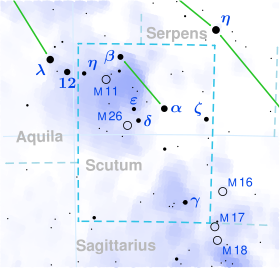
스쿠티 엡실론
Epsilon Scuti| 관측 데이터 에폭 J2000 이쿼녹스 J2000 | |
|---|---|
| 별자리 | 스쿠텀 |
| 우측 상승 | 18h 43m 31.252s[1] |
| 탈위임 | −8° 16′ 30.80″[1] |
| 겉보기 크기(V) | 4.88[2] |
| 특성. | |
| 스펙트럼형 | G8IIB[3] |
| U-B색지수 | +0.88[4] |
| B-V색지수 | +1.12[5] |
| 아스트로메트리 | |
| 방사 속도(Rv) | -9.8±0.6km[6]/s |
| 적정운동(μ) | RA: +21.06마스[7]/yr Dec.: +9.11마스[7]/yr |
| 시차(시차) | 6.06 ± 0.64 마스[7] |
| 거리 | 약 540리 (약 170pc) |
| 절대치수(MV) | -1.18[2] |
| 세부 사항 | |
| 루미도 | 403[2] L☉ |
| 표면 중력(log g) | 1.00[8] cgs |
| 온도 | 4500K[8] |
| 금속성 [Fe/H] | +0.05[2] 덱스 |
| 회전 속도(v sin i) | 5.1km[9]/s |
| 기타 지정 | |
| 데이터베이스 참조 | |
| 심바드 | 자료 |
ε 스쿠티에서 라틴어로 표기된 엡실론 스쿠티는 스쿠텀 별자리에 있을 가능성이 있는 점성계 2항성계다.육안으로는 시야 크기가 +4.88로 희미하게 보인다.[2]지구에서 볼 수 있는 6.06마스의 연간 시차 변화를 바탕으로 태양으로부터 약 540광년 떨어진 곳에 위치한다.[7]그것은 -9.8 km/s의 반지름 속도로 태양 가까이 이동하고 있다.[6]엡실론 스쿠티는 후자의 아킬레 3의 지명이었다.[11]
눈에 보이는 성분은 G형 밝은[3] 거성을 가진 황후빛 거성. 태양 광도의 403배인[2] 태양 광도를 4,500K의 유효온도로 방사하고 있다.[8]엡실론 스쿠티에는 적어도 3개의 희미한 시각적 동반자가 있는데, 2개의 14번째 크기 별인 B와 D가 각각 13.6과 15.4 아크초 떨어져 있고, 13번째 크기 C는 38 아크초 떨어져 있다.[12]
참조
- ^ a b Høg, E.; Fabricius, C.; Makarov, V. V.; Urban, S.; Corbin, T.; Wycoff, G.; Bastian, U.; Schwekendiek, P.; Wicenec, A. (2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H.
- ^ a b c d e f Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. S2CID 119257644. Vizier 카탈로그 항목
- ^ a b Keenan, Philip C.; McNeil, Raymond C. (1989). "The Perkins catalog of revised MK types for the cooler stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 71: 245. Bibcode:1989ApJS...71..245K. doi:10.1086/191373.
- ^ Mermilliod, J. C. (2006). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: Homogeneous Means in the UBV System (Mermilliod 1991)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: II/168. Originally Published in: Institut d'Astronomie. 2168. Bibcode:2006yCat.2168....0M.Vizier 카탈로그 항목
- ^ Mallama, A. (2014). "Sloan Magnitudes for the Brightest Stars". The Journal of the American Association of Variable Star Observers. 42 (2): 443. Bibcode:2014JAVSO..42..443M.Vizier 카탈로그 항목
- ^ a b Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv:1606.08053. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. S2CID 119231169.
- ^ a b c d Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600. Vizier 카탈로그 항목
- ^ a b c Soubiran, Caroline; Le Campion, Jean-François; Brouillet, Nathalie; Chemin, Laurent (2016). "The PASTEL catalogue: 2016 version". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 591: A118. arXiv:1605.07384. Bibcode:2016A&A...591A.118S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201628497. S2CID 119258214.
- ^ De Medeiros, J. R.; Mayor, M. (1999). "A catalog of rotational and radial velocities for evolved stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series. 139 (3): 433. arXiv:astro-ph/0608248. Bibcode:1999A&AS..139..433D. doi:10.1051/aas:1999401. Vizier 카탈로그 항목
- ^ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008), "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 389 (2): 869–879, arXiv:0806.2878, Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x, S2CID 14878976.
- ^ Wagman, M. (August 1987). "Flamsteed's Missing Stars". Journal for the History of Astronomy. 18 (3): 212. Bibcode:1987JHA....18..209W. doi:10.1177/002182868701800305. S2CID 118445625.
- ^ Mason, Brian D.; Wycoff, Gary L.; Hartkopf, William I.; Douglass, Geoffrey G.; Worley, Charles E. (2001). "The 2001 US Naval Observatory Double Star CD-ROM. I. The Washington Double Star Catalog". The Astronomical Journal. 122 (6): 3466. Bibcode:2001AJ....122.3466M. doi:10.1086/323920. Vizier 카탈로그 항목