갈매기과
R Carinae| 관찰 데이터 Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| 콘스텔레이션 | 카리나 |
| 적경 | 09h 32m 14.59964s[2] |
| 적위 | -62°47°20.0452°[2] |
| 겉보기 등급(V) | 3.9~10[3].5 |
| 특성. | |
| 진화 단계 | AGB[4] |
| 스펙트럼형 | M6/7pe[5] |
| B-V 색지수 | 0.906±0.009[6] |
| 변수 유형 | 미라[3] |
| 아스트로메트리 | |
| 반지름 속도(Rv) | +28.1±1[6].0km/s |
| 고유운동(μ) | RA: - 37.900[2] mas/년 Dec.: +22.232[2] mas/년 |
| 시차()) | 2.5813 ± 0.4460 mas[2] |
| 거리 | 약 1,300년 (약 390개) |
| 절대 등급(MV) | 1.48[6](mv = 7.43) |
| 세부 사항 | |
| 덩어리 | 0.87+0.47 −0.31[4] M☉ |
| 반지름 | 241.0+37.6 −32.6[4] R☉ |
| 광도 | 4,571+1,331 −1,031[4] L☉ |
| 온도 | 2,800[7] K |
| 기타 명칭 | |
| 데이터베이스 참조 | |
| 심바디 | 데이터. |
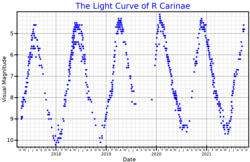
용골자리 R은 용골자리 남쪽의 쌍성이다.밝은 성분은 밝기가 [9]최고조에 달할 때 육안으로 볼 수 있는 변광성이지만 보통 망원경 없이는 볼 수 없을 정도로 희미하며 겉보기 등급은 7.43 [6]정도로 변동합니다.이 별은 시차를 기준으로 태양으로부터 약 1,300광년 거리에 있으며, 반경 속도 +28km/[6]s로 더 멀리 표류하고 있습니다.
주성분은 M6/7pe [5]등급의 점근거성[4] 가지에 있는 노화된 적색거성이다.이 별은 미라형 맥동 변광성으로 분류되며 303.99±1.08 d의 기간에 걸쳐 평균 진폭이 4.25 등급으로 변한다.평균 최대 시각 밝기는 5.05±0.[9]45이지만 관측된 최대 밝기는 3.9이다[3].이 별은 철분이 부족한 규산염이나 코룬담과 일치하는 성질을 가진 먼지 껍질로 둘러싸여 있으며, 항성 반지름 약 3개에서 [10]바깥쪽으로 뻗어 있습니다.
이 동반성은 [11]2015년 기준으로 주성으로부터 132°의 위치 각도를 따라 2.10° 각도로 떨어져 있는 등급 11.30의 별이다.
레퍼런스
- ^ "Download Data". aavso.org. AAVSO. Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- ^ a b c d e Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. VizieR에서 이 소스에 대한 Gaia DR2 레코드.
- ^ a b c Samus, N. N.; et al. (2017), "General Catalogue of Variable Stars", Astronomy Reports, 5.1, 61 (1): 80–88, Bibcode:2017ARep...61...80S, doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085, S2CID 125853869.
- ^ a b c d e Takeuti, Mine; et al. (2013), "A Method to Estimate the Masses of Asymptotic Giant Branch Variable Stars", Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan, 65 (3): 60, Bibcode:2013PASJ...65...60T, doi:10.1093/pasj/65.3.60.
- ^ a b Houk, Nancy; Cowley, A. P. (1979), Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars, vol. 1, Ann Arbor, Michigan: Dept. of Astronomy, University of Michigan, Bibcode:1978mcts.book.....H.
- ^ a b c d e Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv:1108.4971, Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- ^ McDonald, I.; Zijlstra, A. A.; Boyer, M. L. (2012), "Fundamental parameters and infrared excesses of Hipparcos stars", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 427 (1): 343, arXiv:1208.2037, Bibcode:2012MNRAS.427..343M, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21873.x, S2CID 118665352.
- ^ "R Car". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2020-01-30.
- ^ a b Vogt, N.; et al. (2016), "Determination of Pulsation Periods and Other Parameters of 2875 Stars Classified As Mira in the All Sky Automated Survey (Asas)", The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 227 (1): 6, arXiv:1609.05246, Bibcode:2016ApJS..227....6V, doi:10.3847/0067-0049/227/1/6, S2CID 119295645.
- ^ Ireland, M. J.; et al. (July 2005), "Dust scattering in the Miras R Car and RR Sco resolved by optical interferometric polarimetry", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 361 (1): 337–344, arXiv:astro-ph/0505112, Bibcode:2005MNRAS.361..337I, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09181.x, S2CID 14724805.
- ^ Mason, B. D.; et al. (2014), "The Washington Visual Double Star Catalog", The Astronomical Journal, 122 (6): 3466, Bibcode:2001AJ....122.3466M, doi:10.1086/323920.