맵은 WikiPathways에서 편집할 수 있다."FluoropyrimidineActivity_WP1601".
참고 항목
메모들
- ^ Berg, J. M.; Tymoczko, J. L.; Stryer, L. (2002). Biochemistry (5th ed.). New York: W H Freeman. ISBN 978-1-4641-2610-9.
- ^ Shambaugh, G. E. (June 1979). "Pyrimidine biosynthesis". The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 32 (6): 1290–1297. doi:10.1093/ajcn/32.6.1290. PMID 35970.
- ^ Garrett, Reginald H.; Grisham, Charles M. (2013). Biochemistry (6th ed.). Belmont, CA: Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning. p. 949. ISBN 9781133106296.


