파라폴리스 세포
Parafollicular cell| 파라폴리스 세포 | |
|---|---|
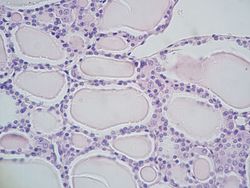 엽상피세포가 줄지어 있는 모낭을 보이는 갑상선의 미세한 부분과 그 사이에 더 큰 파라폴릭세포가 있다. | |
| 세부 사항 | |
| 위치 | 갑상선 |
| 함수 | 칼시토닌 분비물 |
| 식별자 | |
| TH | H3.08.02.4.00009 |
| 미세조영술의 해부학적 용어 | |
파라폴릭셀(Parafollicular cell)은 갑상선 내 신경내분비 세포라고도 한다. 이 세포들의 주된 기능은 캘시토닌을 분비하는 것이다. 그들은 갑상선 모낭에 인접해 있으며 결합조직에 거주한다. 이 세포들은 크고 엽세포에 비해 옅은 얼룩을 가지고 있다. 텔레오스트와 조류종에서 이 세포들은 최후통첩성 몸이라는 갑상선 바깥의 구조를 차지하고 있다.
구조
파라폴리스 세포는 갑상선에서 소수에서 발견되는 창백한 상태의 세포로 일반적으로 모낭 루멘과 직접 접촉하지 않고 상피에 기초하여 위치한다. 그것들은 항상 모낭 전체를 둘러싸고 있는 지하 막 안에 위치한다.
개발
Parafollicular cells는 인두내막에서 파생된다.[1][2] 발생학적으로 그들은 네 번째(또는 다섯 번째) 인두 주머니의 복측 유도체인 최후통첩체체와 연관된다. 파라폴릭 세포는 메추라기 치메라스의 일련의 실험에 근거하여 신경의 볏에서 유래된 것으로 이전에 믿어졌다.[3][4] 그러나 쥐를 대상으로 한 혈통추적 실험에서 파라폴릭세포는 내분자(ndooderm) 기원에서 유래한다는 사실이 밝혀졌다.[5]
함수
파라폴리스 세포는 칼슘 신진대사의 규제에 참여하는 호르몬인 칼시토닌을 분비한다. 칼시토닌은 골수성형에 의한 뼈의 재흡수를 억제하여 칼슘의 혈중 수치를 낮추고, 칼슘의 농도에 비례하여 분비량이 증가한다.[6]
파라폴릭셀은 세로토닌, 소마토스타틴 또는 CGRP와 같은 여러 신경내분비 펩타이드도 소량으로 분비하는 것으로 알려져 있다.[7][8][9] 그들은 또한 티로트로핀을 방출하는 호르몬을 표현하기 때문에 갑상선 호르몬의 생산을 현지에서 조절하는 역할을 할 수도 있다.[10][11]
임상적 유의성
파라폴리스 세포가 암에 걸리면 갑상선의 중상암으로 이어진다.[citation needed]
참고 항목
참조
- ^ Nilsson M, Williams D (July 2016). "On the Origin of Cells and Derivation of Thyroid Cancer: C Cell Story Revisited". European Thyroid Journal. 5 (2): 79–93. doi:10.1159/000447333. PMC 4949372. PMID 27493881.
- ^ 요한슨, E, 안데르손, L, 외른로스, J, 칼손, T, 인게손-칼손, C, 량, S, …닐손, M. (2015) 쥐와 인간에게 갑상선 C세포의 배아 기원을 수정한다. 개발, 142(20), 3519–3528. http://doi.org/10.1242/dev.126581
- ^ Le Douarin N, Fontaine J, Le Lièvre C (March 1974). "New studies on the neural crest origin of the avian ultimobranchial glandular cells--interspecific combinations and cytochemical characterization of C cells based on the uptake of biogenic amine precursors". Histochemistry. 38 (4): 297–305. doi:10.1007/bf00496718. PMID 4135055. S2CID 7551942.
- ^ Barasch J, Gershon MD, Nunez EA, Tamir H, al-Awqati Q (December 1988). "Thyrotropin induces the acidification of the secretory granules of parafollicular cells by increasing the chloride conductance of the granular membrane". The Journal of Cell Biology. 107 (6 Pt 1): 2137–47. doi:10.1083/jcb.107.6.2137. PMC 2115661. PMID 2461947.
- ^ Johansson E, Andersson L, Örnros J, Carlsson T, Ingeson-Carlsson C, Liang S, Dahlberg J, Jansson S, Parrillo L, Zoppoli P, Barila GO, Altschuler DL, Padula D, Lickert H, Fagman H, Nilsson M (October 2015). "Revising the embryonic origin of thyroid C cells in mice and humans". Development. 142 (20): 3519–28. doi:10.1242/dev.126581. PMC 4631767. PMID 26395490.
- ^ Melmed S, Polonsky KS, Larsen PR, Kronenberg HM (2011). Williams Textbook of Endocrinology (12th ed.). Saunders. pp. 1250–1252. ISBN 978-1437703245.
- ^ Zabel M (December 1984). "Ultrastructural localization of calcitonin, somatostatin and serotonin in parafollicular cells of rat thyroid". The Histochemical Journal. 16 (12): 1265–72. doi:10.1007/bf01003725. PMID 6152264. S2CID 7889687.
- ^ Barasch JM, Mackey H, Tamir H, Nunez EA, Gershon MD (September 1987). "Induction of a neural phenotype in a serotonergic endocrine cell derived from the neural crest". The Journal of Neuroscience. 7 (9): 2874–83. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02874.1987. PMC 6569149. PMID 3305802.
- ^ Bernd P, Gershon MD, Nunez EA, Tamir H (March 1981). "Separation of dissociated thyroid follicular and parafollicular cells: association of serotonin binding protein with parafollicular cells". The Journal of Cell Biology. 88 (3): 499–508. doi:10.1083/jcb.88.3.499. PMC 2112761. PMID 7217200.
- ^ Gkonos PJ, Tavianini MA, Liu CC, Roos BA (December 1989). "Thyrotropin-releasing hormone gene expression in normal thyroid parafollicular cells". Molecular Endocrinology. 3 (12): 2101–9. doi:10.1210/mend-3-12-2101. PMID 2516877.
- ^ Morillo-Bernal J, Fernández-Santos JM, Utrilla JC, de Miguel M, García-Marín R, Martín-Lacave I (August 2009). "Functional expression of the thyrotropin receptor in C cells: new insights into their involvement in the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis". Journal of Anatomy. 215 (2): 150–8. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01095.x. PMC 2740962. PMID 19493188.
추가 읽기
- Kameda Y (October 1987). "Localization of immunoreactive calcitonin gene-related peptide in thyroid C cells from various mammalian species". The Anatomical Record. 219 (2): 204–12. doi:10.1002/ar.1092190214. PMID 3120623. S2CID 12517073.
- Kameda Y, Nishimaki T, Miura M, Jiang SX, Guillemot F (January 2007). "Mash1 regulates the development of C cells in mouse thyroid glands". Developmental Dynamics. 236 (1): 262–70. doi:10.1002/dvdy.21018. PMID 17103415. S2CID 24848963.
- Kameda Y, Nishimaki T, Chisaka O, Iseki S, Sucov HM (October 2007). "Expression of the epithelial marker E-cadherin by thyroid C cells and their precursors during murine development". The Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 55 (10): 1075–88. doi:10.1369/jhc.7a7179.2007. PMID 17595340.
- Kameda Y, Ito M, Nishimaki T, Gotoh N (March 2009). "FRS2alpha is required for the separation, migration, and survival of pharyngeal-endoderm derived organs including thyroid, ultimobranchial body, parathyroid, and thymus". Developmental Dynamics. 238 (3): 503–13. doi:10.1002/dvdy.21867. PMID 19235715. S2CID 13504555.
- Kameda Y (March 2016). "Cellular and molecular events on the development of mammalian thyroid C cells". Developmental Dynamics. 245 (3): 323–41. doi:10.1002/dvdy.24377. PMID 26661795. S2CID 12161896.
- Baber EC (1876). "Contributions to the Minute Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland of the Dog". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. 166: 557–568. doi:10.1098/rstl.1876.0021. JSTOR 109205.
외부 링크
- 역사학 이미지: 오클라호마 대학 보건 센터 42_04
- 역사학 이미지: 14302loa – 보스턴 대학교 역사학 학습 시스템
- KUMC의 역사학 엔도/엔도10
- Anatomy Atlases - Microical Anatomy, 그림 15.287


