높은 메모리 영역
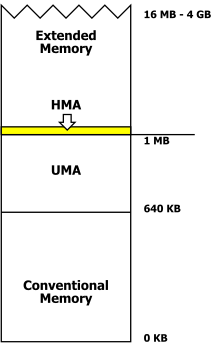
High memory areaDOS 메모리 관리에서, HMA(High Memory Area)는 IBM AT 또는 호환되는 컴퓨터의 1메가바이트 이상에서 처음 65520바이트로 구성된 RAM 영역이다.
실제 모드에서 Intel8086과 후속 프로세서의 분할 아키텍처는 (세그먼트) × 16 + (오프셋)를 통해 물리적 주소로 분해되는 16비트 세그먼트와 16비트 오프셋을 가진 메모리 위치를 식별한다.1MB(2바이트20)의 메모리만 처리하도록 의도되었지만 세그먼트:오프셋 주소:FFFF:00101MB를 초과하는 기준 메모리(FFFF0 + 0010 = 100000). 따라서 80286 및 후속 프로세서에서 이 모드는 실제로 1MB 마크 이전에 16바이트를 시작하는 64KB 범위의 일부로 65520바이트의 확장 메모리를 처리할 수 있다.FFFF:0000 (0xFFFF0)로FFFF:FFFF (0x10FFEF). 1MB의 메모리와 20개의 주소 라인만 있는 Intel 8086 및 8088 프로세서가 20번째 비트로 감싸져 있으므로 해당 주소FFFF:0010와 동등했다0000:0000.[1]
이 기능에 의존하는 기존 DOS 프로그램 실행을 허용하기 위해 IBM은 마더보드에 포장을 시뮬레이션하기 위해 마더보드에 특별한 회로를 추가했다.이 회로는 마더보드의 나머지 부분으로부터 마이크로프로세서의 21번째 어드레싱 라인 A20을 분리할 수 있는 단순한 논리 게이트였다.이 게이트는 처음에는 키보드 컨트롤러를 통해 전체 RAM에 액세스하려는 프로그램을 실행하도록 제어할 수 있었다.[1]
소위 A20 핸들러는 주소 지정 모드를 동적으로 제어할 수 있으므로 프로그램이 1024–1088KB 영역으로 로드되어 실제 모드로 실행될 수 있다.[1][1]
코드는 해병 공격 헬기 대대에서 처형될 적합한 가설 위치 독립(단지 상대적인 추천서를 써)[2][1]은 해병 공격 헬기 대대(일반적으로 오직 하나 또는 코드의 대부분이 두개의 조각에서 해병 공격 헬기 대대를 공유하도록 허용함)의 특정한 주소에서 일하기 편집이 아니면paragraph 경계 또는 심지어 모든 광고(과 재배치 가능을 상쇄하도록 설계해야 하게 계획되어야 한다.dresse(하중 시 고정)[2][1]
CPU로 HMA의 코드(또는 데이터)를 처리하려면 해당 드라이버가 HMA가 매핑되어 있는지 확인해야 한다.이를 위해서는 이러한 모든 요청이 HMA 외부의 메모리에 남아 있는 스텁을 통해 터널링되어야 하며, 이는 A20 게이트를 활성화(임시)하기 위해 A20 핸들러를 호출한다.[2][1]운전자가 공공 데이터 구조를 나타내지 않고 기본 운영 체제에서 이미 제어하는 인터럽트나 호출만 사용하는 경우, 시스템이 A20 자체를 처리하므로 별도의 스텁이 필요하지 않도록 시스템에 드라이버를 등록할 수 있다.[1][nb 1]
마이크로소프트 제품 중 HMA의 첫 번째 사용자는 1988년 HIMEM을 도입한 윈도/286 2.1이었다.SYS 장치 드라이버.1990년부터 디지털 리서치의 DR DOS 5[3].0(및 CONFIG를 통해).SYS ) 및 MS-DOS 5[3].0(을 통해 )을 사용한 1991년부터 운영 체제의 BIOS와 커널의 일부를 HMA에도 로드할 수 있어 최대 46KB의 기존 메모리를 확보할 수 있었다.[3][5][1]장치 드라이버 및 TSRs 같은 기타 구성 요소는 적어도 상위 메모리 영역(일정외 정비 활동)이 아닌 해병 공격 헬기 대대로. DOS5.0과 높은 하에서, DOS=HIGH을 추가로 할당은 HMA.[5]에 DRDOS6.0및 높은(1991년)에 따라 디스크 버퍼, 파(를 통해 HIBUFFERS, 그리고 후에 또한 BUFFERSHIGH)디스크 버퍼를 옮기려 했다고 로드될 수 있다.T라는 명령 처리 기구 콜로라도의MMAND.COM뿐만 아니라 KEYB, NLSFUNC 및 SHARE와 같은 특수한 자동 배치 드라이버도 HMA에 로딩(옵션 사용)할 수 있으므로 기존 DOS 소프트웨어가 사용할 수 있는 기존 메모리와 상위 메모리를 훨씬 더 자유롭게 사용할 수 있다.[1]TASKMAX도 HMA로 일부를 이전한 것으로 보인다.[6][7]NetWare Lite의 Novell NLCACHE와 Personal NetWare 및 Novell DOS 7의 NWCACHE 초기 버전도 HMA를 활용할 수 있다.[8][9][7]MS-DOS/PC DOS에서 CA. 2KB의 COMMAND 공유 부분.COM은 디스플레이뿐만 아니라 [10]HMA로 이전할 수 있다.준비된 코드 페이지에 대한 SYS 비트맵.[10][11]MS-DOS 6.2(1993) 이상에서는 DBLSPACE의 ca. 5KB 부분.빈/DRVSpace.BIN은 HMA에서 DOS와 공존할 수 있다(DBLSPACE/DRVSPACE를 호출하지 않는 한).[5][12]PC DOS 7.0(1995) 및 2000에 따르면 DOSKEY는 HMA에 로드되며([13]사용 가능한 경우), SHARE도 HMA에 로드할 수 있다(선택사항이 주어지지 않는 경우).[13]MS-DOS 7.0(1995년) ~ 8.0(2000년)에서는 HMA의 일부를 스크래치패드로 사용하여 로딩된 리얼 모드 드라이버의 다양한 속성을 기록하는 증가하는 데이터 구조를 보유하기도 한다.[7][14][15]
참고 항목
- 메모리 부족(메모리 용량이 처음 64KB)
- 확장 메모리(XMS)
- 확장 메모리(EMS)
- 언리얼 모드
- 리바싱
- 단락 경계 재배치
- 세그먼트 내 오프셋 재배치
- 셸하이(CONFIG).SYST 지침) 기본 HMA 사전 할당을 재정의하는 SIZE=xxxx 매개 변수(DR-DOS 7.02 이상에만 해당)[16]
- 흐마레아(CONFIG).SYS 지침) DR DOS HIDOS와 유사한 HMA 세그먼트(PTS-DOS만 해당)를 지정한다.SYS /BDOS=xxxx 매개 변수
메모들
참조
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j 폴, 마티아스 R.(2002-02-02)."Treiber dynamischnachladen(Intra-Segment-Offset-Relokation 예 라덴 폰 TSRs 다이 해병 공격 헬기 대대에서)"[Loading 운전자 동적으로(Intra-segment은 해병 공격 헬기 대대에 로드하 TSRs으로 재배치함를 상쇄함)](독일어로).뉴스:de.comp.os.msdos.그 2017-09-09에 원래에서 Archived..(NB. 해병 공격 헬기 대대의 역사와"자연"과 분명하지 설계 제약 조건들은 해병 공격 헬기 대대로 로드될 것 시스템 확장 개발하고 관찰되기에. 그것은 또한 여러분이 이러한 문제들 이전 법 DR-D에서 사용하는 오프셋 stubs, backdoors, intra-segment을 사용하여를 해결하기 위해 설명하는 포괄적인 개요를 제공하 2017-07-02 Retrieved.OS드라이버의 능력HMA로 이전하고 저자의 FreeKEYB 드라이버에서 동적 데드 코드 제거의 기초로 사용되는 (더 정교한) 방법과 유사하다.)
- ^ a b c Ingenoso, Tony (1998-12-20). "Chapter 13 - The A20 gate and the HMA". Making Code Work Better - How to minimize the size of 80x86 code and sometimes make it faster (e-book). Archived from the original on 2019-11-18. Retrieved 2019-11-18.
- ^ a b c Dryfoos, Mike, ed. (1991-09-18) [1991-07-19]. "MS-DOS 5.0 Development Post-Mortem Report" (PDF) (mail as court document). Microsoft. p. 10. MS-PCA1179169 (MS-PCA1179159-MS-PCA1179191). MS7020988 (MS7020978-MS7021010). Depo. Ex. 1109. Comes v Microsoft Plaintiff's Exhibit 3473. CA.No.2:96CV645B Plaintiff's Exhibit 477. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2019-04-02. Retrieved 2019-07-22.
[…] One of the most important stimulanta for adding features was competitive pressure from DRDOS 5.0, which we first learnt of in the spring of 1990. The DRDOS feature set led us to add UMB support, task swapping, and Undelete. […] Considerable amounts of the team's management attention was diverted to new features such as file transfer software, undelete and network installation […] Eventually this situation reached a crisis point at the end of July 1990, and, led by BradS, the team's management spent an arduous series of meetings nailing down a schedule and process for closing the project down […]
(1+32 pages) - ^ Banta, K.; Partridge, D. (1994-08-18). "Third Party Memory Managers". DR DOS 6.0 (Technical information document). Revision A. Novell. TID800074 (replaces FYI-M-1303). Archived from the original on 2021-12-15. Retrieved 2021-12-15.
- ^ a b c 슐먼 앤드류, 브라운, 랄프 D.;Maxey, 데이비드. 미헬스, 레이먼드 J., 카일, 짐(1994년)[1993년 11월].윌리엄스, 앤드류(교육.).Undocumented 도스:예약된 MS-DOS를 사용하는 기능과 데이터 구조-MS-DOS6, 노벨 도스와 Windows3.1을 포함하도록 확장에 대한 프로그래머의 가이드입니다.그 앤드류 슐만 프로그래밍 시리즈(1,2판).,:매사추세츠 미국을 읽는 것 애디슨 웨슬리 출판사.를 대신하여 서명함. 42, 349–350, 437–438.아이 에스비엔 0-201-63287-X.아이 에스비엔 978-0-201-63287-3.(xviii+856+vi 페이지,3.5"-floppy[1])Errata:[2][3].
- ^ "Format of HMA Memory Block (DR DOS 6.0 kernel loaded in HMA)". RBIL. 2000. Archived from the original on 2020-02-18. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ a b c Paul, Matthias R. (2002-04-10). "[fd-dev] HMA access from TSR". freedos-dev. Archived from the original on 2017-09-09. Retrieved 2017-09-09.
[…] MS-DOS 7.0+ adds INT 21h/AX=4A03h and INT 21h/AX=4A04h. RBIL61 INT 21h/AH=52h has some info on the MS-DOS 7.0+ HMA MCB chain […] HMA relocation for TSRs makes much sense for DR-DOS: Although you can load large parts of the BIOS and BDOS, the resident part of the shell, the BUFFERS, and DR-DOS TSRs like SHARE, KEYB, and NLSFUNC (and in some issues parts of TASKMGR and NWCACHE) into the HMA, there is usually still free space available, typically around 10 Kb (up to ca. 20 Kb when you use a 3rd party shell). It also makes sense for MS-DOS 5.0 - 6.22 and PC DOS up to 2000, which typically leave 4 - 7 Kb of the HMA memory unused (SHARE, KEYB, and NLSFUNC cannot load into the HMA, but DBLSPACE and HIMEM can to some extent). Available HMA space can be rather tight with MS-DOS 7.0+, since this issue introduced a new and for the most part undocumented RMD data structure usually located in the HMA. The kernel collects and records configuration and Real Mode Driver data during boot (type of driver, interrupts hooked by driver, CONFIG.SYS line of invocation, etc.) and stores this information in an […] complicated […] and […] growing data structure. Presumably this info is meant to be used by the Windows core to get a better picture of the loaded Real Mode drivers instead of treating DOS as a monolithic block, or even […] attempt to unhook or unload some of them, however, it is only used to a very limited extent (for example you can see some of the info reflected in the log files created on Windows 9x startup, and some parts of the Windows configuration manager also make use of it), leaving room for speculation much beyond the technical side - in particular because nothing of the interesting stuff is documented… […]
- ^ Paul, Matthias R. (1997-07-30) [1994-05-01]. "II.4. Undokumentierte Eigenschaften externer Kommandos". NWDOS-TIPs — Tips & Tricks rund um Novell DOS 7, mit Blick auf undokumentierte Details, Bugs und Workarounds. MPDOSTIP. Release 157 (in German) (3 ed.). Archived from the original on 2016-11-05. Retrieved 2012-01-11. (NB).
NWDOSTIP.TXTNovell DOS 7과 OpenDOS 7.01에 대한 포괄적인 저작물로서, 많은 미등록 기능 및 내부 기능에 대한 설명을 포함한다.그것은 저자의 일부분이다.MPDOSTIP.ZIP수집은 2001년까지 유지되었고 그 당시 많은 사이트에 배포되었다.제공된 링크는 HTML 변환 이전 버전의 파일을 가리킨다.)[4] - ^ Paul, Matthias R. (2001-04-09). "II.4. Undokumentierte Eigenschaften externer Kommandos". NWDOS-TIPs — Tips & Tricks rund um Novell DOS 7, mit Blick auf undokumentierte Details, Bugs und Workarounds. MPDOSTIP. Release 183 (in German) (3 ed.).
- ^ a b Chappell, Geoff (January 1994). Schulman, Andrew; Pedersen, Amorette (eds.). DOS Internals. The Andrew Schulman Programming Series (1st printing, 1st ed.). Addison Wesley Publishing Company. pp. 4, 21, 100–106, 127–129. ISBN 978-0-201-60835-9. ISBN 0-201-60835-9. (xxvi+738+iv 페이지, 3.5"-플로피[5][6]) 에라타: [7][8][9]
- ^ Paul, Matthias R. (2002-12-04). "[fd-dev] DISPLAY CON?". freedos-dev. Archived from the original on 2021-12-08.
[…] some issues of DISPLAY.SYS (of PC DOS 7/2000, for example) store the currently unused fonts in XMS memory. Some earlier issues of MS-DOS/PC DOS DISPLAY.SYS seem to have had a facility to store them in the HMA […]
- ^ Cooper, Jim (2002). Using MS-DOS 6.22 (special 3rd ed.). Que Publishing. p. 669. ISBN 0-78972573-8. ISBN 978-0-78972573-8. Archived from the original on 2020-02-18. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
- ^ a b Brooks, Vernon C. (2014). "This is a detailed list of the changes I made in PC DOS 7.0". PC DOS Retro. Archived from the original on 2020-02-18. Retrieved 2020-02-18.
[…] DOSKEY.COM […] Move code to HMA if available. […] SHARE.EXE […] Move code to HMA if available and added /NOHMA option force loading low. […]
- ^ Sweger, Kristofer (2007) [2002-07-15]. "ANSIPLUS and Windows". Archived from the original on 2021-11-28. Retrieved 2021-11-28.
[…] ANSIPLUS's code cannot be loaded to the HMA under MS-DOS 7 (Windows 9x only) because there apparently is not enough unused HMA memory available. […]
- ^ Paul, Matthias R. (2002-08-13). "Suche freien Speicherbereich unterhalb von 1 MB, der nicht von OS überschrieben wird" (in German). Newsgroup: de.comp.lang.assembler.x86. Archived from the original on 2017-09-04. Retrieved 2017-09-03.
- ^ Paul, Matthias R. (1997-10-02) [1997-09-29]. "Caldera OpenDOS 7.01/7.02 Update Alpha 3 IBMBIO.COM - README.TXT and BOOT.TXT - A short description of how OpenDOS is booted". Archived from the original on 2003-10-04. Retrieved 2009-03-29. [10]
추가 읽기
- Necasek, Michal (2011-09-13). "Who needs the address wraparound, anyway?". OS/2 Museum. Archived from the original on 2020-02-19. Retrieved 2020-02-19.
[…] 86-DOS, and hence PC DOS/MS-DOS, used a clever trick. The byte at offset 5 of the PSP contained a far call opcode (9Ah); the word at offset 6 of the PSP contained the appropriate value to indicate program segment size, and also the offset part of the far call. The word at offset 8, which served as the segment part of the far call, was crafted such that when combined with the offset, it would wrap around (a well understood feature of the 8086 CPU) and point to address 0:C0h, which contains interrupt vector 30h. […] the CALL 5 interface works even in DOS emulation under Windows NT and OS/2, and those systems most certainly cannot run with the A20 line disabled. How does that work then? […] Rather than chopping off address bits, the system mirrors the five bytes at 0:C0h at 1000C0h. The same technique had been in fact used in DOS 5 and above running with DOS=HIGH. In that case, DOS makes sure that linear address 1000C0h contains the appropriate far call. […]
- Kozierok, Charles M. (2001-04-17) [1997]. "High Memory Area (HMA)". The PC Guide. 2.2.0. Archived from the original on 2006-10-16. Retrieved 2006-10-15.