만디불라포사
Mandibular fossa| 만디불라포사 | |
|---|---|
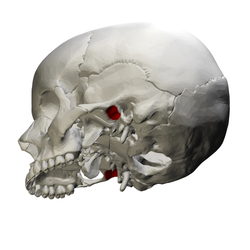 왼쪽 측두골.외부 표면. (왼쪽에서 세 번째 라벨이 부착된 만두형 fossa. | |
 두개골 베이스열등면. (왼쪽 중앙에 라벨이 붙어 있는 만두형 포사.측두골은 분홍색이다.) | |
| 세부 사항 | |
| 의 일부 | 측두골 |
| 시스템 | 골격의 |
| 식별자 | |
| 라틴어 | 포사 만디불라목 |
| TA98 | A02.1.06.071 |
| TA2 | 712 |
| FMA | 75313 |
| 해부학적 뼈 용어 | |
일부 치과 문헌에서 글레노이드 포사로도 알려진 하악골은 하악골과 관절하는 측두골의 우울증이다.
구조
측두골에서 하악골은 앞쪽으로 관절결절, 뒤로는 측두골의 고엽부에 의해 경계가 되어 외부 음향미투스와 분리된다.fossa는 좁은 슬릿에 의해 두 부분으로 나뉜다, petrotympanic fissure (Glaserian fissure).하악의 응고 과정을 받기 위해 오목한 모양을 하고 있다.[1]
개발
하악골 포사는 콘딜라 연골에서 발달한다.이는 마우스 모델에서 보듯이 SOX9 또는 ALK2에 의해 자극될 수 있다.[2]
함수
하악관절의 콘딜로이드 과정은 하악관 fossa에서 두개골의 측두골과 결합한다.[3][4]
임상적 유의성
배아 발달 중 형태생식에 문제가 생기면 하악골이 형성되지 않을 수 있다.[2]이는 SOX9 또는 ALK2에 대한 돌연변이로 인해 발생할 수 있다.[2]
만약 하악골 포사가 매우 얕다면, 이것은 고악골 관절의 강도에 문제를 일으킬 수 있다.[5]이로 인해 관절과 트리스무스(잠금턱)가 쉽게 소급될 수 있다.[5]종종 임시방편성 이형화의 일부인 하악골 포사의 변형은 개에게 비슷한 문제를 일으킨다.[6][7]이것은 자연적으로 해결되거나 수술이 필요할 수 있다.[7]
역사
하악골 포사는 일부 치과 문헌에서 글레노이드 포사로도 알려져 있다.[1][8]
다른동물
하악골 포사는 개를 포함한 다양한 다른 동물들의 두개골의 특징이다.[6]
참고 항목
참조
![]() 이 글은 20일자 140면부터 공공영역의 텍스트를 통합하고 있다. 그레이스 아나토미 (1918)
이 글은 20일자 140면부터 공공영역의 텍스트를 통합하고 있다. 그레이스 아나토미 (1918)
- ^ a b Mehta, Noshir R.; Scrivani, Steven J.; Maciewicz, Raymond (2008). "25 - Dental and Facial Pain". Raj's Practical Management of Pain (4th ed.). Mosby. pp. 505–527. doi:10.1016/B978-032304184-3.50028-5. ISBN 978-0-323-04184-3.
- ^ a b c Hinton, Robert J.; Jing, Junjun; Feng, Jian Q. (2015). "Four - Genetic Influences on Temporomandibular Joint Development and Growth". Current Topics in Developmental Biology. Vol. 115. Elsevier. pp. 85–109. doi:10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.07.008. ISBN 978-0-12-408141-3. ISSN 0070-2153.
- ^ Lantz, Gary C.; Verstraete, Frank J. M. (2012). "33 - Fractures and luxations involving the temporomandibular joint". Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery in Dogs and Cats. Saunders. pp. 321–332. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-4618-6.00033-6. ISBN 978-0-7020-4618-6.
- ^ Willard, V. P.; Zhang, L.; Athanasiou, K. A. (2011). "5.517 - Tissue Engineering of the Temporomandibular Joint". Comprehensive Biomaterials. Vol. 5. Elsevier Science. pp. 221–235. doi:10.1016/B978-0-08-055294-1.00250-6. ISBN 978-0-08-055294-1.
- ^ a b Lantz, Gary C. (2012). "55 - Temporomandibular joint dysplasia". Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery in Dogs and Cats. Saunders. pp. 531–537. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-4618-6.00055-5. ISBN 978-0-7020-4618-6.
- ^ a b Jerram, Richard M. (2006-01-01). "97 - Fractures and Dislocations of the Mandible". Saunders Manual of Small Animal Practice (3rd ed.). Saunders. pp. 1037–1042. doi:10.1016/B0-72-160422-6/50099-1. ISBN 978-0-7216-0422-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: 날짜 및 연도(링크) - ^ a b Kealy, J. Kevin; McAllister, Hester; Graham, John P. (2011-01-01). "5 - The Skull and Vertebral Column". Diagnostic Radiology and Ultrasonography of the Dog and Cat (5th ed.). Saunders. pp. 447–541. ISBN 978-1-4377-0150-0.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: 날짜 및 연도(링크) - ^ Groell, R; Fleischmann, B (1999-03-01). "The pneumatic spaces of the temporal bone: relationship to the temporomandibular joint". Dentomaxillofacial Radiology. 28 (2): 69–72. doi:10.1038/sj/dmfr/4600414. ISSN 0250-832X – via DMFR.
외부 링크
- 해부학 그림: SUNY 다운스테이트 메디컬 센터 Human Anatomy Online에서 22:4b-07
- 해부 사진:SUNY 다운스테이트 의료센터 27:st-0311

