가우스 로그
Gaussian logarithm수학에서는 덧셈과 뺄셈 로그나 가우스 로그 등을 활용하면 값 자체를 알지 못한 채 로그가 알려진 한 쌍의 값의 합과 차이의 로그 값을 찾을 수 있다.[1]
그들의 수학적 기초는 1800년대 초 제키니 레오넬리와[2][3] 칼 프리드리히 가우스로[4][1][5] 거슬러 올라간다.[2][3][4][1][5]
덧셈과 뺄셈의 연산은 다음 공식으로 계산할 수 있다.
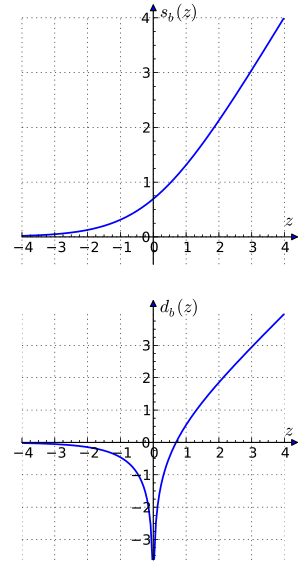
where , , the "sum" function is defined by , and the "difference" function by 함수 ( ) 및 ( ) 는 가우스 로그라고도 한다.
= 을(를) 가진 자연 로그의 경우 쌍곡선 함수를 가진 다음과 같은 ID가 존재한다.
이는 s 가 테일러 팽창(Taylor expansion)이며, 첫 번째 항을 제외한 모든 합리적이고, 선형 항을 제외한 모든 홀수 항이 0인 것을 보여준다.
곱셈, 나누기, 뿌리, 힘의 단순화는 덧셈과 뺄셈을 위해 이들 기능을 평가하는 비용에 의해 균형을 이룬다.
참고 항목
참조
- ^ a b c "Logarithm: Addition and Subtraction, or Gaussian Logarithms". Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition.
- ^ a b Leonelli, Zecchini (1803) [1802]. Supplément logarithmique. Théorie des logarithmes additionels et diductifs (in French). Bordeaux: Brossier. (NB. 1802/1803년은 프랑스 공화국 달력에서 XI년이다.)
- ^ a b Leonhardi, 고트프리트 빌헬름(1806년).LEONELLIs logarithmische Supplemente,als ein 문화, Mängelgewöhnlichen Logarithmentafeln zu ersetzen이다.아우스 dem Französischen nebsteinigen Zusätzen von GOTTFRIED WILHELM LEONHARDI, Feldartilleriecorps(독일어로)sächsischenSouslieutenantbeim kurfürstlichen.드레스덴:Walther'sche Hofbuchhandlung.(NB다. Zecchini Leonelli의 Supplément logarithmique의 확대에는 번역. Theri des logarithmes et didirifs.)
- ^ a b Gauß, Johann Carl Friedrich (1808-02-12). "LEONELLI, Logarithmische Supplemente". Allgemeine Literaturzeitung (in German). Halle-Leipzig (45): 353–356.
- ^ a b Dunnington, Guy Waldo (2004) [1955]. Gray, Jeremy; Dohse, Fritz-Egbert (eds.). Carl Friedrich Gauss - Titan of Science. Spectrum series (revised ed.). Mathematical Association of America (MAA). ISBN 978-0-88385-547-8. ISBN 0-88385-547-X.
추가 읽기
- Stark, Bruce D. (1997) [1995]. Stark Tables for Clearing the Lunar Distance and Finding Universal Time by Sextant Observation Including a Convenient Way to Sharpen Celestial Navigation Skills While On Land (2 ed.). Starpath Publications. ISBN 978-0914025214. 091402521X. Retrieved 2015-12-02. (NB. 가우스 로그 lg(1+10−x) 표 포함)
- Kalivoda, Jan (2003-07-30). "Bruce Stark - Tables for Clearing the Lunar Distance and Finding G.M.T. by Sextant Observation (1995, 1997)" (Review). Prague, Czech Republic. Archived from the original on 2004-01-12. Retrieved 2015-12-02.
…] Bruce Stark […] uses the Gaussian logarithms that make possible to remain in world of logarithms all the time of calculation and transform an addition of natural numbers to the addition and subtraction of their common and special logarithmic values by use of a special table. It is much easier than to convert logs to their natural values, to add them and again to convert them to logs. Moreover, Gaussian logs yield greater accuracy of result than the traditional computing method and help 5-digit log values to be sufficiently accurate for this method. […] The use of "Gaussians" by Bruce is original in the field of navigation. I don't know another example of using them by seamen or aviators - with the exception of Soviet navigators, which had Gaussians in their standard table sets up to ca. 1960. […] haversine that was not allowed to the Soviet navigational practice. […] Gaussians coact peacefully with haversines in rationalizing the LD procedure […]
[1][2] - Kremer, Hermann (2002-08-29). "Gauss'sche Additionslogarithmen feiern 200. Geburtstag". de.sci.mathematik (in German). Archived from the original on 2018-07-07. Retrieved 2018-07-07.
- Kühn, Klaus (2008). "C. F. Gauß und die Logarithmen" (PDF) (in German). Alling-Biburg, Germany. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-07-14. Retrieved 2018-07-14.