스트루베 2398
Struve 2398좌표:![]() 18hm 42 46.67934s, +59° 37° 49.4724°
18hm 42 46.67934s, +59° 37° 49.4724°
| 관찰 데이터 Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| 콘스텔레이션 | 드라코 |
| 스트루베 2398 A | |
| 적경 | 18h 42m 46.67934s[1] |
| 적위 | +59°37°49.4724°[1] |
| 겉보기 등급(V) | 8.94[2] |
| 스트루베 2398 B | |
| 적경 | 18h 42m 46.96652s[1] |
| 적위 | +59° 37° 36.3471°[1] |
| 겉보기 등급(V) | 9.70 |
| 특성. | |
| 스펙트럼형 | M3 V + M3.5 V[3] |
| U-B 색지수 | 1.11/1.14 |
| B-V 색지수 | 1.53/1.59 |
| 변수 유형 | 플레어 별 |
| 아스트로메트리 | |
| 스트루베 2398 A | |
| 반지름 속도(Rv) | – 1.07[4] km/s |
| 고유운동(μ) | RA: – 1311.33[1] mas/년 Dec.: +1795.08[1] mas/년 |
| 시차()) | 283.8401 ± 0.0220 mas[5] |
| 거리 | 11.4908 ± 0.0009 ly (3.5231 ± 0.0003 pc) |
| 스트루베 2398 B | |
| 반지름 속도(Rv) | 1.09[4] km/s |
| 고유운동(μ) | RA: –194.75mas[1]/년 Dec.: +180.53[1] mas/년 |
| 시차()) | 283.8378 ± 0.0287 mas[6] |
| 거리 | 11.491 ± 0.001 ly (3.5231 ± 0.0004 pc) |
| 세부 사항 | |
| 스트루베 2398 A | |
| 덩어리 | 0.334±0.033[3] M☉ |
| 반지름 | 0.351±0.013[3] R☉ |
| 광도 | 0.039 L☉ |
| 온도 | 3,441±60[3] K |
| 금속성 [Fe/H] | −0.23±0.08[3] 덱스 |
| 회전 속도(v sin i) | 2.5 km[7]/s 미만 |
| 나이 | 3.0년식[3] |
| 스트루베 2398 B | |
| 덩어리 | 0.248±0.025[3] M☉ |
| 반지름 | 0.273±0.011[3] R☉ |
| 광도 | 0.021 L☉ |
| 온도 | 3,345±60[3] K |
| 금속성 [Fe/H] | - 0.30±0.08[3] 덱스 |
| 회전 속도(v sin i) | 2.5 km[7]/s 미만 |
| 나이 | 2.4[3] Gyr |
| 궤도[8] | |
| 동반자 | 스트루베 2398 B |
| 기간(P) | 294.7년 |
| 반장축(a) | 10.50″ |
| 편심(e) | 0.70 |
| 기울기(i) | 52.5° |
| 노드의 경도(δ) | 139.9° |
| 근일점 에폭(T) | 1778.0 |
| 근일점 인수()) (세컨더리) | 203.8° |
| 기타 명칭 | |
| Struve 2398 A: G227-046, HD 173739, HIP 91768, LHS 58, Vyssotsky 184. | |
| Struve 2398 B: G227-047, HD 173740, HIP 91772, LHS 91772 | |
| 데이터베이스 참조 | |
| 심바디 | 시스템 |
| A | |
| B | |
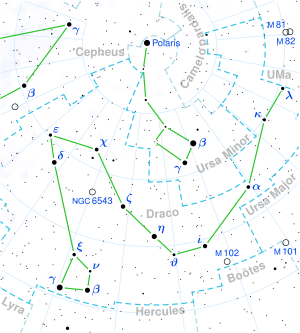
용자리 스트루베 2398의 위치 | |
Struve 2398(글리제 725)은 북쪽 용골자리에 있는 쌍성계이다.스트루베 2398은 발트해-독일 천문학자 프리드리히 게오르크 빌헬름 폰 스트루베의 '스트루베 이중성 목록'에 있는 2398번 별이다.천문학자의 성, 즉 별 식별자는 때때로 그리스 시그마 δ로 표시된다.성분은 너무 희미해서 육안으로 볼 수 없지만, 이 항성계는 태양에 가장 가까운 곳에 있습니다.히파르코스 우주선에 의한 시차 측정은 그들에게 약 11.6광년 [1]떨어진 것으로 추정됩니다.
두 별 모두 작은 적색왜성으로 각각 태양의 질량과 반지름의 약 3분의 1을 가지고 있습니다.이들은 각각 플레어 [9]별에 공통적으로 나타나는 변동성을 나타내며, 이들의 활동적인 표면은 X선 [10]방출의 원천이다.쌍성의 공전 주기는 약 295년이고 평균 거리는 약 56 천문단위이며,[11] 궤도 이심률은 0.70이다.
이 쌍은 연간 2.2 아크초의 비교적 높은 고유 운동을 가지고 있다.이 시스템은 이심률이 0.05인 은하수를 통과하는 궤도에 있으며 은하 중심에서 8kpc, 9kpc 떨어져 있습니다.은하 궤도의 [12]평면은 은하면에서 463-489pc 떨어져 있습니다.
행성계
2016년에는 Struve 2398 B 주변에서 2.7일 궤도의 행성 후보가 제안되었지만, 이 신호는 계기 소음 [13]층과 비슷한 것으로 밝혀졌다.2019년에는 이전 [14]후보를 발견하지 못한 채 반경 속도법을 사용하여 성분 B 주위의 궤도에서 두 개의 후보 행성이 탐지되었다.
| 동반자 (별부터 순서대로) | 덩어리 | 세미마조르 축 (AU) | 공전 주기 (일) | 편심 | 기울기 | 반지름 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 15.7±5.7M🜨 | 0.261+0.022 −0.028 | 91.29+0.31 −0.24 | 0.06+0.26 −0.06 | — | — |
| c | 13.1+8.1 −6.4 M🜨 | 0.428+0.037 −0.045 | 192.4+2.2 −1.9 | 0.03+0.22 −0.03 | — | — |
「 」를 참조해 주세요.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c d e f g h i van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600.
- ^ Rojas-Ayala, Bárbara; et al. (April 2012). "Metallicity and Temperature Indicators in M Dwarf K-band Spectra: Testing New and Updated Calibrations with Observations of 133 Solar Neighborhood M Dwarfs". The Astrophysical Journal. 748 (2): 93. arXiv:1112.4567. Bibcode:2012ApJ...748...93R. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/748/2/93. S2CID 41902340. 표 3을 참조해 주세요.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Mann, Andrew W.; et al. (May 2015), "How to Constrain Your M Dwarf: Measuring Effective Temperature, Bolometric Luminosity, Mass, and Radius", The Astrophysical Journal, 804 (1): 38, arXiv:1501.01635, Bibcode:2015ApJ...804...64M, doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/1/64, S2CID 19269312, 64.
- ^ a b Nidever, David L.; et al. (August 2002). "Radial Velocities for 889 Late-Type Stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 141 (2): 503–522. arXiv:astro-ph/0112477. Bibcode:2002ApJS..141..503N. doi:10.1086/340570. S2CID 51814894.
- ^ Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 649: A1. arXiv:2012.01533. Bibcode:2021A&A...649A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. S2CID 227254300. (에라타: doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657e).VizieR에서 이 소스에 대한 Gaia EDR3 레코드.
- ^ Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (2021). "Gaia Early Data Release 3: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 649: A1. arXiv:2012.01533. Bibcode:2021A&A...649A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657. S2CID 227254300. (에라타: doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202039657e).VizieR에서 이 소스에 대한 Gaia EDR3 레코드.
- ^ a b Reiners, Ansgar; et al. (April 2012), "A Catalog of Rotation and Activity in Early-M Stars", The Astronomical Journal, 143 (4): 15, arXiv:1201.5774, Bibcode:2012AJ....143...93R, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/143/4/93, S2CID 118425326, 93.
- ^ Baize, P. (October 1976). "Orbital elements of eighteen visual double stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series. 26: 177–193. Bibcode:1976A&AS...26..177B. ADS 11632로 표시됩니다.
- ^ Pettersen, B. R. (1991), "The nearby flare stars", Società Astronomica Italiana, Memorie, 62: 217–242, Bibcode:1991MmSAI..62..217P.
- ^ Schmitt, J. H. M. M.; Fleming, T. A.; Giampapa, M. S. (September 1995). "The X-ray view of the low-mass stars in the solar neighborhood". The Astrophysical Journal. 450 (9): 392–400. Bibcode:1995ApJ...450..392S. doi:10.1086/176149.
- ^ "Struve 2398 AB". Retrieved 2010-10-22.
- ^ Allen, C.; Herrera, M. A. (1998), "The galactic orbits of nearby UV Ceti stars", Revista Mexicana de Astronomía y Astrofísica, 34: 37–46, Bibcode:1998RMxAA..34...37A.
- ^ High-cadence spectroscopy of M-dwarfs. I. Analysis of systematic effects in HARPS-N line profile measurements on the bright binary GJ 725A+B, 2016, arXiv:1604.05312
- ^ Barnes, J. R.; et al. (2019-06-11), Frequency of planets orbiting M dwarfs in the Solar neighbourhood, arXiv:1906.04644v1