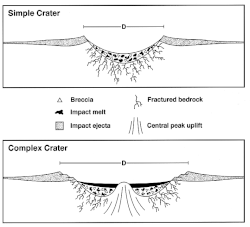
충격 구조
Impact structure충격 구조는 구조물의 침식 단계가 무엇이든 행성 표면에 충돌하여 생성된 기형 암반이나 침전물의 일반적으로 원형 또는 분화구 같은 지질 구조물이다. 이와는 대조적으로, 충격 분화구는 충격 구조물의 표면 표현이다. 많은 경우 지구에서는 침식으로 충격 분화구가 파괴되어 충격 구조의 기형적인 바위나 침전물만 남겨두고 있다.[1] 이것은 달에 보존된 고대 자연 그대로의 분화구와 태양계의 오래된 표면을[2] 가진 지질학적으로 활동하지 않는 다른 암석체들과는 달리 지구에 있는 거의 모든 오래된 충돌 분화구의 운명이다. 충격 구조는 "별의 상처"[3]를 의미하는 아스트로블렘이라는 용어와 동의어다.
충격 구조에서 충격 분화구의 전형적인 가시적 및 지형적 표현은 더 이상 분명하지 않다. 한때 존재했을지도 모르는 운석 파편들은 침식된 지 오래되었을 것이다. 가능한 충격 구조물은 처음에는 변칙적인 지질학적 특성이나 지구물리학적 표현으로 인식할 수 있다. 충격 광물(특히 충격을 받은 석영), 분쇄 원추, 외계 물질의 지질학적 증거 또는 다른 방법의 존재에 의해 충격 구조로 여전히 확인될 수 있다.
참고 항목
- 복합 분화구
- Earth Impact Database
- 임팩트 이벤트
- 지구의 충격 크레이터 목록
- 지구에서 발생할 수 있는 충격 구조물 목록
- 달과 행성 연구소의 재앙의 흔적 - 충격 분화구 과학에 대한 포괄적인 참조
- 피크 링(크레이터)
참조
- ^ Neuendorf, K.E., J.P. Mehl Jr., J.A. Jackson, Eds. (2005) 지질학의 용어집 (5차) 알렉산드리아, 버지니아, 미국 지질 연구소 779쪽 ISBN0-922152-76-4
- ^ Moore, Jeffrey M.; Black, Greg; Buratti, Bonnie; Phillips, Cynthia B.; Spencer, John; Sullivan, Robert (2009). "Surface Properties, Regolith, and Landscape Degradation". In Pappalardo, Robert T. (ed.). Europa. The University of Arizona space science series. McKinnon, William B.; Khurana, Krishan. Tucson: The University of Arizona Press. p. 341. ISBN 978-0-8165-2844-8.
Bodies with current geological activity such as Io and Earth have very few recognizable impact craters—Io, in fact, is so volcanically active that not a single impact crater, of any size, has been found on its surface to date. The Earth has about 150 recognized craters, but many have been geologically modified and would be difficult to recognize from orbit. On the other hand, geologically inactive bodies with old surfaces, such as Earth's Moon or Callisto, are covered with impact craters of all sizes.
- ^ French, Bevan M (1998). Traces of Catastrophe: A Handbook of Shock-Metamorphic Effects in Terrestrial Meteorite Impact Structures. Houston, Texas: Lunar and Planetary Institute. p. 120. LPI Contribution No. 954.
외부 링크
- 달·행성연구소 지상충격분화구
- Earth Impact Database