RV 코르비
RV Corvi| 관측 데이터 신기루 J2000.0 이쿼녹스 J2000.0 | |
|---|---|
| 별자리 | 코르부스 |
| 우측 상승 | 12h 37m 40.711s[2] |
| 탈위임 | −19° 34′ 40.03″[2] |
| 겉보기 크기 (V) | 8.77[3] (8.6 - 9.16)[4] |
| 특성. | |
| 진화 단계 | 주계열 |
| 스펙트럼형 | F0V[5](F0 + G0)[6] |
| B-V색지수 | 0.404±0.026[3] |
| 변수형 | β 리르[7] |
| 아스트로메트리 | |
| 방사 속도 (Rv) | 19.0±4.6km[8]/s |
| 고유 운동 (μ) | RA: -29.326마스[2]/yr Dec.: 8.954[2] mas/yr |
| 시차 (π) | 4.7351 ± 0.0812[2] 마스 |
| 거리 | 690 ± 10 리 (211 ± 4 pc) |
| 절대치수 (MV) | 2.32[3] |
| 궤도[9] | |
| 기간 (P) | 0.7473 d |
| 편심성 (e) | 0.00 |
| 페리아스트론 신기원을 이루다 (T) | 2445792.3578 |
| 페리아스트론의 인수 (ω) (2차) | 0.00° |
| 반암도 (K1) (iii) | 64km/s |
| 반암도 (K2) (2차) | 시속 235km |
| 세부 사항 | |
| 1차 | |
| 미사 | 1.64±0.14[9] M☉ |
| 반지름 | 2.16 또는 2.18 ± 0.08[9] |
| 루미도 | 8.4 또는 8.5 ± 0[9].6 |
| 이차적 | |
| 미사 | 0.44±0.03[9] M☉ |
| 반지름 | 1.19 또는 1.20 ±0.04[9] |
| 루미도 | 1.2 또는 1.5 ± 0[9].1 |
| 기타 지정 | |
| 데이터베이스 참조 | |
| 심바드 | 자료 |
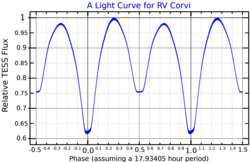
RV Corvi는 Corvus의 남쪽 별자리에 있는 생략형 이항성계통이다.쌍의 밝기는 18시간 동안 8.6에서 9.16까지 일정한 시각적 범위에서 나타나며,[4] 가장 밝은 것조차 육안으로 볼 수 없을 정도로 희미하다.이 시스템은 시차 측정을 기반으로 태양으로부터 약 690광년 거리에 위치하며, 방사상 속도 ~19km/s로 더 멀리 떠내려가고 있다.[8]
이 체계의 변동성은 H. H. Swope에 의해 발견되었다.[11]1942년 아이린 G. 버터리는 이 시스템에 대한 궤도 주기가 0.74728일이라는 것을 발표했는데, 이는 생략하는 이진법임을 보여준다.[12]조석 상호작용의 효과를 보여주는 두 항성 모두와 근접한 이항성으로, 면면은 궤도 이격의 10% 미만이지만 접촉하지 않는다.[13]한 개 또는 두 개의 별 모두 마주보는 면에 광도가 초과될 수 있다.[9]이 시스템은 0.7473일마다 서로 공전하는 F0과 G0의 스펙트럼 타입의 별들로 구성되어 있다.[6]
참조
- ^ "MAST: Barbara A. Mikulski Archive for Space Telescopes". Space Telescope Science Institute. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ a b c d Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 616. A1. arXiv:1804.09365. Bibcode:2018A&A...616A...1G. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. 이 소스에 대한 가이아 DR2 기록 VizieR.
- ^ a b c Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. S2CID 119257644.
- ^ a b Watson, Christopher (4 January 2010). "RV Corvi". The International Variable Star Index. American Association of Variable Star Observers. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- ^ Houk, Nancy; Smith-Moore, M. (1978). "Michigan catalogue of two-dimensional spectral types for the HD stars". 4. Ann Arbor: Dept. of Astronomy, University of Michigan. Bibcode:1988mcts.book.....H.
{{cite journal}}:Cite 저널은 필요로 한다.journal=(도움말) - ^ a b Malkov, O. Yu.; et al. (2006). "A catalogue of eclipsing variables". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 446 (2): 785–89. Bibcode:2006A&A...446..785M. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053137.
- ^ Samus, N. N.; et al. (2017). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars". Astronomy Reports. 5.1. 61 (1): 80–88. Bibcode:2017ARep...61...80S. Retrieved 2021-11-27.
- ^ a b Gontcharov, G. A. (November 2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv:1606.08053. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. S2CID 119231169.
- ^ a b c d e f g h McFarlane, T. M.; et al. (December 1986). "Contact and near-contact binary systems - V. RV Corvi". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 223: 595–606. Bibcode:1986MNRAS.223..595M. doi:10.1093/mnras/223.3.595.
- ^ "RV Crv". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 21 July 2015.
- ^ Abhyankar, K. D.; Parthasarathy, M.; Sanwal, N. B.; Sarma, M. B. K. (January 1974). "UBV photometry of RV CrV". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement. 13: 101. Bibcode:1974A&AS...13..101A.
- ^ Buttery, Irene G. (1942). "Twenty-two new variable stars in MWF 10". Annals of Harvard College Observatory. 109: 25–26. Bibcode:1942AnHar.109...25B.
- ^ Shaw, J. Scott; et al. (April 1996). "Near-Contact Binary Systems in the ROSAT All-Sky Survey". Astrophysical Journal. 461: 951. Bibcode:1996ApJ...461..951S. doi:10.1086/177116.