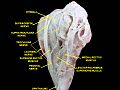
내측직근
Medial rectus muscle| 내측직경 | |
|---|---|
 | |
 눈의 내측근과 외측근의 신경화 모드를 나타내는 그림. | |
| 세부 사항 | |
| 기원. | 안와 정점의 일반적인 힘줄 고리 |
| 삽입 | 림버스 안쪽 5.5mm |
| 신경 | 안구 운동 신경의 하분할 |
| 행동들 | 안구를 추가(안쪽으로 이동하지 않음) |
| 식별자 | |
| 라틴어 | 내측 벌비근 |
| TA98 | A15.2.07.012 |
| TA2 | 2044 |
| FMA | 49037 |
| 근육의 해부학적 용어 | |
내측직근은 눈 근처 안와근육이다.그것은 안구외 근육 중 하나입니다.그것은 일반적인 힘줄 고리에서 유래하여 눈의 자궁내막 표면에 삽입됩니다.그것은 안구운동신경(II)의 하분할에 의해 공급된다.그것은 안구를 안쪽(내측)으로 회전시킨다.
구조.
내측직근은 다른 외인성 안구근육과 기원을 공유하는데, 일반적인 힘줄 고리입니다.그것은 눈의 [1]자궁내막 표면에 삽입된다.이 삽입부의 폭은 약 11mm입니다.[1]
신경 공급
내측직근은 안구운동신경(II)[2]의 하부분할에 의해 공급된다.그것의 한 가지는 그것의 [2]길이를 따라 약 5분의 2정도의 근육으로 들어간다.보통 2개의 작은 가지, 때로는 [2]3개로 나뉩니다.이것들은 더 세분화되어 근육의 길이로 갈수록 작아지며,[2] 근육의 삽입으로부터 약 17mm의 표준 염색에 의해 감지되지 않게 된다.
관계
내측직근의 삽입은 상직근의 삽입으로부터 약 7.5mm, 하직근으로부터 [1]약 6mm입니다.그것은 다른 안와직근보다 [3]짧지만 강하다.다른 안구외 [4]근육과 달리 수축할 때 위치가 크게 바뀌는 경우는 거의 없습니다.
기능.
내측직근은 안구를 내측으로 회전시킨다.[5]그것은 눈의 [5]앞쪽 표면을 따라 구부러지는 도르래 시스템을 사용하여 작동한다.
임상적 의의
스트라비스무스
사시(안구)는 [4]두개골의 궤도에 너무 높게 위치한 내측직근에 의해 발생할 수 있습니다.
측직근의 [6]약화나 마비를 일으키는 6번째 신경마비에 의해서도 사시가 발생할 수 있다.때때로 보툴리누스 독소가 내측 직장 [6]근육에 주입될 수 있다.이것은 눈을 유괴하고 추적하기 위해 부가하는 능력을 감소시키는 반면, 이것은 난사를 교정하고, 그래서 일반적으로 [6]시력을 향상시킨다.
압축
내측직근은 [7]두개골의 궤도 바로 옆에 있다.이로 인해 두개골 골절 시 압박(삽입)되기 쉬워져 [7][8]눈의 움직임을 방해할 수 있습니다.이것은 보통 두개골 골절을 [7]고치면 해결된다.
외과적 손상
내시경적 정맥동 [9]수술과 같은 눈 수술이나 두개골 수술 중에 내시경적 직장 근육이 손상될 수 있습니다.상처는 타박상과 같이 경미하거나 근육을 부분적으로 또는 완전히 절단하거나 신경 손상과 [9]같이 심각할 수 있습니다.
기타 이미지
「 」를 참조해 주세요.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c Apt, L (1980). "An anatomical reevaluation of rectus muscle insertions". Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society. 78: 365–375. ISSN 0065-9533. PMC 1312149. PMID 7257065.
- ^ a b c d Shin, Hyun Jin; Lee, Shin-Hyo; Ha, Tae-jun; Song, Wu-Chul; Koh, Ki-Seok (2019-05-04). "Intramuscular Nerve Distribution in the Medial Rectus Muscle and Its Clinical Implications". Current Eye Research. 44 (5): 522–526. doi:10.1080/02713683.2018.1562556. ISSN 0271-3683. PMID 30624996. S2CID 58560563.
- ^ Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice (41 ed.). Elsevier Limited. pp. 666–685. ISBN 978-0-7020-5230-9.
- ^ a b Clark, R. A.; Miller, J. M.; Demer, J. L. (1997-01-01). "Location and stability of rectus muscle pulleys. Muscle paths as a function of gaze". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 38 (1): 227–240. ISSN 1552-5783. PMID 9008649.
- ^ a b Porter, J. D.; Poukens, V.; Baker, R. S.; Demer, J. L. (1996-02-01). "Structure-function correlations in the human medial rectus extraocular muscle pulleys". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 37 (2): 468–472. ISSN 1552-5783. PMID 8603853.
- ^ a b c Rosenbaum, Arthur L.; Kushner, Burton J.; Kirschen, David (1989-06-01). "Vertical Rectus Muscle Transposition and Botulinum Toxin (Oculinum) to Medial Rectus for Abducens Palsy". Archives of Ophthalmology. 107 (6): 820–823. doi:10.1001/archopht.1989.01070010842025. ISSN 0003-9950. PMID 2730398.
- ^ a b c McCulley, T.J.; Yip, C.C.; Kersten, R.C.; Kulwin, D.R. (2004-07-01). "Medial Rectus Muscle Incarceration in Pediatric Medial Orbital Wall Trapdoor Fractures". European Journal of Ophthalmology. 14 (4): 330–333. doi:10.1177/112067210401400409. ISSN 1120-6721. PMID 15309979. S2CID 196310817.
- ^ Brannan, Paul A.; Kersten, Robert C.; Kulwin, Dwight R. (May 2006). "Isolated Medial Orbital Wall Fractures With Medial Rectus Muscle Incarceration". Ophthalmic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery. 22 (3): 178–183. doi:10.1097/01.iop.0000217565.69261.4f. ISSN 0740-9303. PMID 16714925. S2CID 34406704.
- ^ a b Huang, Christine M.; Meyer, Dale R.; Patrinely, James R.; Soparkar, Charles N. S.; Dailey, Roger A.; Maus, Marlon; Rubin, Peter A. D.; Yeatts, R. Patrick; Bersani, Thomas A.; Karesh, James W.; Harrison, Andrew R. (January 2003). "Medial Rectus Muscle Injuries Associated With Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: Characterization and Management". Ophthalmic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery. 19 (1): 25–37. doi:10.1097/00002341-200301000-00004. ISSN 0740-9303. PMID 12544790. S2CID 43492945.
외부 링크
- 해부도 수치: SUNY Downstate Medical Center Human Anatomy Online 29:01-06
- 웨슬리 노먼(조지타운 대학)의 해부학 수업에서의 레슨 3 (orbit4)
- 그림(howstuffworks.com)