BRD4
BRD4브로모도메인 함유단백질 4는 BRD4 유전자에 [3][4]의해 인체 내에서 암호화되는 단백질이다.
BRD4는 BRD2, BRD3, BRDT를 [5]포함하는 BET(Bromodomain and extra terminal domain) 패밀리의 일원입니다.BRD4는 다른 BET 패밀리와 마찬가지로 아세틸화 리신 [6]잔기를 인식하는 2개의 브롬도메인을 포함하고 있습니다.또한 BRD4에는 다른 BET 패밀리 [5]멤버에 대한 시퀀스호몰로지가 거의 없는 확장 C-단말 도메인이 있습니다.
구조.
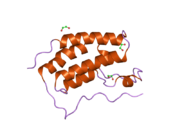
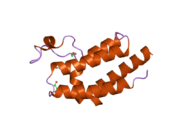
BRD4의 두 브로모도메인 BD1과 BD2는 2개의 [7]루프로 연결된 4개의 알파-헬리크로 구성됩니다.ET 도메인 구조는 3개의 알파 헬리크와 1개의 [8]루프로 구성됩니다.BRD4의 C 말단 도메인은 전사 신장 인자 P-TEFb 및 RNA 중합효소 [9][10][11]II와의 상호작용을 통해 유전자 전사를 촉진하는 데 관여하고 있다.
기능.
이 유전자에 의해 코드된 단백질은 유사분열 중에 염색체와 관련된 쥐 단백질 MCAP과 세린/트레오닌 키나아제인 인간 BRD2(RING3) 단백질과 상동한다.이들 단백질 각각은 2개의 브롬도메인을 포함하고 있으며, 이 브롬도메인은 염색질 타겟팅에 관여할 수 있는 보존 배열 모티브이다.이 유전자는 NUT 중간선 암을 정의하는 전위 t(15;19)(q13;p13.1)의 19번 염색체 표적으로 관련되었다.대체적으로 스플라이스된 두 가지 트랜스크립트 변형이 [4]설명되었습니다.
암에서의 역할
NUT 중간선 암의 대부분의 사례는 NUT 유전자와 BRD4 [12]유전자의 전이를 포함한다.BRD4는 다발성 골수종, 급성 골수성 백혈병, 급성 림프아구성 [13]백혈병을 포함한 혈액암에서 Myc와 다른 "종양 구동" 종양유전자의 발현에 종종 필요하다.
BRD4는 현재 임상시험에서 평가되고 있는 의약품인 BET 억제제의 주요 대상이다.[13][14]
상호 작용
특히 BRD4는 P-TEFb 상호작용 도메인(PID)을 통해 P-TEFb와 상호작용하여 키나아제 활성을 자극하고 RNA 중합효소 [15]II의 카르복시 말단 도메인(CTD)의 인산화를 촉진한다.최근 [16]리뷰
BRD4는 GATA1,[17] JMJD6,[18] RFC2,[19] RFC3,[19] RFC1,[19] RFC4[19] 및 [19]RFC5와 상호 작용하는 것으로 나타났습니다.
BRD4는 디아세틸화된 트위스트 단백질과의 결합에도 관여하고 있으며, 이러한 상호작용의 중단은 기저부 유방암의 [20]종양유전 발생을 억제하는 것으로 나타났다.
또한 BRD4는 MS417과 같은 다양한 억제제와 상호작용하는 것으로 나타났다. MS417에 의한 BRD4의 억제는 HIV 관련 신장 [21]질환에서 나타나는 NF-δB 활성을 하향 조절하는 것으로 나타났다.BRD4는 또한 아테롬성 동맥경화증 및 심혈관 질환 치료를 위해 평가되고 있는 아파벳아론(RVX-208)[22]과도 상호작용한다.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c GRCh38: 앙상블 릴리즈 89: ENSG00000141867 - 앙상블, 2017년 5월
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Dey A, Ellenberg J, Farina A, Coleman AE, Maruyama T, Sciortino S, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Ozato K (Sep 2000). "A bromodomain protein, MCAP, associates with mitotic chromosomes and affects G(2)-to-M transition". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 20 (17): 6537–49. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.17.6537-6549.2000. PMC 86127. PMID 10938129.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: BRD4 bromodomain containing 4".
- ^ a b Zeng L, Zhou MM (Feb 2002). "Bromodomain: an acetyl-lysine binding domain". FEBS Letters. 513 (1): 124–8. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(01)03309-9. PMID 11911891. S2CID 29706103.
- ^ Shi J, Vakoc CR (Jun 2014). "The mechanisms behind the therapeutic activity of BET bromodomain inhibition". Molecular Cell. 54 (5): 728–736. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.05.016. PMC 4236231. PMID 24905006.
- ^ Devaiah BN, Singer DS (1 January 2013). "Two faces of brd4: mitotic bookmark and transcriptional lynchpin". Transcription. 4 (1): 13–17. doi:10.4161/trns.22542. PMC 3644036. PMID 23131666.
- ^ Wu SY, Chiang CM (May 2007). "The double bromodomain-containing chromatin adaptor Brd4 and transcriptional regulation". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 282 (18): 13141–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.r700001200. PMID 17329240.
- ^ Itzen, F; Greifenberg, A. K.; Bösken, C. A.; Geyer, M (2014). "Brd4 activates P-TEFb for RNA polymerase II CTD phosphorylation". Nucleic Acids Research. 42 (12): 7577–90. doi:10.1093/nar/gku449. PMC 4081074. PMID 24860166.
- ^ Jonkers, I; Lis, J. T. (2015). "Getting up to speed with transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II". Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 16 (3): 167–77. doi:10.1038/nrm3953. PMC 4782187. PMID 25693130.
- ^ Yang, Z; Yik, J. H.; Chen, R; He, N; Jang, M. K.; Ozato, K; Zhou, Q (2005). "Recruitment of P-TEFb for stimulation of transcriptional elongation by the bromodomain protein Brd4". Molecular Cell. 19 (4): 535–45. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.029. PMID 16109377.
- ^ French CA (Jun 2010). "Demystified molecular pathology of NUT midline carcinomas". Journal of Clinical Pathology. 63 (6): 492–6. doi:10.1136/jcp.2007.052902. PMID 18552174. S2CID 2200842.
- ^ a b Da Costa, D.; Agathanggelou, A.; Perry, T.; Weston, V.; Petermann, E.; Zlatanou, A.; Oldreive, C.; Wei, W.; Stewart, G. (2013-07-19). "BET inhibition as a single or combined therapeutic approach in primary paediatric B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia". Blood Cancer Journal. 3 (7): e126. doi:10.1038/bcj.2013.24. PMC 3730202. PMID 23872705.
- ^ Shi J, Vakoc CR (Jun 2014). "The mechanisms behind the therapeutic activity of BET bromodomain inhibition". Molecular Cell. 54 (5): 728–36. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2014.05.016. PMC 4236231. PMID 24905006.
- ^ Itzen F, Greifenberg AK, Bösken CA, Geyer M (Jul 2014). "Brd4 activates P-TEFb for RNA polymerase II CTD phosphorylation". Nucleic Acids Research. 42 (12): 7577–7590. doi:10.1093/nar/gku449. PMC 4081074. PMID 24860166.
- ^ Quaresma, AJ; Bugai A; Barboric M. (2016). "Cracking the control of RNA polymerase II elongation by 7SK snRNP and P-TEFb". Nucleic Acids Research. 44 (8): 7527–7539. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw585. PMC 5027500. PMID 27369380.
- ^ Lamonica JM, Deng W, Kadauke S, Campbell AE, Gamsjaeger R, Wang H, Cheng Y, Billin AN, Hardison RC, Mackay JP, Blobel GA (May 2011). "Bromodomain protein Brd3 associates with acetylated GATA1 to promote its chromatin occupancy at erythroid target genes". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (22): E159–68. doi:10.1073/pnas.1102140108. PMC 3107332. PMID 21536911.
- ^ Liu W, Ma Q, Wong K, Li W, Ohgi K, Zhang J, Aggarwal AK, Rosenfeld MG (Dec 2013). "Brd4 and JMJD6-associated anti-pause enhancers in regulation of transcriptional pause release". Cell. 155 (7): 1581–95. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.056. PMC 3886918. PMID 24360279.
- ^ a b c d e Maruyama T, Farina A, Dey A, Cheong J, Bermudez VP, Tamura T, Sciortino S, Shuman J, Hurwitz J, Ozato K (Sep 2002). "A Mammalian bromodomain protein, brd4, interacts with replication factor C and inhibits progression to S phase". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 22 (18): 6509–20. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.18.6509-6520.2002. PMC 135621. PMID 12192049.
- ^ Shi J, Wang Y, Zeng L, Wu Y, Deng J, Zhang Q, Lin Y, Li J, Kang T, Tao M, Rusinova E, Zhang G, Wang C, Zhu H, Yao J, Zeng YX, Evers BM, Zhou MM, Zhou BP (Feb 2014). "Disrupting the interaction of BRD4 with diacetylated Twist suppresses tumorigenesis in basal-like breast cancer". Cancer Cell. 25 (2): 210–225. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.01.028. PMC 4004960. PMID 24525235.
- ^ Zhang G, Liu R, Zhong Y, Plotnikov AN, Zhang W, Zeng L, Rusinova E, Gerona-Nevarro G, Moshkina N, Joshua J, Chuang PY, Ohlmeyer M, He JC, Zhou MM (Aug 2012). "Down-regulation of NF-κB transcriptional activity in HIV-associated kidney disease by BRD4 inhibition". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 287 (34): 28840–28851. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.359505. PMC 3436579. PMID 22645123.
- ^ McLure KG, Gesner EM, Tsujikawa L, Kharenko OA, Attwell S, Campeau E, Wasiak S, Stein A, White A, Fontano E, Suto RK, Wong NC, Wagner GS, Hansen HC, Young PR (31 December 2013). "RVX-208, an inducer of ApoA-I in humans, is a BET bromodomain antagonist". PLOS ONE. 8 (12): e83190. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...883190M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0083190. PMC 3877016. PMID 24391744.
외부 링크
- UCSC Genome Browser의 인간 BRD4 게놈 위치 및 BRD4 유전자 세부 정보 페이지.
추가 정보
- French CA, Miyoshi I, Aster JC, Kubonishi I, Kroll TG, Dal Cin P, Vargas SO, Perez-Atayde AR, Fletcher JA (Dec 2001). "BRD4 bromodomain gene rearrangement in aggressive carcinoma with translocation t(15;19)". The American Journal of Pathology. 159 (6): 1987–92. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63049-0. PMC 1850578. PMID 11733348.
- Maruyama T, Farina A, Dey A, Cheong J, Bermudez VP, Tamura T, Sciortino S, Shuman J, Hurwitz J, Ozato K (Sep 2002). "A Mammalian bromodomain protein, brd4, interacts with replication factor C and inhibits progression to S phase". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 22 (18): 6509–20. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.18.6509-6520.2002. PMC 135621. PMID 12192049.
- French CA, Miyoshi I, Kubonishi I, Grier HE, Perez-Atayde AR, Fletcher JA (Jan 2003). "BRD4-NUT fusion oncogene: a novel mechanism in aggressive carcinoma". Cancer Research. 63 (2): 304–7. PMID 12543779.
- You J, Croyle JL, Nishimura A, Ozato K, Howley PM (Apr 2004). "Interaction of the bovine papillomavirus E2 protein with Brd4 tethers the viral DNA to host mitotic chromosomes". Cell. 117 (3): 349–60. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00402-7. PMID 15109495. S2CID 14781328.
- Colland F, Jacq X, Trouplin V, Mougin C, Groizeleau C, Hamburger A, Meil A, Wojcik J, Legrain P, Gauthier JM (Jul 2004). "Functional proteomics mapping of a human signaling pathway". Genome Research. 14 (7): 1324–32. doi:10.1101/gr.2334104. PMC 442148. PMID 15231748.
- Beausoleil SA, Jedrychowski M, Schwartz D, Elias JE, Villén J, Li J, Cohn MA, Cantley LC, Gygi SP (Aug 2004). "Large-scale characterization of HeLa cell nuclear phosphoproteins". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 101 (33): 12130–5. Bibcode:2004PNAS..10112130B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0404720101. PMC 514446. PMID 15302935.
- Farina A, Hattori M, Qin J, Nakatani Y, Minato N, Ozato K (Oct 2004). "Bromodomain protein Brd4 binds to GTPase-activating SPA-1, modulating its activity and subcellular localization". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 24 (20): 9059–69. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.20.9059-9069.2004. PMC 517877. PMID 15456879.
- Baxter MK, McPhillips MG, Ozato K, McBride AA (Apr 2005). "The mitotic chromosome binding activity of the papillomavirus E2 protein correlates with interaction with the cellular chromosomal protein, Brd4". Journal of Virology. 79 (8): 4806–18. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.8.4806-4818.2005. PMC 1069523. PMID 15795266.
- Haruki N, Kawaguchi KS, Eichenberger S, Massion PP, Gonzalez A, Gazdar AF, Minna JD, Carbone DP, Dang TP (Jul 2005). "Cloned fusion product from a rare t(15;19)(q13.2;p13.1) inhibit S phase in vitro". Journal of Medical Genetics. 42 (7): 558–64. doi:10.1136/jmg.2004.029686. PMC 1736105. PMID 15994877.
- Schweiger MR, You J, Howley PM (May 2006). "Bromodomain protein 4 mediates the papillomavirus E2 transcriptional activation function". Journal of Virology. 80 (9): 4276–85. doi:10.1128/JVI.80.9.4276-4285.2006. PMC 1472042. PMID 16611886.
- Wu SY, Lee AY, Hou SY, Kemper JK, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Chiang CM (Sep 2006). "Brd4 links chromatin targeting to HPV transcriptional silencing". Genes & Development. 20 (17): 2383–96. doi:10.1101/gad.1448206. PMC 1560413. PMID 16921027.
- You J, Srinivasan V, Denis GV, Harrington WJ, Ballestas ME, Kaye KM, Howley PM (Sep 2006). "Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen interacts with bromodomain protein Brd4 on host mitotic chromosomes". Journal of Virology. 80 (18): 8909–19. doi:10.1128/JVI.00502-06. PMC 1563901. PMID 16940503.
- Sénéchal H, Poirier GG, Coulombe B, Laimins LA, Archambault J (Feb 2007). "Amino acid substitutions that specifically impair the transcriptional activity of papillomavirus E2 affect binding to the long isoform of Brd4". Virology. 358 (1): 10–7. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2006.08.035. PMID 17023018.
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (Nov 2006). "Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks". Cell. 127 (3): 635–48. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.026. PMID 17081983. S2CID 7827573.
- Abbate EA, Voitenleitner C, Botchan MR (Dec 2006). "Structure of the papillomavirus DNA-tethering complex E2:Brd4 and a peptide that ablates HPV chromosomal association". Molecular Cell. 24 (6): 877–89. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2006.11.002. PMID 17189190.
- Schweiger MR, Ottinger M, You J, Howley PM (Sep 2007). "Brd4-independent transcriptional repression function of the papillomavirus e2 proteins". Journal of Virology. 81 (18): 9612–22. doi:10.1128/JVI.00447-07. PMC 2045424. PMID 17626100.
- Bisgrove DA, Mahmoudi T, Henklein P, Verdin E (Aug 2007). "Conserved P-TEFb-interacting domain of BRD4 inhibits HIV transcription". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (34): 13690–5. Bibcode:2007PNAS..10413690B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0705053104. PMC 1959443. PMID 17690245.