원핵 작은 리보솜 소단위
Prokaryotic small ribosomal subunit이 기사는 고고학에 대한 정보가 누락되어 있다. 진핵과 같은 IF, 침전율, 구조용 PMID23222135(2020년 4월) |
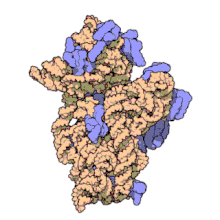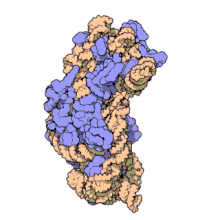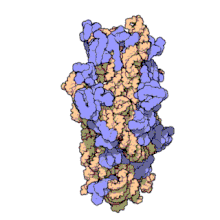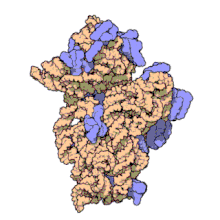
원핵 소립자 또는 30S 소립자는 원핵생물에서 발견되는 70S 리보솜의 더 작은 단위다.16S 리보솜 RNA(rRNA)와 19개 단백질의 복합체다.[1]이 콤플렉스는 전달 RNA(mRNA)에 대한 전달 RNA(mRNA)의 결합에 관여한다.[2]작은 서브 유닛은 번역 시 mRNA의 바인딩과 판독을 담당한다.rRNA와 그 단백질인 작은 서브 유닛은 원핵 세포에서 70S 원핵 리보솜을 형성하기 위해 큰 50S 서브 유닛과 콤플렉스를 가지고 있다.이 70S 리보솜은 mRNA를 단백질로 변환하는데 사용된다.
함수
30S 서브유닛은 mRNA 번역의 필수적인 부분이다.그것은 IF-1, IF-2, IF-3의 세 가지 원핵생물학적 개시요소를 결합한다.[3]
30S 서브 유닛(16S rRNA)의 일부분은 시작 코돈에서 업스트림하는 약 8개의 기본 쌍인 샤인-달가르노 시퀀스를 인식하여 mRNA의 시작 코돈(5㎛-AUG-(3㎛)을 제자리에 안내한다.[4]이렇게 하면 리보솜이 정확한 위치에서 번역을 시작할 수 있다.mRNA의 샤인-달가르노 수열과 16S rRNA 수열의 밀착성은 번역이 얼마나 효율적으로 진행되는지를 결정한다.[4]16S rRNA가 mRNA start codon을 인식하면, 특별한 전달 RNA인 f-Met-tRNA가 결합하고 단백질 번역이 시작된다.[5]30S 리보솜 서브유닛에 f-Met-tRNA의 결합 부지를 "D-site"[6]라고 한다. 이 단계는 단백질 합성이 일어나기 위해 필요하다.그러면 큰 리보솜 서브유닛이 결합되고 단백질 합성이 계속될 것이다.[7]대형 서브 유닛의 결합은 70S에 순응적 변화를 일으키며, 이것은 단백질 번역을 위한 또 다른 사이트를 열어준다.[6]
In order to form the translation complex with the 50S subunit, the 30S subunit must bind IF-1, IF-2, IF-3, mRNA, and f-met-tRNA. Next, the 50S subunit binds and a guanosine triphosphate is cleaved to guanosine diphosphate and inorganic phosphate, thus dissociating the initiation factors and resulting in protein translation.[8][5]이 과정을 "초기화"라고 하며 번역의 가장 느린 과정이다.[5]
구조
작은 리보솜 부위는 16S rRNA와 19개의 완전 단백질로 구성되어 있다.[9]26개의 아미노산으로 구성된 하나의 폴리펩타이드 체인도 있다.[10]통상적으로 rRNA는 고해상도 영상의 나선 번호를 나타내기 위해 "H#"로 라벨을 표시한다.단백질은 "S#"로 라벨을 붙여 rRNA 안정화에 관련된 다양한 펩타이드들을 나타낸다.S11과 H45는 샤인달가르노 바인딩 현장 부근에 위치해 있으며, IF-3 바인딩 현장 근처에도 있다.단백질 S3, S4, S5, S12는 H18과 함께 30S 서브유닛에 mRNA가 존재하는 채널 근처에 위치한다.[1]
억제
30S 서브유닛은 테트라사이클린과 젠타미닌과 같은 항생제의 대상이다.[11]이러한 항생제는 특히 원핵 리보솜을 대상으로 하므로 진핵생물의 박테리아 감염을 치료하는데 유용하다.테트라사이클린은 소형 서브 유닛의 H27과 상호작용하며 대형 서브 유닛의 A-사이트에 결합한다.[11]푸로마이신은 리보솜 번역의 억제제다.[6]Pactamycin은 작은 서브 유닛의 Shine-Dalgarno 바인딩 구역의 바인딩을 방해하여 활동을 방해한다.히그로마이신 B도 H44와 상호작용하며 단백질 합성 시 필요한 번역 운동을 억제한다.[11]
참고 항목
참조
- ^ a b c Schluenzen, Frank; Tocilj, Ante; Zarivach, Raz; Harms, Joerg; Gluehmann, Marco; Janell, Daniela; Bashan, Anat; Bartels, Heike; Agmon, Ilana (2000-09-01). "Structure of Functionally Activated Small Ribosomal Subunit at 3.3 Å Resolution". Cell. 102 (5): 615–623. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00084-2. PMID 11007480.
- ^ Thompson, John F.; Hearst (1983). "Structure-Function Relations in E. coli 16s RNA" (PDF). Cell. 33 (1): 19–24. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.625.7760. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(83)90330-6. PMID 6380748. S2CID 13069755.
- ^ L Gold; D Pribnow; T Schneider; S Shinedling; B S Singer; Stormo, and G. (1981). "Translational Initiation in Prokaryotes". Annual Review of Microbiology. 35 (1): 365–403. doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. PMID 6170248.
- ^ a b Malys, Naglis (2012-01-01). "Shine-Dalgarno sequence of bacteriophage T4: GAGG prevails in early genes". Molecular Biology Reports. 39 (1): 33–39. doi:10.1007/s11033-011-0707-4. ISSN 0301-4851. PMID 21533668. S2CID 17854788.
- ^ a b c Gualerzi, Claudio O.; Pon, Cynthia L. (1990). "Initiation of mRNA translation in prokaryotes". Biochemistry. 29 (25): 5881–5889. doi:10.1021/bi00477a001. PMID 2200518.
- ^ a b c Igarashi, Kazuei; Tanaka, Shigeaki; Kaji, Akira (1971-02-11). "On the aminoacyl-tRNA binding site of the 30-S ribosomal subunit and its relation to the chain initiation site of the ribosome". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis. 228 (3): 728–731. doi:10.1016/0005-2787(71)90737-4. PMID 4929429.
- ^ Slobin, Lawrence I (December 1972). "Structural and Functional Properties of Ribosomes Crosslinked with Dimethylsuberimidate". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 69 (12): 3769–3773. Bibcode:1972PNAS...69.3769S. doi:10.1073/pnas.69.12.3769. PMC 389868. PMID 4566460.
- ^ Milon P, Carotti M, Konevega AL, Wintermeyer W, Rodnina MV, Gualerzi CO (2010). "The ribosome-bound initiation factor 2 recruits initiator tRNA to the 30S initiation complex". EMBO Reports. 11 (4): 312–316. doi:10.1038/embor.2010.12. PMC 2854590. PMID 20224578.
- ^ Tsiboli, Paraskevi; Herfurth, Elke; Choli, Theodora (1994-11-01). "Purification and Characterization of the 30S Ribosomal Proteins from the Bacterium Thermus thermophilus". European Journal of Biochemistry. 226 (1): 169–177. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.0t169.x. ISSN 1432-1033. PMID 7957245.
- ^ Choli T, Franceschi F, Yonath A, Wittmann-Liebold B (1993). "Isolation and characterization of a new ribosomal protein from the thermophilic eubacteria, Thermus thermophilus, T. aquaticus and T. flavus" (PDF). Biological Chemistry Hoppe-Seyler. 374 (6): 377–383. doi:10.1515/bchm3.1993.374.1-6.377. PMID 8357533.
- ^ a b c Brodersen, Ditlev E.; Clemons, William M.; Carter, Andrew P.; Morgan-Warren, Robert J.; Wimberly, Brian T.; Ramakrishnan, V. (2000-12-22). "The Structural Basis for the Action of the Antibiotics Tetracycline, Pactamycin, and Hygromycin B on the 30S Ribosomal Subunit". Cell. 103 (7): 1143–1154. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00216-6. PMID 11163189.
외부 링크
- 16S rRNA, BioMineWiki
- http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/mayer/antibiot.htm
- 16S+리보솜+미국 국립 의학 도서관 RNA 의료 과목 제목(MesH)