PAK1
PAK1세린/스레오닌-단백질 키나아제 PAK 1은 인간에서 PAK1 유전자에 의해 인코딩되는 효소다.[5][6]
PAK1은 그룹 I(PAK1, PAK2 및 PAK3)와 그룹 II(PAK4, PAK6, PAK5/7)로 크게 구분되는 세린/트레오닌 키나제스의 6개 PAK 계열 중 하나이다.[7][8]PAK는 진화적으로 보존되어 있다.[9]PAK1은 세포질과 핵에서 구별되는 하위 세포영역에서 국소화한다.[10]PAK1은 시토스켈레톤 리모델링, 표현파 신호, 유전자 발현을 조절하며 방향 운동성, 침공, 전이, 성장, 세포 주기 진행, 혈관신생 등 다양한 세포 과정에 영향을 미친다.[10][11]PAK1-서명 의존 세포 기능은 PAK1이 인간 암에서 광범위하게 과도하게 압박되고 과다 자극되기 때문에 암을 포함한 생리학적 과정과 질병 과정을 모두 조절한다.[10][12][13]
디스커버리
PAK1은 1994년 맨저와 동료들에 의해 쥐의 뇌에서 Ro GTPases의 이펙터로 처음 발견되었다.[7]인간 PAK1은 중성미자의 세포질 분율에서 Rac1이나 Cdc42의 GTP 의존적 상호작용 파트너로 확인되었으며, 보완 DNA는 1995년 마틴과 동료에 의해 인간 태반 도서관에서 복제되었다.[8]
함수
PAK 단백질은 Rho 계열의 GTPases(Rho GTPases)와 Cytoskeleton 재구성과 핵신호를 연결하는 임계효과의 물질이다.세린/트레오닌 p21 활성화 키나제 계열인 PAK 단백질에는 PAK1, PAK2, PAK3, PAK4가 포함된다.이 단백질들은 작은 GTP 결합 단백질인 Cdc42와 Rac의 표적 역할을 하며 광범위한 생물학적 활동에 관여해왔다.PAK1은 세포 운동성과 형태학을 조절한다.이 유전자의 대체 성분은 발견되었지만, 그들의 전신 성질은 결정되지 않았다.[14]
PAK1 활동의 자극은 생물체계에 기초하는 일련의 세포 과정을 수반한다.결절 신호 분자인 PAK1은 업스트림 활성제뿐 아니라 세포 표면의 단백질에 의해 촉발된 다수의 신호의 수렴 스테이션에 작용하며, 구체적인 표현형으로 해석된다.생화학적 수준에서 이러한 활동은 PAK1의 이펙터가 상호작용하는 기판을 인산화하는 능력에 의해 조절되며, 이는 세포 표현형 응답으로 축적되는 일련의 생화학적 사건을 차례로 설정한다.또한, PAK1 작용은 비계 활동에도 영향을 받는다.PAK1 조절 세포 공정의 예로는 액틴과 미세관섬유, 세포주기 진행 중 중요한 단계, 운동성과 침입, 복스와 에너지 대사, 세포 생존, 혈관신생, DNA-수리, 호르몬 민감성, 유전자 발현 등이 있다.PAK1 신호의 기능적 함의는 종양 발생,[9] 바이러스성 병원체 발생,[15][16] 심혈관계 장애 [17]및 신경 장애에서의 역할에 의해 예시된다.[18]
유전자와 스플라이스 변형
인간 PAK1 유전자는 길이가 153kb이며 23 exon, 5'-UTR의 경우 6 exon, 단백질 코딩(Gene from review)의 경우 17 exon으로 구성된다.6개의 엑손의 대체 스플라이싱은 308-bp에서 3.7-kb 길이까지 20개의 대본을 생성하지만, 12개의 분할된 대본만이 판독 프레임을 개방하고 있으며 10개의 단백질과 2개의 폴리펩타이드 코드를 기록할 것으로 예측된다.나머지 8개 대본 범위는 길이 308-bp에서 863-bp까지 코딩되지 않는 긴 RNA에 대한 것이다.인간 PAK1과는 달리 뮤린 PAK1 유전자는 508-bp에서 3.0-kb 길이까지의 단백질 코드 3개, 비코딩 RNA의 경우 약 900-bp의 2개 등 5개의 대본을 생성한다.
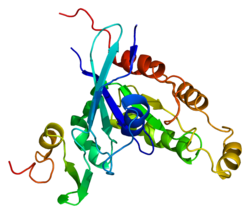
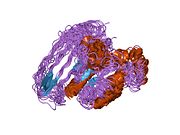
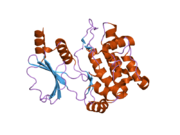
단백질 도메인
PAK 계열의 핵심 도메인은 C-터미널 영역의 키나세 도메인, p21 바인딩 도메인(PBD), 그룹 I PAK의 자동 수신 도메인(AID)을 포함한다.그룹 I PAKs는 한 분자의 AID가 다른 분자의 키나제 영역에 결합되고 GTPase 의존성과 독립적인 방식 모두에서 활성화되는 비활성화된 폐쇄 호모디머 순응으로 존재한다.[13]
활성화/금지
PAK1은 키나제 영역의 촉매 활동을 억제하는 자동 억제 도메인을 포함한다.PAK1 활성제는 이러한 자동 인시브레이션을 완화하고 키나제 활성화로 이어지는 순응적 재배열 및 자동 인산화 이벤트를 개시한다.
IPA-3 (1,1′-disulfanedieldinaphalen-2-ol)는 PAK1의 작은 분자 알로스테릭 억제제다.사전 활성화된 PAK1은 IPA-3에 내성이 있다.활선 셀에서의 억제는 PDGF 자극 ERK 활성화에서 PAK의 중요한 역할을 지원한다.[19]IPA-3를 PAK1 규제 영역으로 되돌릴 수 있는 공밸런트 바인딩은 GTPase 도킹을 방지하고 이후 촉매 활성 상태로 전환하는 것을 방지한다.[20]
전립선암 세포의 PAK1 녹다운은 운동성 감소, MMP9 분비량 감소, TGFβ 발현 증가와 관련이 있는데, 이 경우 성장 억제제다.그러나 IPA-3의 약동학적 특성과 세포 내 바람직하지 않은 리독스 효과는 황하이드리 모이티(sulfhydryl moiety)의 지속적인 감소로 인해 임상 발달에 부적합하다.[20]
업스트림 액티베이터
PAK1 활동 상부 활성기 체인에서는 및 신호의 큰 숫자 EGF,[21]에서 이르기까지 heregulin-beta 1,[22]VEGF,[23]기본 phosphoinositides,[28]fibroblast 성장 factor,[24]혈소판 유래 성장 factor,[25]estrogen,[26]lysophosphatidic acid,[27]ETK,[29]AKT,[30]JAK2,[31일]ERK,[32]카세인 인산화 효소 II,[33]Rac3,[34]인체 자극이 된다.(C-X-C motif)리간드 1,[35]유방 암anti-estrogen 사건.istance 3,[36] Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-G protein-coupled receptor,[37] ARG-binding protein 2γ,[38] hepatitis B virus X protein,[39] STE20-related kinase adaptor protein α,[40] RhoI,[41] Klotho,[42] N-acetylglucosaminyl transferase V,[43] B-Raf proto-oncogene,[44] casein kinase 2-interacting protein 1,[45] and filamin A.[46]
다운스트림 이펙터 대상
PAK1의 기능은 다운스트림 이펙터 기판을 인지하는 능력, 비계 활동, 구별되는 아세포 세포 하위 영역으로의 재분배, 직간접적으로 또는 이 모든 메커니즘에 의해 조절된다.암세포의 대표적인 PAK1 이펙터 기판은 다음과 같다.전사 5a-S779,[52]C말단 결합 단백질의 Stathmin-S16,[47]Merlin-S518,[48]Vimentin-S25-S38-S50-S65-S72,[49]히스톤 H3-S10,[50]FilaminA-S2152,[46]에스트로겐 receptor-alpha-S305,[51]신호 변환기와 활성기 1-S158,[53]Raf1-S338,[54]Arpc1b-T21,[55]DLC1-S88,[56]1-T466,[57]SMART/HDAC1-associated을 억누르다 phosphoglucomutase.아니면 Tubulin Cofactor B-S65- protein-S3486-T3568,[58].S128,[59]Snail-S246 혈관 endothelial-cadherin-S665,[61]poly(RC)결합 단백질 1-T60-S246,[62]integrin-linked 인산화 효소 1-T173-S246,[63]epithelium-specific Ets전사 인자 1-S207,[64]ErbB3 결합 단백질 1-T261,[65]핵 receptor-interacting 인자 3-S28,[66]SRC3-delta4-T56-S659-676,[67]beta-catenin-S675,[68]BAD-S111, -LSB- 69[60].]BAD-S112, S136,[70]MEK1-S298,[71][72]CRKII-S41,[73]MORC.CW형 아연 핑거 2-S739,[74][75] 팍실린-S258,[15] 팍실린-S273 패밀리.[76]
게놈 목표물
PAK1 및/또는 PAK1 종속 신호는 혈관 내피 성장 인자,[23] Cyclin D1, [77]인포프락토키나제-근육 이소형,[78] 활성 T세포의 핵 인자,[78] Cyclin B1,[79] 조직 인자 및 조직 인자 경로 억제제,[9][80] Metricoprotinase 9 [81]및 섬유ectin을 포함하여 게놈 표적의 표현을 변조한다.[82]
상호작용
PAK1은 다음과 상호 작용하는 것으로 나타났다.
메모들
이 글의 2016년 버전은 외부 전문가가 이중 출판 모델로 업데이트했다.해당 학술적 동료 검토 기사는 진에 게재되었으며, 다음과 같이 인용할 수 있다. Rakesh Kumar; Rahul Sanawar; Xiaodong Li; Feng Li (19 December 2016). "Structure, biochemistry, and biology of PAK kinases". Gene. Gene Wiki Review Series. 605: 20–31. doi:10.1016/J.GENE.2016.12.014. ISSN 0378-1119. PMC 5250584. PMID 28007610. Wikidata Q38779105. |
참조
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리스 89: ENSG00000149269 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ a b c GRCm38: 앙상블 릴리스 89: ENSMUSG000030774 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Brown JL, Stowers L, Baer M, Trejo J, Coughlin S, Chant J (May 1996). "Human Ste20 homologue hPAK1 links GTPases to the JNK MAP kinase pathway". Current Biology. 6 (5): 598–605. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00546-8. PMID 8805275. S2CID 9697114.
- ^ Bekri S, Adélaïde J, Merscher S, Grosgeorge J, Caroli-Bosc F, Perucca-Lostanlen D, Kelley PM, Pébusque MJ, Theillet C, Birnbaum D, Gaudray P (Apr 1998). "Detailed map of a region commonly amplified at 11q13-->q14 in human breast carcinoma". Cytogenetics and Cell Genetics. 79 (1–2): 125–31. doi:10.1159/000134699. PMID 9533029.
- ^ a b Manser E, Leung T, Salihuddin H, Zhao ZS, Lim L (January 1994). "A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1". Nature. 367 (6458): 40–6. doi:10.1038/367040a0. PMID 8107774. S2CID 4332455.
- ^ a b Martin GA, Bollag G, McCormick F, Abo A (May 1995). "A novel serine kinase activated by rac1/CDC42Hs-dependent autophosphorylation is related to PAK65 and STE20". The EMBO Journal. 14 (9): 1970–8. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07189.x. PMC 398296. PMID 7744004.
- ^ a b c Kumar A, Molli PR, Pakala SB, Bui Nguyen TM, Rayala SK, Kumar R (July 2009). "PAK thread from amoeba to mammals". Journal of Cellular Biochemistry. 107 (4): 579–85. doi:10.1002/jcb.22159. PMC 2718766. PMID 19350548.
- ^ a b c Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R (December 2003). "P21-activated kinases in human cancer". Cancer and Metastasis Reviews. 22 (4): 385–93. doi:10.1023/a:1023729130497. PMID 12884913. S2CID 5763102.
- ^ Kumar R, Gururaj AE, Barnes CJ (June 2006). "p21-activated kinases in cancer". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 6 (6): 459–71. doi:10.1038/nrc1892. PMID 16723992. S2CID 35272474.
- ^ Radu M, Semenova G, Kosoff R, Chernoff J (January 2014). "PAK signalling during the development and progression of cancer". Nature Reviews. Cancer. 14 (1): 13–25. doi:10.1038/nrc3645. PMC 4115244. PMID 24505617.
- ^ a b Kumar R, Li DQ (2016). PAKs in Human Cancer Progression: From Inception to Cancer Therapeutic to Future Oncobiology. Advances in Cancer Research. Vol. 130. pp. 137–209. doi:10.1016/bs.acr.2016.01.002. ISBN 9780128047897. PMID 27037753.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: PAK1 p21/Cdc42/Rac1-activated kinase 1 (STE20 homolog, yeast)".
- ^ a b Lee JH, Wittki S, Bräu T, Dreyer FS, Krätzel K, Dindorf J, Johnston IC, Gross S, Kremmer E, Zeidler R, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U, Lichtenheld M, Saksela K, Harrer T, Schuler G, Federico M, Baur AS (February 2013). "HIV Nef, paxillin, and Pak1/2 regulate activation and secretion of TACE/ADAM10 proteases". Molecular Cell. 49 (4): 668–79. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2012.12.004. PMID 23317503.
- ^ Van den Broeke C, Radu M, Chernoff J, Favoreel HW (March 2010). "An emerging role for p21-activated kinases (Paks) in viral infections". Trends in Cell Biology. 20 (3): 160–9. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2009.12.005. PMC 6489496. PMID 20071173.
- ^ Ke Y, Wang X, Jin XY, Solaro RJ, Lei M (December 2014). "PAK1 is a novel cardiac protective signaling molecule". Frontiers of Medicine. 8 (4): 399–403. doi:10.1007/s11684-014-0380-9. PMID 25416031. S2CID 7182791.
- ^ Ma QL, Yang F, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (April 2012). "PAK in Alzheimer disease, Huntington disease and X-linked mental retardation". Cellular Logistics. 2 (2): 117–125. doi:10.4161/cl.21602. PMC 3490962. PMID 23162743.
- ^ Deacon SW, Beeser A, Fukui JA, Rennefahrt UE, Myers C, Chernoff J, Peterson JR (April 2008). "An isoform-selective, small-molecule inhibitor targets the autoregulatory mechanism of p21-activated kinase". Chemistry & Biology. 15 (4): 322–31. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.03.005. PMC 4353635. PMID 18420139.
- ^ a b Goc A, Al-Azayzih A, Abdalla M, Al-Husein B, Kavuri S, Lee J, Moses K, Somanath PR (February 2013). "P21 activated kinase-1 (Pak1) promotes prostate tumor growth and microinvasion via inhibition of transforming growth factor β expression and enhanced matrix metalloproteinase 9 secretion". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 288 (5): 3025–35. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.424770. PMC 3561527. PMID 23258534.
- ^ Galisteo ML, Chernoff J, Su YC, Skolnik EY, Schlessinger J (August 1996). "The adaptor protein Nck links receptor tyrosine kinases with the serine-threonine kinase Pak1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (35): 20997–1000. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.35.20997. PMID 8798379.
- ^ Adam L, Vadlamudi R, Kondapaka SB, Chernoff J, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R (October 1998). "Heregulin regulates cytoskeletal reorganization and cell migration through the p21-activated kinase-1 via phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (43): 28238–46. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.43.28238. PMID 9774445.
- ^ a b Bagheri-Yarmand R, Vadlamudi RK, Wang RA, Mendelsohn J, Kumar R (December 2000). "Vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulation via p21-activated kinase-1 signaling regulates heregulin-beta1-mediated angiogenesis". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (50): 39451–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006150200. PMID 10967114.
- ^ Shin KS, Shin EY, Lee CS, Quan SH, Woo KN, Soung NK, Kwak SJ, Kim SR, Kim EG (May 2002). "Basic fibroblast growth factor-induced translocation of p21-activated kinase to the membrane is independent of phospholipase C-gamma1 in the differentiation of PC12 cells". Experimental & Molecular Medicine. 34 (2): 172–6. doi:10.1038/emm.2002.25. PMID 12085993.
- ^ He H, Levitzki A, Zhu HJ, Walker F, Burgess A, Maruta H (July 2001). "Platelet-derived growth factor requires epidermal growth factor receptor to activate p21-activated kinase family kinases". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (29): 26741–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.C100229200. PMID 11356824.
- ^ Mazumdar A, Kumar R (January 2003). "Estrogen regulation of Pak1 and FKHR pathways in breast cancer cells". FEBS Letters. 535 (1–3): 6–10. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(02)03846-2. PMID 12560069. S2CID 28855687.
- ^ Jung ID, Lee J, Lee KB, Park CG, Kim YK, Seo DW, Park D, Lee HW, Han JW, Lee HY (April 2004). "Activation of p21-activated kinase 1 is required for lysophosphatidic acid-induced focal adhesion kinase phosphorylation and cell motility in human melanoma A2058 cells". European Journal of Biochemistry. 271 (8): 1557–65. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04066.x. PMID 15066181.
- ^ Strochlic TI, Viaud J, Rennefahrt UE, Anastassiadis T, Peterson JR (November 2010). "Phosphoinositides are essential coactivators for p21-activated kinase 1". Molecular Cell. 40 (3): 493–500. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.10.015. PMC 3026281. PMID 21070974.
- ^ a b Bagheri-Yarmand R, Mandal M, Taludker AH, Wang RA, Vadlamudi RK, Kung HJ, Kumar R (August 2001). "Etk/Bmx tyrosine kinase activates Pak1 and regulates tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (31): 29403–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M103129200. PMID 11382770.
- ^ Zhou GL, Zhuo Y, King CC, Fryer BH, Bokoch GM, Field J (November 2003). "Akt phosphorylation of serine 21 on Pak1 modulates Nck binding and cell migration". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 23 (22): 8058–69. doi:10.1128/mcb.23.22.8058-8069.2003. PMC 262366. PMID 14585966.
- ^ Rider L, Shatrova A, Feener EP, Webb L, Diakonova M (October 2007). "JAK2 tyrosine kinase phosphorylates PAK1 and regulates PAK1 activity and functions". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 282 (42): 30985–96. doi:10.1074/jbc.M701794200. PMID 17726028.
- ^ Yuan L, Santi M, Rushing EJ, Cornelison R, MacDonald TJ (October 2010). "ERK activation of p21 activated kinase-1 (Pak1) is critical for medulloblastoma cell migration". Clinical & Experimental Metastasis. 27 (7): 481–91. doi:10.1007/s10585-010-9337-9. PMC 2954413. PMID 20526801.
- ^ Shin YJ, Kim YB, Kim JH (September 2013). "Protein kinase CK2 phosphorylates and activates p21-activated kinase 1". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 24 (18): 2990–9. doi:10.1091/mbc.E13-04-0204. PMC 3771959. PMID 23885116.
- ^ Mira JP, Benard V, Groffen J, Sanders LC, Knaus UG (January 2000). "Endogenous, hyperactive Rac3 controls proliferation of breast cancer cells by a p21-activated kinase-dependent pathway". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (1): 185–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.1.185. PMC 26637. PMID 10618392.
- ^ Wang D, Sai J, Richmond A (February 2003). "Cell surface heparan sulfate participates in CXCL1-induced signaling". Biochemistry. 42 (4): 1071–7. doi:10.1021/bi026425a. PMC 2667446. PMID 12549928.
- ^ Cai D, Iyer A, Felekkis KN, Near RI, Luo Z, Chernoff J, Albanese C, Pestell RG, Lerner A (October 2003). "AND-34/BCAR3, a GDP exchange factor whose overexpression confers antiestrogen resistance, activates Rac, PAK1, and the cyclin D1 promoter". Cancer Research. 63 (20): 6802–8. PMID 14583477.
- ^ Dadke D, Fryer BH, Golemis EA, Field J (December 2003). "Activation of p21-activated kinase 1-nuclear factor kappaB signaling by Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpes virus G protein-coupled receptor during cellular transformation". Cancer Research. 63 (24): 8837–47. PMID 14695200.
- ^ Yuan ZQ, Kim D, Kaneko S, Sussman M, Bokoch GM, Kruh GD, Nicosia SV, Testa JR, Cheng JQ (June 2005). "ArgBP2gamma interacts with Akt and p21-activated kinase-1 and promotes cell survival". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 280 (22): 21483–90. doi:10.1074/jbc.M500097200. PMID 15784622.
- ^ Xu J, Liu H, Chen L, Wang S, Zhou L, Yun X, Sun L, Wen Y, Gu J (July 2012). "Hepatitis B virus X protein confers resistance of hepatoma cells to anoikis by up-regulating and activating p21-activated kinase 1". Gastroenterology. 143 (1): 199–212.e4. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.03.053. PMID 22484303.
- ^ Eggers CM, Kline ER, Zhong D, Zhou W, Marcus AI (May 2012). "STE20-related kinase adaptor protein α (STRADα) regulates cell polarity and invasion through PAK1 signaling in LKB1-null cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287 (22): 18758–68. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.316422. PMC 3365778. PMID 22493453.
- ^ Ho H, Aruri J, Kapadia R, Mehr H, White MA, Ganesan AK (November 2012). "RhoJ regulates melanoma chemoresistance by suppressing pathways that sense DNA damage". Cancer Research. 72 (21): 5516–28. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0775. PMC 3548429. PMID 22971344.
- ^ Chen L, Liu H, Liu J, Zhu Y, Xu L, He H, Zhang H, Wang S, Wu Q, Liu W, Liu Y, Pan D, Ren S, Xu J, Gu J (2013). "Klotho endows hepatoma cells with resistance to anoikis via VEGFR2/PAK1 activation in hepatocellular carcinoma". PLOS ONE. 8 (3): e58413. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058413. PMC 3596390. PMID 23516476.
- ^ Liu J, Liu H, Zhang W, Wu Q, Liu W, Liu Y, Pan D, Xu J, Gu J (September 2013). "N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase V confers hepatoma cells with resistance to anoikis through EGFR/PAK1 activation". Glycobiology. 23 (9): 1097–109. doi:10.1093/glycob/cwt049. PMID 23811795.
- ^ McCarty SK, Saji M, Zhang X, Knippler CM, Kirschner LS, Fernandez S, Ringel MD (2014). "BRAF activates and physically interacts with PAK to regulate cell motility". Endocrine-Related Cancer. 21 (6): 865–77. doi:10.1530/ERC-14-0424. PMC 4487662. PMID 25228413.
- ^ Kim YB, Shin YJ, Roy A, Kim JH (August 2015). "The Role of the Pleckstrin Homology Domain-containing Protein CKIP-1 in Activation of p21-activated Kinase 1 (PAK1)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 290 (34): 21076–85. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.675124. PMC 4543665. PMID 26160174.
- ^ a b Vadlamudi RK, Li F, Adam L, Nguyen D, Ohta Y, Stossel TP, Kumar R (September 2002). "Filamin is essential in actin cytoskeletal assembly mediated by p21-activated kinase 1". Nature Cell Biology. 4 (9): 681–90. doi:10.1038/ncb838. PMID 12198493. S2CID 36460759.
- ^ Daub H, Gevaert K, Vandekerckhove J, Sobel A, Hall A (January 2001). "Rac/Cdc42 and p65PAK regulate the microtubule-destabilizing protein stathmin through phosphorylation at serine 16". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (3): 1677–80. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000635200. PMID 11058583.
- ^ Xiao GH, Beeser A, Chernoff J, Testa JR (January 2002). "p21-activated kinase links Rac/Cdc42 signaling to merlin". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (2): 883–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.C100553200. PMID 11719502.
- ^ Goto H, Tanabe K, Manser E, Lim L, Yasui Y, Inagaki M (February 2002). "Phosphorylation and reorganization of vimentin by p21-activated kinase (PAK)". Genes to Cells. 7 (2): 91–7. doi:10.1046/j.1356-9597.2001.00504.x. PMID 11895474. S2CID 28180002.
- ^ Li F, Adam L, Vadlamudi RK, Zhou H, Sen S, Chernoff J, Mandal M, Kumar R (August 2002). "p21-activated kinase 1 interacts with and phosphorylates histone H3 in breast cancer cells". EMBO Reports. 3 (8): 767–73. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kvf157. PMC 1084211. PMID 12151336.
- ^ Wang RA, Mazumdar A, Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R (October 2002). "P21-activated kinase-1 phosphorylates and transactivates estrogen receptor-alpha and promotes hyperplasia in mammary epithelium". The EMBO Journal. 21 (20): 5437–47. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdf543. PMC 129075. PMID 12374744.
- ^ Wang RA, Vadlamudi RK, Bagheri-Yarmand R, Beuvink I, Hynes NE, Kumar R (May 2003). "Essential functions of p21-activated kinase 1 in morphogenesis and differentiation of mammary glands". The Journal of Cell Biology. 161 (3): 583–92. doi:10.1083/jcb.200212066. PMC 2172951. PMID 12732616.
- ^ Barnes CJ, Vadlamudi RK, Mishra SK, Jacobson RH, Li F, Kumar R (August 2003). "Functional inactivation of a transcriptional corepressor by a signaling kinase". Nature Structural Biology. 10 (8): 622–8. doi:10.1038/nsb957. PMID 12872159. S2CID 12312851.
- ^ Gurdon JB (January 1992). "The generation of diversity and pattern in animal development". Cell. 68 (2): 185–99. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(92)90465-o. PMID 1733498. S2CID 43600561.
- ^ Vadlamudi RK, Li F, Barnes CJ, Bagheri-Yarmand R, Kumar R (February 2004). "p41-Arc subunit of human Arp2/3 complex is a p21-activated kinase-1-interacting substrate". EMBO Reports. 5 (2): 154–60. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400079. PMC 1298990. PMID 14749719.
- ^ a b Vadlamudi RK, Bagheri-Yarmand R, Yang Z, Balasenthil S, Nguyen D, Sahin AA, den Hollander P, Kumar R (June 2004). "Dynein light chain 1, a p21-activated kinase 1-interacting substrate, promotes cancerous phenotypes". Cancer Cell. 5 (6): 575–85. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2004.05.022. PMID 15193260.
- ^ Gururaj A, Barnes CJ, Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R (October 2004). "Regulation of phosphoglucomutase 1 phosphorylation and activity by a signaling kinase". Oncogene. 23 (49): 8118–27. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1207969. PMID 15378030.
- ^ Vadlamudi RK, Manavathi B, Singh RR, Nguyen D, Li F, Kumar R (June 2005). "An essential role of Pak1 phosphorylation of SHARP in Notch signaling". Oncogene. 24 (28): 4591–6. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1208672. PMID 15824732.
- ^ Vadlamudi RK, Barnes CJ, Rayala S, Li F, Balasenthil S, Marcus S, Goodson HV, Sahin AA, Kumar R (May 2005). "p21-activated kinase 1 regulates microtubule dynamics by phosphorylating tubulin cofactor B". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 25 (9): 3726–36. doi:10.1128/MCB.25.9.3726-3736.2005. PMC 1084301. PMID 15831477.
- ^ Yang Z, Rayala S, Nguyen D, Vadlamudi RK, Chen S, Kumar R (April 2005). "Pak1 phosphorylation of snail, a master regulator of epithelial-to-mesenchyme transition, modulates snail's subcellular localization and functions". Cancer Research. 65 (8): 3179–84. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3480. PMID 15833848.
- ^ Gavard J, Gutkind JS (November 2006). "VEGF controls endothelial-cell permeability by promoting the beta-arrestin-dependent endocytosis of VE-cadherin". Nature Cell Biology. 8 (11): 1223–34. doi:10.1038/ncb1486. PMID 17060906. S2CID 36686511.
- ^ Meng Q, Rayala SK, Gururaj AE, Talukder AH, O'Malley BW, Kumar R (April 2007). "Signaling-dependent and coordinated regulation of transcription, splicing, and translation resides in a single coregulator, PCBP1". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (14): 5866–71. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701065104. PMC 1851583. PMID 17389360.
- ^ Acconcia F, Barnes CJ, Singh RR, Talukder AH, Kumar R (April 2007). "Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of nuclear localization and functions of integrin-linked kinase". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (16): 6782–7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0701999104. PMC 1871862. PMID 17420447.
- ^ Manavathi B, Rayala SK, Kumar R (July 2007). "Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of stability and transforming potential of ETS transcriptional factor ESE-1 by p21-activated kinase 1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 282 (27): 19820–30. doi:10.1074/jbc.M702309200. PMID 17491012.
- ^ Akinmade D, Talukder AH, Zhang Y, Luo WM, Kumar R, Hamburger AW (March 2008). "Phosphorylation of the ErbB3 binding protein Ebp1 by p21-activated kinase 1 in breast cancer cells". British Journal of Cancer. 98 (6): 1132–40. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6604261. PMC 2275482. PMID 18283314.
- ^ Talukder AH, Li DQ, Manavathi B, Kumar R (September 2008). "Serine 28 phosphorylation of NRIF3 confers its co-activator function for estrogen receptor-alpha transactivation". Oncogene. 27 (39): 5233–42. doi:10.1038/onc.2008.151. PMC 3621709. PMID 18521086.
- ^ Long W, Yi P, Amazit L, LaMarca HL, Ashcroft F, Kumar R, Mancini MA, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ, O'Malley BW (February 2010). "SRC-3Delta4 mediates the interaction of EGFR with FAK to promote cell migration". Molecular Cell. 37 (3): 321–32. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.01.004. PMC 2824333. PMID 20159552.
- ^ Zhu G, Wang Y, Huang B, Liang J, Ding Y, Xu A, Wu W (February 2012). "A Rac1/PAK1 cascade controls β-catenin activation in colon cancer cells". Oncogene. 31 (8): 1001–12. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.294. PMID 21822311.
- ^ Ye DZ, Jin S, Zhuo Y, Field J (2011). "p21-Activated kinase 1 (Pak1) phosphorylates BAD directly at serine 111 in vitro and indirectly through Raf-1 at serine 112". PLOS ONE. 6 (11): e27637. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0027637. PMC 3214075. PMID 22096607.
- ^ Schürmann A, Mooney AF, Sanders LC, Sells MA, Wang HG, Reed JC, Bokoch GM (January 2000). "p21-activated kinase 1 phosphorylates the death agonist bad and protects cells from apoptosis". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 20 (2): 453–61. doi:10.1128/mcb.20.2.453-461.2000. PMC 85099. PMID 10611223.
- ^ Shrestha Y, Schafer EJ, Boehm JS, Thomas SR, He F, Du J, Wang S, Barretina J, Weir BA, Zhao JJ, Polyak K, Golub TR, Beroukhim R, Hahn WC (July 2012). "PAK1 is a breast cancer oncogene that coordinately activates MAPK and MET signaling" (PDF). Oncogene. 31 (29): 3397–408. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.515. PMC 3291810. PMID 22105362.
- ^ Slack-Davis JK, Eblen ST, Zecevic M, Boerner SA, Tarcsafalvi A, Diaz HB, Marshall MS, Weber MJ, Parsons JT, Catling AD (July 2003). "PAK1 phosphorylation of MEK1 regulates fibronectin-stimulated MAPK activation". The Journal of Cell Biology. 162 (2): 281–91. doi:10.1083/jcb.200212141. PMC 2172784. PMID 12876277.
- ^ Rettig M, Trinidad K, Pezeshkpour G, Frost P, Sharma S, Moatamed F, Tamanoi F, Mortazavi F (2012). "PAK1 kinase promotes cell motility and invasiveness through CRK-II serine phosphorylation in non-small cell lung cancer cells". PLOS ONE. 7 (7): e42012. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0042012. PMC 3407072. PMID 22848689.
- ^ Li DQ, Nair SS, Ohshiro K, Kumar A, Nair VS, Pakala SB, Reddy SD, Gajula RP, Eswaran J, Aravind L, Kumar R (December 2012). "MORC2 signaling integrates phosphorylation-dependent, ATPase-coupled chromatin remodeling during the DNA damage response". Cell Reports. 2 (6): 1657–69. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2012.11.018. PMC 3554793. PMID 23260667.
- ^ Wang G, Song Y, Liu T, Wang C, Zhang Q, Liu F, Cai X, Miao Z, Xu H, Xu H, Cao L, Li F (2015). "PAK1-mediated MORC2 phosphorylation promotes gastric tumorigenesis". Oncotarget. 6 (12): 9877–86. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.3185. PMC 4496403. PMID 25888627.
- ^ Nayal A, Webb DJ, Brown CM, Schaefer EM, Vicente-Manzanares M, Horwitz AR (May 2006). "Paxillin phosphorylation at Ser273 localizes a GIT1-PIX-PAK complex and regulates adhesion and protrusion dynamics". The Journal of Cell Biology. 173 (4): 587–9. doi:10.1083/jcb.200509075. PMC 2063867. PMID 16717130.
- ^ Balasenthil S, Sahin AA, Barnes CJ, Wang RA, Pestell RG, Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R (January 2004). "p21-activated kinase-1 signaling mediates cyclin D1 expression in mammary epithelial and cancer cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (2): 1422–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309937200. PMID 14530270.
- ^ a b Singh RR, Song C, Yang Z, Kumar R (May 2005). "Nuclear localization and chromatin targets of p21-activated kinase 1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 280 (18): 18130–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M412607200. PMID 15749698.
- ^ Liu F, Li X, Wang C, Cai X, Du Z, Xu H, Li F (December 2009). "Downregulation of p21-activated kinase-1 inhibits the growth of gastric cancer cells involving cyclin B1". International Journal of Cancer. 125 (11): 2511–9. doi:10.1002/ijc.24588. PMID 19610058. S2CID 43415843.
- ^ Sánchez-Solana B, Motwani M, Li DQ, Eswaran J, Kumar R (November 2012). "p21-activated kinase-1 signaling regulates transcription of tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287 (47): 39291–302. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.404061. PMC 3501013. PMID 23038262.
- ^ Goc A, Al-Azayzih A, Abdalla M, Al-Husein B, Kavuri S, Lee J, Moses K, Somanath PR (February 2013). "P21 activated kinase-1 (Pak1) promotes prostate tumor growth and microinvasion via inhibition of transforming growth factor β expression and enhanced matrix metalloproteinase 9 secretion". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 288 (5): 3025–35. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.424770. PMC 3561527. PMID 23258534.
- ^ Jagadeeshan S, Krishnamoorthy YR, Singhal M, Subramanian A, Mavuluri J, Lakshmi A, Roshini A, Baskar G, Ravi M, Joseph LD, Sadasivan K, Krishnan A, Nair AS, Venkatraman G, Rayala SK (January 2015). "Transcriptional regulation of fibronectin by p21-activated kinase-1 modulates pancreatic tumorigenesis". Oncogene. 34 (4): 455–64. doi:10.1038/onc.2013.576. PMID 24561527. S2CID 23631950.
- ^ Zenke FT, Krendel M, DerMardirossian C, King CC, Bohl BP, Bokoch GM (April 2004). "p21-activated kinase 1 phosphorylates and regulates 14-3-3 binding to GEF-H1, a microtubule-localized Rho exchange factor". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (18): 18392–400. doi:10.1074/jbc.M400084200. PMID 14970201.
- ^ Vadlamudi RK, Li F, Barnes CJ, Bagheri-Yarmand R, Kumar R (February 2004). "p41-Arc subunit of human Arp2/3 complex is a p21-activated kinase-1-interacting substrate". EMBO Reports. 5 (2): 154–60. doi:10.1038/sj.embor.7400079. PMC 1298990. PMID 14749719.
- ^ Zang M, Hayne C, Luo Z (February 2002). "Interaction between active Pak1 and Raf-1 is necessary for phosphorylation and activation of Raf-1". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (6): 4395–405. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110000200. PMID 11733498.
- ^ a b Seoh ML, Ng CH, Yong J, Lim L, Leung T (March 2003). "ArhGAP15, a novel human RacGAP protein with GTPase binding property". FEBS Letters. 539 (1–3): 131–7. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00213-8. PMID 12650940. S2CID 27574424.
- ^ a b Zhang B, Chernoff J, Zheng Y (April 1998). "Interaction of Rac1 with GTPase-activating proteins and putative effectors. A comparison with Cdc42 and RhoA". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (15): 8776–82. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.15.8776. PMID 9535855.
- ^ Rashid T, Banerjee M, Nikolic M (December 2001). "Phosphorylation of Pak1 by the p35/Cdk5 kinase affects neuronal morphology". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 276 (52): 49043–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105599200. PMID 11604394.
- ^ Edwards DC, Sanders LC, Bokoch GM, Gill GN (September 1999). "Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics". Nature Cell Biology. 1 (5): 253–9. doi:10.1038/12963. PMID 10559936. S2CID 25250183.
- ^ Ku GM, Yablonski D, Manser E, Lim L, Weiss A (February 2001). "A PAK1-PIX-PKL complex is activated by the T-cell receptor independent of Nck, Slp-76 and LAT". The EMBO Journal. 20 (3): 457–65. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.3.457. PMC 133476. PMID 11157752.
- ^ Braverman LE, Quilliam LA (February 1999). "Identification of Grb4/Nckbeta, a src homology 2 and 3 domain-containing adapter protein having similar binding and biological properties to Nck". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (9): 5542–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.9.5542. PMID 10026169.
- ^ Bokoch GM, Wang Y, Bohl BP, Sells MA, Quilliam LA, Knaus UG (October 1996). "Interaction of the Nck adapter protein with p21-activated kinase (PAK1)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (42): 25746–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.42.25746. PMID 8824201.
- ^ Xia C, Ma W, Stafford LJ, Marcus S, Xiong WC, Liu M (May 2001). "Regulation of the p21-activated kinase (PAK) by a human Gbeta -like WD-repeat protein, hPIP1". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (11): 6174–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.101137298. PMC 33441. PMID 11371639.
- ^ Katoh H, Negishi M (July 2003). "RhoG activates Rac1 by direct interaction with the Dock180-binding protein Elmo". Nature. 424 (6947): 461–4. doi:10.1038/nature01817. PMID 12879077. S2CID 4411133.
외부 링크
- 웨이백 시스템에 보관된 2014-12-11 셀 마이그레이션 게이트웨이에 링크가 있는 PAK1 정보
- Andrei, Mihai (March 23, 2016). "Researchers zoom in on potential treatment for prostate cancer". ZME Science. Retrieved 2016-04-23.