뉴질랜드의 코로나19 범유행
COVID-19 pandemic in New Zealand| 뉴질랜드의 코로나19 범유행 | |
|---|---|
 지역 보건 위원회별[a] 뉴질랜드 인구 10만 명당 사례 지도 | |
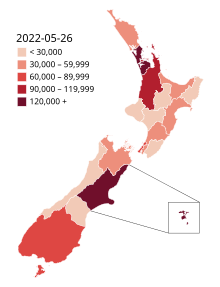 지역 보건 위원회별[a] 뉴질랜드 사례 총계 지도 | |
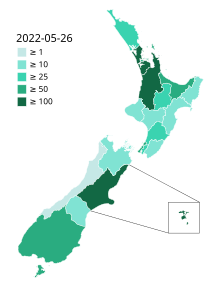 지역 보건 위원회별[a] 뉴질랜드 사망자 지도 | |
| 질병 | 코로나19 |
| 바이러스주 | SARS-CoV-2 |
| 위치 | 뉴질랜드 |
| 첫발병 | 우한, 후베이, 중국 |
| 인덱스케이스 | 오클랜드, 오클랜드 리전 |
| 도착일자 | 2020년2월28일 (3년 7개월 1주일 전) |
| 확진자 | 2,240,441[1] (총) |
| 활성사례 | 12,799[1] |
| 의심사례‡ | 60,255[1](총) |
| 복구됨 | 2,283,778[1] |
데스 | 2,716[1] |
| 치사율 | 0.121% |
| 정부홈페이지 | |
| www | |
| ‡의심되는 사례들은 실험실 테스트를 통해 일부 다른 변종들이 배제되었을 수도 있지만 이 변종 때문인 것으로 확인되지 않았습니다. | |
뉴질랜드의 코로나19 대유행은 중증 급성 호흡기 증후군 코로나바이러스 2(SARS-CoV-2)로 인한 코로나바이러스 질병 2019(COVID-19) 대유행의 일부였습니다.2020년 2월 28일 뉴질랜드에서 첫 번째 질병 사례가 보고되었습니다.227만4370건(확진 221만7047건, 발생[b] 가능성 57,323건)을 기록했습니다.전염병으로 인해 3,000명 이상이 사망했으며, 20개 지역 보건 위원회(DHB) 전 지역에서 사례가 기록되었습니다.[1]팬데믹은 2020년 4월 초에 처음으로 정점을 찍었으며, 하루에 89건의 신규 환자와 929건의 활성 환자가 기록되었습니다.2021년 10월 22일 134건의 신규 사례가 보고되면서 다시 정점을 찍었습니다.[2]
2020년 2월 말 첫 발병에 대응하여 뉴질랜드 정부는 국경을 폐쇄하고 봉쇄 조치를 취했습니다.[3]2020년 3월 21일 뉴질랜드 내 발생을 관리하기 위해 4단계 경보 수준 시스템이 도입되었습니다.[4]이후 2020년 3월 26일부터 5월 27일까지 두 달간 전국적으로 봉쇄된 후, 오클랜드 지역이 2020년 8월부터 9월까지, 2021년 2월부터 3월까지 두 차례 봉쇄에 들어간 지역별 경계 수준 변경이 사용되었습니다.[5][6]그 후 이 나라는 지역 사회 전파 없이 몇 달 동안 관리 격리 시스템으로 모든 사례가 제한되었습니다.[7]
2021년 8월, 뉴질랜드는 오클랜드에서 델타 변이 바이러스의 지역사회 전파 사례로 인해 전국적인 봉쇄에 들어갔고, 오클랜드와 웰링턴에서 지역사회 사례가 잇따랐습니다.[7]전국적으로 증가하는 사례로 인해, 정부는 백신 접종 개시를 가속화하면서 제거 전략을 포기했습니다.[8]오클랜드는 2021년 12월 3일 새로운 COVID-19 Protection Framework (" 신호등 시스템")가 발효될 때까지 봉쇄의 형태를 유지했습니다.[9]2022년 2월부터 5월까지 정부는 국경 제한, 대중 집회 제한, 백신 의무화 요건을 단계적으로 완화했습니다.[10][11][12]2022년 9월, 정부는 코로나19 보호 프레임워크를 종료하고 남은 백신 의무와 마스크 요구 사항을 해제했습니다.[13]2023년 8월 15일, 뉴질랜드 정부는 남아있는 모든 코로나19 제한을 해제했습니다.[14]
배경
2020년 1월 12일, 세계보건기구(WHO)는 2019년 12월 31일 WHO에 보고된 중화인민공화국 후베이성 우한시의 한 집단에서 발견된 신종 코로나바이러스(SARS-CoV-2)가 호흡기 질환(코로나19)의 원인임을 확인했습니다.[15][16]
2003년 사스에 비해 COVID-19의 경우 치명률은 훨씬 낮았지만,[17][18] 전염성은 훨씬 더 큰 것으로 알려졌습니다.세계보건기구 협력 센터인 임페리얼 칼리지 런던의 MRC 글로벌 전염병 분석 센터의 아즈라 가니 씨.[19][17]
전송 타임라인
2020년 2월 28일, 뉴질랜드는 최근 이란을[25][26] 방문한 60대 여성의 첫 번째 사례를 확인했습니다. 뉴질랜드는 최근 이탈리아 북부에서 귀국한 여성의 두 번째 사례를 3월 4일 확인했습니다.[27]2020년 3월까지 큰 폭으로 증가하여 3월 31일까지 총 647건(확진 600건, 발생 가능 47건), 74건의 회복을 기록했습니다.[28]
3월 29일, 뉴질랜드에서도 서부 해안 지역에서 온 70대 여성이 코로나바이러스와 관련된 첫 사망자를 발표했습니다.[29][30]
2020년 4월 5일, 코로나19에 걸린 사람의 74%가 파케하, 8.3%가 아시아, 7.6%가 마오리, 3.3%가 파시피카인 것으로 나타났습니다.[31]7월 31일까지, 총 환자 수는 1,560명에 달했고, 총 환자 수는 1,518명으로 증가했고, 사망자 수는 22명으로 증가했습니다.[32]
102일 동안 지역사회 전파가 없었던 이후, 2020년 8월 11일 오클랜드에서 4건의 사례가 보고되어 도시는 다시 봉쇄 상태에 빠졌습니다.[33]1 뉴스에 따르면, 오클랜드에서 8월에 발생한 지역사회 발병의 75%를 태평양 섬 주민들이 차지했습니다.[34]9월 5일, 쿡 제도의 전 총리 조 윌리엄스의 사망으로 전국 사망자 수는 24명에 달했습니다.[35]
일부 커뮤니티 사례를 제외하고 2020년 하반기 동안 뉴질랜드에서 보고된 대부분의 사례는 국경에서 보고되었습니다.[36][37][38]2020년 12월 31일까지 뉴질랜드에서 2,082명의 환자가 발생하였고, 25명의 사망자가 발생하였습니다.[39]

2021년 1월 25일, 뉴질랜드는 남아프리카 공화국에서 발생한 것으로 추정되는 코로나 바이러스 변종에 대해 56세 여성이 양성 반응을 보인 후 일요일 2020년 11월 이후 첫 지역 사회 확산 사례를 확인했습니다.[41][42]2월 14일, 오클랜드 파파토에토의 한 가족 내에서 3건의 지역사회 전파 사례가 보고되었습니다.[43]일부 커뮤니티 사례를 제외하고 뉴질랜드에서 기록된 대부분의 사례는 2021년 8월 이전에 국경에서 발생했습니다.2021년 7월 30일까지 총 환자 수는 2,870명에 달했고, 총 환자 수는 2,799명, 사망자 수는 26명에 달했습니다.[44]
2021년 8월 17일, 보건부는 오클랜드에서 코로나19의 새로운 지역사회 사례를 발표했습니다.[45]이에 따라 정부는 2021년 8월 17일 오후 11시 59분부터 국가를 경보 레벨 4로 이동시켰습니다.[46]8월 19일까지 지역사회 사례는 21건에 달했고, 대부분은 델타 변이 바이러스였습니다.[47]2021년 8월 오클랜드에서 발생한 이후 뉴질랜드의 지역사회 및 국경 사례 수는 크게 증가하여 2021년 12월 31일까지 총 14,118건에 달했습니다.총 복구 건수도 12,870건에 달했고 사망자는 51명으로 늘었습니다.[48]2021년 12월 29일, 영국의 음악가 로버트 에더리지(Dimension)가 미국 최초의 오미크론 사례로 확인되었습니다.[49]
2022년 초, 총 기록 건수는 기하급수적으로 증가하여 1월 31일 16,416건에서 2월 28일 100,821건으로 증가했습니다.또한 2022년 2월 28일 사망자는 56명, 총 복구 건수는 18,332건에 달했습니다.[50][51]코로나19 모델링 아오테아로아 프로젝트 리더 디온 오닐은 2022년 2월 보고된 사례가 급증한 것은 중합효소 연쇄반응(PCR) 검사 및 데이터 처리 분야의 밀린 업무와 최근 공공용 신속항원검사(RATS) 도입 때문이라고 분석했습니다.[52]
응답

중앙정부 대응
뉴질랜드 정부는 국립보건조정센터(NHCC)를 설립하여 전 세계적인 코로나19 팬데믹에 대응하였습니다.[53]2020년 2월 초, 정부는 우한에서 시작된 전 세계적인 코로나19 범유행에 대응하여 중국에서 오는 대부분의 여행객의 입국을 금지했습니다.[54]또한, 정부는 2020년 2월 우한을 시작으로 귀국 시민, 거주민 및 가족을 위한 여러 송환 항공편을 후원했습니다.[55]
2020년 3월 19일, 저신다 아던 총리는 해외 여행 및 지역 사회 내에서 증가하는 사례에 대응하여 비시민 및 비거주자에 대한 국경을 폐쇄했습니다.[56][57]3월 21일, 정부는 4단계 경보 단계 시스템을 도입하여 3월 25일부터 국가 인구와 경제의 상당 부분을 봉쇄했습니다.[58][4]정부의 코로나19 퇴치 전략의 성공으로 인해 4월 28일, 5월 11일,[59][60] 5월 25일,[61] 6월 8일 이동, 친목회, 경제 활동에 대한 봉쇄가 점진적으로 해제되었습니다.[62]6월 8일 경보 레벨 1 제한이 해제되면서 사회적 거리두기와 봉쇄 제한은 사라졌지만 국경 제한은 유지되었습니다.[62]5월 13일, 정부는 논란이 되고 있는 COVID-19 공중 보건 대응법 2020을 통과시켰는데, 이 법안은 법 집행 기관이 봉쇄 제한을 시행하기 위해 영장 없이 집과 다른 장소에 들어갈 수 있도록 허용했습니다.[63][64]
2020년 8월 11일 오클랜드에서 지역사회 전파가 두 번째로 발생함에 따라 정부는 봉쇄 제한을 복원했습니다.[5]2020년 8월 30일,[65] 9월 23일,[66] 10월 7일에 오클랜드와 뉴질랜드의 나머지 지역의 봉쇄 규제가 점진적으로 사라졌습니다.[67]11월 초, 정부는 뉴질랜드에 입국하는 여행객들에게 뉴질랜드로 여행하기 전에 관리 격리된 장소를 예약하도록 요구했습니다.[68]2020년 12월 중순, 정부는 2021년 쿡 제도 및 호주와 여행 거품을 구축할 계획을 발표했습니다.[69][70]
2021년 2월 14일 사우스오클랜드의 파파토에토 교외에서 지역사회가 발생한 후 정부는 오클랜드에 경보 3단계 봉쇄령을, 2월 17일까지 나머지 지역에 경보 2단계 봉쇄령을 내렸습니다.[71]2월 17일 오클랜드의 봉쇄령은 경보 2단계로 낮아졌고 나머지 국가들은 경보 1단계로 복귀했습니다.[72]2월 22일 정부는 오클랜드가 2월 22일 경보 1단계로 복귀할 것이라고 발표했습니다.[73]오클랜드 2월 클러스터와 관련된 새로운 커뮤니티 사례에 따라 정부는 2021년 2월 28일부터 7일간 오클랜드에 경보 레벨 3 봉쇄를, 나머지 국가에 경보 레벨 2 봉쇄를 시행했습니다.[6]
2021년 8월 오클랜드에서 새로운 커뮤니티가 발생하자 뉴질랜드 정부는 2021년 8월 17일 경보 레벨 4 제한을 복원했습니다.[7]오클랜드와 북섬의 일부 지역에서 증가하는 사례로 인해 정부는 백신 접종 개시를 가속화하는 한편, 백신 접종 전략을 포기했습니다.[74][8]이후 2021년 12월 3일부터 시행된 COVID-19 Protection Framework("신호등 시스템")로 "경보 수준 시스템"이 대체되었습니다.[75]또한 정부는 2021년 11월 16일부터 코로나19 예방접종 패스 제도를 시행했습니다.[76]정부는 지난 11월 23일 특정 직종에 대한 '신호등 제도'와 백신 의무화를 위한 법적 틀을 마련한 '2021년 코로나19 대응(백신 접종) 법제화법'을 통과시켰습니다.[77]
2022년 1월 17일, 정부는 5세에서 12세 사이의 어린이들을 위한 백신 출시를 시작했습니다.[78]정부는 지난 1월 말 접촉 추적, 검사 및 자가 격리를 기반으로 SARS-CoV-2 오미크론 변종 확산 방지를 위한 3단계 계획도 착수했습니다.[79]2월 3일, 정부는 또한 2022년까지 뉴질랜드 국경을 다시 개방하기 위한 5단계 계획을 시작했습니다.[10]3월 23일, 정부는 공공 집회 제한, 백신 패스 요건, 대부분의 직업에 대한 백신 의무화, NZ COVID Tracer QR 코드 스캔 요건을 포함한 몇 가지 "신호등" 제한을 완화했습니다.[11]2022년 5월, 정부는 또한 다양한 직업, 방문객, 학생 비자 수업을 위해 국경 재개방을 가속화했습니다.[12]2022년 9월 중순, 정부는 "신호등 제도"를 폐지하고, 대부분 남아있는 코로나19 마스크, 백신, 밀접 접촉 격리 명령 및 제한을 종료했습니다.[13]
2022년 10월 중순, 정부는 봉쇄, 격리 및 격리 관리(MIQ), 국경 폐쇄, 백신 패스 및 의무화를 이행하는 권한을 포함한 2020년 코로나 공중 보건 대응법의 여러 조항을 폐기했습니다.그러나 정부는 의회가 더 새로운 일반적인 유행병 법안을 통과시킬 때까지 7일간의 격리 기간, 마스크 사용 및 국경 진입 요건에 대한 법 조항을 유지하기로 선택했습니다.정부는 또 전염병 경보를 해제하면서 긴급 관리에서 코로나19 장기 관리로의 전환을 예고했습니다.[80][81]또한 크리스 힙킨스 COVID-19 대응부 장관은 정부가 코로나19 팬데믹에 대한 대응에 대한 왕립 조사 위원회를 개최할 것이라고 확인했습니다.[82]
유전체 염기서열 분석
2020년 8월 오클랜드에서 코로나19 환자가 추가로 발생하는 동안,[83] 게놈 시퀀싱은 정부의 팬데믹 관리 전략의 "새로운 도구"로 주목받았습니다.Ashley Bloomfield는 "우리는 또한 양성 반응을 보인 모든 사람들과 관리 격리 및 격리 상태에서 우리의 최근 사례와 현재 사례들에 대해 게놈 시퀀싱을 실시하고 있습니다"[84]라고 말했습니다. 계통역학 전문가는 약 1000명 중 25명만이 시퀀싱 된 첫 번째 발병에 비해,"바이러스의 확산을 추적하기 위해 확인된 COVID-19 사례로부터 바이러스의 유전자 서열을 매핑하는 것은 뉴질랜드의 코로나바이러스 대응에 필수적인 부분입니다.클러스터를 식별하는 데 더 큰 확실성을 제공하고 접촉 추적자의 조사에 집중하는 데 도움이 됩니다."[85]블룸필드 박사는 염기서열 분석을 통해 발병 원인에 대한 정보를 얻을 수 있을 것이라고 말했습니다. 오타고 대학의 바이러스 진화 수석 강사이자 환경과학연구소(ESR)에서 유전체 염기서열 분석을 연구하고 있는 제마 게오게건 씨는 뉴질랜드 라디오와의 인터뷰에서 다음과 같이 말했습니다.
새로운 사례들의 게놈을 격리시설의 게놈과 세계 인구 및 뉴질랜드의 다른 사례들과 비교함으로써, 우리는 그 전염 연쇄가 잠재적으로 얼마나 오래 지속되고 있는지 이해하기 시작할 수 있고, 그 바이러스가 뉴질랜드에 처음 출현하고 도착한 시기를 추정할 수 있을 것입니다.[86]
2020년 11월 에어 뉴질랜드 승무원이 코로나19 양성 반응을 보였을 때 ESR의 과학자인 조엘 드 리트는 염기서열 분석이 전국에서 일어나고 있는 일에 대한 좋은 그림을 제공했다고 상당히 확신하지만 지역 사회에서 확인되지 않은 무언가가 있을 가능성은 여전히 있다고 말했습니다.항공 승무원의 유전체를 특정한 염기서열 분석은 뉴질랜드 게놈과 관련이 있는지, 아니면 해외 염기서열 분석에서 나온 정보와 관련이 있는지를 보여주며, 이는 우리가 여행과 관련된 감염일 가능성이 높으며, 공항을 더 자세히 조사하기 시작할 수 있습니다.어떤 사람의 움직임과 관련된 항공사들을 말입니다."[87]Geoghegan은 귀환하는 항공 승무원과 같은 경우에 게놈 시퀀싱의 중요성을 강조했는데, 이것은 나중에 기내 전파 사례를 입증하는 데 사용되었습니다.[88]
지방정부 및 지방정부 대응
3월 20일 오클랜드 시의회는 오클랜드 아트 갤러리와 뉴질랜드 해양 박물관을 포함한 모든 공공 도서관, 수영장, 레크리에이션 센터를 폐쇄했습니다.[89][90]
3월 21일 오클랜드, 웰링턴, 크라이스트처치, 더니딘, 로워허트, 포리루아의 여러 지방의회는 수영장, 도서관, 레크리에이션 센터, 커뮤니티 센터, 미술관, 박물관 등 공공시설의 폐쇄를 발표했습니다.[91][92][93][94]
3월 24일 오클랜드 시의회는 캠프장을 폐쇄한다고 발표했고 캔터베리 시의회는 뉴질랜드 자동차 카라반 협회 캠핑장도 48시간 이내에 폐쇄할 것이라고 발표했습니다.[95]
오클랜드 카운슬(Auckland Council)은 4월 14일 봉쇄로 인해 중단된 다수의 인프라 프로젝트에 대한 특별 프로젝트 자금 지원을 신청한다고 발표했습니다.[96]
4월 15일, 더딘 애런 호킨스 시장, 팀 카도건 중부 오타고 지구 시장, 짐 볼트 퀸스타운 레이크 지구 시장, 브라이언 카도건 클루타 지구 시장을 포함한 여러 오타고 시장들이 참석했습니다.Waitaki 구청장 Gary Kircher와 Otago 지역 의회 의장 Marian Hobbs는 코로나바이러스 팬데믹 구호 활동을 돕기 위해 급여의 일부를 지역 자선단체에 기부하고 있었습니다.게다가 수 비드로즈 최고경영자를 포함한 몇몇 더니딘 시의회 관계자들은 그들의 지역사회가 코로나19의 영향에 대처하는 것을 돕기 위해 감봉 조치를 취하고 있다고 발표했습니다.[97]
7월 10일 오클랜드 시의회는 코로나19 팬데믹으로 인한 경제적 영향으로 500개의 상시 일자리를 없애겠다고 발표했습니다.[98]
8월 27일 오클랜드 의원 에페소 콜린스는 파시피카 공동체의 구성원들이 코로나19 검사를 위해 나서도록 장려하기 위해 정부가 비자를 초과한 사람들에게 사면을 내릴 것을 요구했습니다.보건부 장관 Chris Hipkins는 정부가 이민 목적으로 검사를 하는 동안 수집된 어떤 정보도 사용하지 않을 것이라고 Pasifika 커뮤니티를 안심시켰습니다.콜린스는 태평양 지역 사회 지도자와 교회 지도자, 보건 전문가들이 오버스테이들이 파장을 두려워하지 않고 코로나19 검사를 받도록 독려할 것을 촉구했습니다.[99]
11월 12일, 필 고프 오클랜드 시장과 지역 보건 당국은 도심에 있는 오클랜드 하이 세인트에 있는 A-Z 콜렉션 가게에서 일했던 지역 사회 전염 사례가 발견된 후 오클랜드 CBD 지역의 사람들에게 재택 근무를 권고했습니다.고프는 또 가게 주인이 코로나19 검사 결과를 기다리는 동안 직원에게 출근하라고 말한 것으로 알려진 것에 대해서도 비판했습니다.가게 주인은 직원이 화요일에 전화를 걸어 목이 아프며 의사를 방문할 것이라고 설명하면서 고프의 진술에 이의를 제기했습니다.[100][101]다음 날, 가게 직원은 중국어 번역기를 제공하지 않은 그녀를 인터뷰한 보건 관계자들을 비난하는 성명서를 발표했고, 그녀의 이전 행적과 행동, 연락처에 대한 잘못된 정보를 야기했습니다.이러한 잘못된 의사소통의 결과로, 그녀의 고용주와 그들의 가족들은 욕설이 섞인 온라인 메시지를 받았습니다.[102][103]
2021년 11월 2일, 존 카터 파노스 구청장은 정부가 노스랜드 지역의 북부 지역에 2건의 미검출 사례에 이어 3단계 봉쇄를 시행하기로 결정한 것을 지지했습니다.그는 사람들에게 검사를 받고 백신을 맞을 것을 촉구했습니다.[104]
보건 부문 응답
3월 19일, 의료 채용 회사 메드월드는 은퇴한 의사와 시간제 의사들이 코로나19 확산 방지를 위한 보건 부문과 정부의 노력을 지원해 줄 것을 호소했습니다.[105][106]
6월 10일, 구급차와 응급처치 서비스를 제공하는 세인트 존 뉴질랜드는 코로나19 범유행으로 인한 3천만 달러의 적자로 인해 직원을 해고할 것이라고 발표했습니다.[107]그 단체는 또한 정부의 임금 보조금 제도를 신청하려고 했지만, 소득이 40% 감소했음에도 불구하고 그것을 받을 자격이 없다고 들었습니다.[108]
8월 27일 파시피카 GP 네트워크의 멤버인 Api Talemaitoga는 정부의 테스트 전략 그룹이 마오리족과 파시피카족 커뮤니티의 구성원들이 테스트에 공정하게 접근할 수 있도록 보장하기 위해 노력할 것이라고 발표했습니다.이러한 조치에는 무료 테스트, 모바일 테스트 센터 및 통역이 가능한 임상의를 제공하는 것이 포함됩니다.보건 당국은 이들 지역 사회 구성원들이 코로나19로 인해 일자리를 잃지 않을 것이라고 안심시키기 위해 노력하기도 했습니다.[99]
델타 지역사회가 중반에 발발한 이후로..2021년 8월 뉴질랜드 간호사 기구(NZNO)는 간호사, 조산사, 의료 보조원의 정신적, 신체적 건강에 대한 우려를 표명했습니다. 부족한 PPE 공급과 마스크 착용 검사의 부족.[109]2021년 9월 중순, NZNO는 고용 관계 당국을 통해 오클랜드 지역 보건 위원회의 "모두를 위한" 방문자 정책에 이의를 제기했습니다.NZNO는 델타 발생 기간 동안 두 명의 방문객을 허용하는 보건위원회의 정책이 환자와 직원들에게 건강상의 위험을 초래한다고 주장했습니다.[110]
2021년 10월, Pharmac은 MSD(Merck Sharp & Dohme)와 실험용 항바이러스제 몰누피라비르 구매 계약을 체결했습니다.메드세이프의 승인을 받으면 파마시에는 6만 코스의 알약이 공급되며, 이 알약은 경증에서 중등증의 코로나19 증상을 가진 뉴질랜드 사람들을 치료하는 데 사용됩니다.[111]파마시는 지난 11월 입원 환자의[112] 결과를 개선하는 경구용 정제인 바리키티닙 500회분을 확보하고 단일클론항체인 로나프레브(일명 리제네론)를 구입했습니다.[113]
보건부는 2021년 9월부터 '지역사회 기반 거품' 속에서 집에서 격리할 수 없는 사람들을 수용하기 위한 지역 방역 시설을 설립하는 것을 목표로 지역 보건 위원회에 자금을 할당하기 시작했습니다.SIQ 프로그램은 증가하는 지역사회 사례와 2022년에 국경을 다시 개방할 계획에 대응하여 설립되었습니다.뉴질랜드는 세계에서 가장 엄격한 코로나 규제를 완화하기 시작하면서 국경을 점진적으로 재개한다고 발표했습니다.백신을 맞은 호주 국적자들은 주 정부의 필수 호텔 검역을 거치지 않고 2월 27일에 귀국할 수 있습니다.저신다 아던 총리에 따르면, 3월 13일부터 다른 나라에서 온 사람들에게 잽을 날리는 것이 허용될 것입니다.사람들은 여전히 10일 동안 자가 격리를 해야 하지만, 집에서 자가 격리를 할 수 있을 것입니다.[114]
2021년 10월 중순, 보건부는 와이라라파 지역 보건 위원회에 지역 SIQ 시설을 설립하기 위해 120,000 뉴질랜드 달러를 할당했습니다.[115]또한 타라나키 지역 보건 위원회, 오클랜드 지역 보건 위원회, 남부 지역 보건 위원회 및 황가누이 지역 보건 위원회를 포함한 다른 지역 보건 위원회는 용도가 변경된 다양한 호텔 및 휴가 공원에 자체 SIQ 시설을 설립할 준비를 했습니다.[116][117][118][119][120]
2022년 2월 17일, 공공 서비스 협회(PSA) 소속 실험실 노동자, 접촉 추적자 및 기타 중요 보건 직원들은 지역 보건 위원회의 급여 제안을 거부하고 2022년 3월에 두 번 파업하기로 투표했습니다.노동자들은 임금 인상, 다른 보건 전문가들과 동등한 대우, 안전한 인력 배치 및 유지를 요구해 왔습니다.노조 대변인 윌 매튜스는 지역 보건 위원회와 15개월간의 협상이 실패한 후 계획된 파업이 이루어졌다고 말했습니다.[121]2022년 2월 중순, 실험실 노동자들의 국가 대표 기관인 의학실험실과학연구소는 지난 2년간 코로나19 대유행으로 열악한 환경에서 운영되어 많은 노동자들이 전소되었다고 보고했습니다.근로자들은 연구실 내의 추가적인 시험 기계로 인해 부족한 사무실과 레크리에이션 공간에 대해 불평했습니다.[122]
2022년 5월 중순, 1만 명의 동맹 보건 노동자들이 DHBs와의 임금 및 근로 조건에 대한 협상이 실패함에 따라 뉴질랜드 전역에서 파업에 돌입했습니다.PSA의 파업 행동은 봉급생활자 의료 전문가 협회(ASMS), 뉴질랜드 치과 협회(NZDA), NZ Council of Trade Unions(CTU)의 지원을 받았습니다.[123]
2022년 6월 초, 더니딘 병원은 병동 내에서 코로나19가 발생함에 따라 방문객에게 폐쇄되었습니다.[124]
경제적 영향

2020년 3월까지 뉴질랜드는 국가의 소유와 통제가 있는 자유 시장인 혼합 경제를 운영했습니다.[125]뉴질랜드 경제 내에서 그들의 정상적인 영향력에서 다소 갑자기 벗어났음에도 불구하고, 기업 부문의 대표들은 다양한 산업에서 인식된 불일치에 반대하는 로비,[126] 기업 신뢰 지표와[127][128] 경제 전망과 같은 습관적인 평가를 공표하는 언론 보도에 계속 출연했습니다.[129]그리고 "평소와 같은 사업"으로 빨리 돌아오기를 간절히 바라고 있습니다.[130]
2020년 9월 17일, 뉴질랜드의 국내 총생산은 코로나19 팬데믹으로 인해 6월 분기에 12.2% 감소하는 등 공식적인 경기 침체에 접어들었습니다.국제 여행 금지와 엄격한 전국적 봉쇄로 소매업, 숙박업, 숙박업, 운송업이 악영향을 받았습니다.[131][132][133]
사회적 영향
코로나19 범유행은 뉴질랜드 사회에 상당한 영향을 끼쳤으며, 교육, 신앙 공동체, 휴일, 마오리, 대중 집회, 스포츠 및 레크리에이션 활동에 상당한 영향을 미쳤습니다.코로나19 확산에 대한 보도로 안면 마스크와 손 소독제에 대한 수요가 높았습니다.[134][135][136][137]
교육
2020년 3월 23일, 정부는 코로나19 확산에 따라 전국적인 봉쇄 조치의 일환으로 모든 학교, 유아센터, 대학교를 폐쇄했습니다.[138][139][140]또한, 5월 13일, 연말 고등학교 국가교육성취도증명서(NCEA) 외부 시험이 2020년 11월 중순으로 연기되었습니다.[64]몇몇 대학들은 집으로 돌아온 학생들에게 계속해서 임대료를 부과해 비난을 받았습니다.[141][142]
신앙공동체
정부의 100인 이상 모임 금지 조치에 따라 몇몇 신앙 공동체들이 공개 모임을 중단하거나 축소한다고 발표했습니다.[143][144][145]경보 레벨 4 이하의 정육점의 폐쇄로 인해 무슬림 공동체의 구성원들은 할랄 음식에 접근하는 데 어려움을 겪었습니다.[146][147][148]5월 14일 처음으로 봉쇄 수준이 경보 2단계로 낮아졌을 때, 종교 모임은 처음에는 10명으로 제한되었고, 이는 뉴질랜드 이슬람 연합(FIANZ)과 가톨릭 주교들, 그리고 운명 교회의 브라이언 타마키 주교의 비판을 받았습니다.[149][150][151]비판이 일자 정부는 예배 인원 제한을 10명에서 100명으로 상향 조정하여 많은 신앙 공동체들이 집회를 재개할 수 있도록 했습니다.[61][152][153]2020년 9월에.파킬라우 마나세 루아 기독교 지도자 태평양 대응 조정팀 위원장과 프랭크 리치 웨슬리언 감리교 목사는 미국의 보수적인 복음주의 및 오순절 교회와 관련하여 교회에 다니는 뉴질랜드 신도들 사이에 코로나19와 관련된 잘못된 정보가 유포되는 것에 대해 우려를 표명했습니다.[154]
마오리족
북섬의 노스랜드, 이스트케이프, 베이 오브 플렌티 지역의 마오리족 공동체는 코로나19 팬데믹에 대응하여 바이러스 확산을 제한하기 위해 도로 블록을 설치했습니다.[155][156]이 검문소들은 공동체의 긴장을 조성했고, 정부와 뉴질랜드 경찰에 의해 그들의 권위에 도전하는 허가받지 않은 것으로 여겨졌습니다.[157][158][159]2021년 1월 말 오클랜드에서 새로운 커뮤니티가 발생한 후 [160]루벤 타이파리와 베테랑 정치인 혼 하라위라를 포함한 노스랜드 마오리는 허가받지 않은 검문소를 설립했고 경찰은 이를 폐쇄했습니다.[161]
대중집회
코로나19 범유행으로 인해 대규모 집회는 바이러스 퇴치를 위한 사회적 거리두기 조치를 준수하지 않았습니다.이에 대응하여, 왕립 뉴질랜드 리턴 앤 서비스 협회는 2020년 모든 ANZAC Day 서비스와 레드 포피 컬렉션을 중단했습니다.[162]2020년 5월 조지 플로이드 살해 사건으로 전 세계적인 시위가 촉발된 이후, 2020년 6월 초 오클랜드, 웰링턴, 크라이스트처치 등 주요 센터 여러 곳에서 '흑인의 생명도 소중하다'는 시위가 열렸습니다.[163][164]이 시위들은 수시 와일스, 저신다 아던 총리, 윈스턴 피터스 부총리 그리고 데이비드 시모어 ACT 당 대표를 포함한 몇몇 보건 및 정치계 인사들에 의해 사회적 거리두기 제한을 무시한 것에 대해 비판을 받았습니다.[165][166][167]또한 2020년 8월부터 9월 사이에 봉쇄 반대 시위가 발생했습니다.[168][169][170][171]
코로나19로 인한 국경 및 사회적 거리두기로 인해 2020년 3월 중순 슈퍼 럭비 시즌과 2020년 워버드 오버 와나카 에어쇼 등 여러 스포츠 및 레크리에이션 행사가 중단되었습니다.[172][173]
2021년 2월 중순 사우스오클랜드에서 새로운 커뮤니티가 발생한 이후, 할버그 어워드는 대중 집회에 대한 경보 레벨 3 제한을 준수하기 위해 연기되었습니다.[174]또한 네이피어의 아트 데코 페스티벌과 오클랜드의 게이 프라이드 퍼레이드도 취소되었습니다.오클랜드의 스플로어 축제는 2021년 3월 26일에서 28일로 연기되었습니다.[175]
2022년 2월 뉴질랜드 의회에서 경찰은 이틀 밤을 불법으로 진을 친 백신 반대 시위자들에게 무단출입 통보를 했습니다.50명 이상이 체포됐습니다.[176]
퍼시픽 아일랜더스
좌파 블로거 마틴 "봄버" 브래드버리는 사우스 오클랜드의 태평양 섬 주민 공동체를 돕기 위해 정부가 초과 체류자들에 대한 사면을 선언하고 재택근무를 할 수 없는 사람들에게 보상금을 지급해야 한다고 주장했습니다.[177]
여행
코로나19 범유행은 뉴질랜드를 오가는 여행에 큰 영향을 미쳤습니다.2020년 뉴질랜드 정부는 항공사 및 여행사와 협력하여 중국, 페루, 호주, 우루과이, 피지 및 인도를 포함한 다양한 해외 지역에 발이 묶인 뉴질랜드인들을 송환했습니다.[178][179][180][181][182][183]3월 24일, 윈스턴 피터스 외무장관은 8만 명의 뉴질랜드인들이 해외에 발이 묶인 것으로 추정했고, 그 중 17,000명이 외교통상부의 "안전한 여행" 프로그램에 등록했습니다.[184]2021년 4월 인도에서 COVID-19 확진자가 급증한 이후, 많은 뉴질랜드 시민들과 그곳에 거주하는 임시 비자 소지자들이 국경 제한 및 항공편 취소로 발이 묶였습니다.[185][186]
코로나19 범유행은 뉴질랜드의 많은 외국인 여행객들과 임시 비자 소지자들에게도 영향을 미쳤습니다.뉴질랜드 정부는 코로나19로 인한 여행 제한으로 인해 모든 임시 비자를 2020년 9월 25일까지 자동으로 연장하였고,[184] 이후 2021년 2월까지 연장하였습니다.[187]정부는 이와 함께 발이 묶인 이주노동자 등 뉴질랜드를 떠날 수 없는 임시비자 소지자들에게 생계비를 지원하는 등 긴급복지 지원도 확대했습니다.[188]국경 제한에도 불구하고, 정부는 크라이스트처치 이슬람 사원 총격범 브렌턴 태런트와 아들의 죽음 이후 요트를 팔려고 하는 영국인 가족의 재판에 참석하는 사람들뿐만 아니라 일부 중요한 필수 노동자들에게 비자 면제를 허용했습니다.[189][190][191]
영국, 독일, 덴마크를 포함한 몇몇 외국 정부들도 뉴질랜드에 발이 묶인 시민들을 송환하기 위해 전세기를 조직했습니다.[192][193]게다가 루프트한자나 카타르 항공과 같은 국제 항공사들도 뉴질랜드로부터의 송환 비행을 용이하게 하는 데 참여했습니다.[194][195]5월 13일까지 피터스 외무장관은 뉴질랜드 정부와 외국 대사관의 송환 항공편 조직 노력에 따라 이주 노동자 5만 명이 본국으로 돌아갔다고 확인했습니다.[196]
2021년 5월 9일, 라디오 뉴질랜드 앤드 스터프는 정부가 팬데믹이 시작된 이후 우한, 인도, 페루를 포함한 다양한 지역에서 해외에 발이 묶인 뉴질랜드인들을 송환하기 위해 600만 뉴질랜드 달러를 지출했다고 보도했습니다.[197]2021년 5월 28일, 정부는 또한 팬데믹 기간 동안 항공권을 구입할 여유가 없는 이주민들을 본국으로 송환하기 위해 900,000달러의 할당금 중 112,000달러를 지출한 것으로 보고되었습니다.게다가, 정부는 팬데믹 기간 동안 이주민 유치에 1,100만 달러를 지출했습니다.또한 정부는 2021년 2월 이민 비자 계정 재정의 적자를 해결하기 위해 2억 4,200만 달러를 지출했으며, 이는 여전히 5,600만 달러의 적자를 남겼습니다.[198]
2021년 8월 11일 데이비드 스케그 교수가 이끄는 전략적 코로나19 공중보건 자문단은 뉴질랜드 국민의 대다수가 백신을 접종했다면 2022년 국경 재개를 위한 단계적 접근을 취해야 한다고 주장했습니다.제안된 계획에 따르면, 여행자들은 백신 접종 상태 및 출신 국가의 팬데믹 상태와 같은 위험 요소에 따라 관리 격리에 들어가는 것을 피할 수 있습니다.다른 제안으로는 여행객을 위한 출발 전 테스트와 뉴질랜드 입국 시 여행객을 위한 신속한 테스트가 있습니다.[199][200]
델타 지역사회가 중반에 발발한 이후로..2021년 8월, 경찰은 노스랜드 마오리이위와 전 정치인 혼 하라위라를 포함한 지도자들로부터 노스랜드와 오클랜드 사이에 고정 검문소를 설치하기 위해 일주일 이상을 기다렸다는 비판을 받았습니다.8월 17일 4급 발표는 오클랜드에서 노스랜드 지역으로 사람들의 유입을 촉발시켰습니다.[201]다른 노스랜드 주민들은 브린더윈 힐스, 카이와카, 만가와이 근처의 경찰 검문소의 위치가 불일치하여 주민들이 식료품과 같은 필수적인 서비스에 접근하는 것을 방해했다고 비판했습니다.[202]
정부는 오미크론 변종의 급속한 확산에 대응하여 계획된 국경 재개를 2022년 2월로 연기하고 출국 전 검사 요건을 높였으며 관리 격리 및 격리(MIQ) 시설 체류 기간을 10일 연장했습니다.[203]
2022년 2월 3일, 아던은 국경 재개를 위한 5단계 계획을 발표했습니다.
- 2월 27일 오후 11시 59분부터 뉴질랜드인과 호주에서 온 다른 자격이 있는 여행객들은 10일간 자가 격리가 허용됩니다.
- 3월 13일 오후 11시 59분부터 뉴질랜드인과 숙련공, 워킹홀리데이 비자 소지자를 포함한 적격 해외여행객은 7일간 자가격리가 허용됩니다.
- 4월 12일 오후 11시 59분부터 대부분의 임시 비자 소지자들과 5,000명의 유학생들 그리고 중요한 노동자들은 7일간 자가 격리가 허용될 것입니다.
- 2022년 7월부터 호주 출신, 비자 면제 여행객, 숙련된 노동자는 누구나 격리할 필요 없이 입국할 수 있게 됩니다.
- 2022년 10월부터 모든 비자 소지자에게 국경이 개방됩니다.
이 협정에 따라 백신을 접종한 뉴질랜드인과 자격이 있는 여행객들은 MIQ 시설에 들어갈 필요 없이 자가 격리에 들어가 도착 시 검사를 받을 수 있게 됩니다.백신을 접종하지 않은 여행객은 여전히 MIQ 시설에 들어가야 합니다.[204]
2022년 2월 28일, 뉴질랜드 정부는 국경 재개에 더욱 박차를 가했습니다.
- 3월 2일 오후 11시 59분부터 백신을 맞은 여행객들은 더 이상 자가격리를 할 필요가 없습니다.
- 3월 4일 오후 11시 59분부터 뉴질랜드인 및 기타 자격이 있는 중요 근로자는 자가 격리 없이 입국할 수 있습니다.
- 3월 13일부터 워킹홀리데이 비자와 계절 근로자를 포함한 대부분의 임시 비자 보유자 범주는 더 이상 자가 격리가 필요하지 않습니다.[205]
2022년 5월 3일, 정부는 뉴질랜드에 거주하는 미접종 비자 소지자, 영주권자 및 호주 시민권자가 관리 격리를 받지 않고 입국할 수 있도록 여행 제한을 완화했습니다.[206]5월 중순, 정부는 뉴질랜드 국경의 재개를 가속화했습니다.
- 5월 16일부터 태평양 제도에서 온 방문객들은 방문 비자를 신청할 수 있습니다.
- 7월 4일부터 모든 취업비자가 입국할 수 있습니다.
- 7월 31일부터 모든 방문객 및 학생 비자 소지자와 크루즈선이 입국할 수 있습니다.[207][208]
국제적인 반응
2020년 9월 8일, 세계보건기구 테워드로스 아드하놈 사무총장은 캄보디아, 일본, 한국, 르완다, 세네갈, 스페인, 베트남과 함께 코로나19 팬데믹에 대한 뉴질랜드의 대응을 높이 평가했습니다.[209]
10월 28일, 후버 인스티튜트의 선임 연구원 빅터 데이비스 핸슨은 폭스 뉴스의 잉그라함 앵글에서 격리 관리를 받고 있는 사람들이 떠나는 조건으로 검사를 받아야 한다는 아던 총리의 요구를 비판했고, 진행자 로라 잉그라함은 MIQ 시설을 코로나바이러스 "격리 캠프"에 비유했습니다.[210]핸슨과 잉그레이엄은 더 스핀오프의 알렉스 브레이를 포함한 뉴질랜드 언론 논평가들로부터 그들의 발언을 뉴질랜드의 봉쇄 정책을 나치 독일에 비유한 전 영국 독립당 정치인 수잔 에반스의 발언과 비교했습니다.[211]뉴스허브의 제이미 엔소르는 잉그라함의 발언에 대해 맥락이 부족하다고 답하며 캠프는 사실 호화로운 호텔과 모텔이었다고 설명했습니다.[212]
법원의 판결
2020년 5월 4일, 고등법원 판사는 모든 해외 여행자에 대한 14일간의 격리 기간을 포함한 정부의 엄격한 봉쇄 명령을 기각하면서 영국에서 여행 온 남성이 사망하는 아버지를 방문하는 것을 허용했습니다.이에 대해 아던 총리는 데이비드 클라크 보건부 장관에게 건강상의 이유로 사망한 친척을 만나달라는 개인의 요청을 보건당국이 차단한 24건의 사례를 검토해달라고 요청했습니다.[213][214]정부의 검토 결과, 한 여성이 59세의 불치병에 걸린 어머니를 면회하기 위해 14일간 의무 격리를 면제받았습니다.[215]
8월 19일 웰링턴 고등법원은 3월 26일부터 4월 3일까지 9일간 경보 레벨 4 봉쇄가 시작될 때 집에 있으라는 정부의 메시지는 정당하지만 불법이며 1990년 뉴질랜드 권리장전법에 반한다고 판결했습니다.4월 3일 법 개정으로 봉쇄가 합법화되었습니다.고등법원의 판결은 변호사 앤드류 보어데일이 제기한 법적 도전에 대한 응답으로 나왔습니다.데이비드 파커 법무장관은 정부의 봉쇄조치를 옹호하면서 판결에 대한 항소를 배제하지 않았습니다.[216][217]
예방접종 노력
2020년 10월 12일 뉴질랜드 정부는 화이자 및 바이오와 협약을 체결하였습니다.엔테크, 화이자-바이오 코로나19 물량 150만대 인수엔텍 코로나19 백신.또한 정부는 코로나19 면역 프로그램을 지원하기 위해 6,630만 달러의 기금을 설립했습니다.[218]
2021년 2월 3일, 정부는 공식적으로 화이자-바이오를 승인했습니다.뉴질랜드에서 사용하기 위한 엔텍 코로나19 백신.이 백신은 16세 이상으로 제한될 예정입니다.[219]2월 20일 100명의 간호사들이 뉴질랜드에서 화이자-바이오를 받은 첫번째 사람들이 되었습니다.엔텍 코로나19 백신.의료 종사자, 필수 종사자, 그리고 가장 위험에 처한 사람들은 올해 2분기에 백신을 맞을 것입니다.일반인들은 하반기에 백신을 접종할 예정입니다.[220]
2021년 10월 16일("슈퍼 토요일"), 하루 종일 전국 백신 텔레톤("백신톤")이 개최되었으며, 유명인 게스트와 건강 전문가들이 출연하여 크로스 플랫폼을 통한 방송을 진행했습니다.[221]이 행사는 오후 3시까지 10만 회 이상의 백신이 배포되면서 기록적인 백신 접종 수치를 기록했습니다.[222]
백신 출시
| 주문 | 우선순위그룹 | 대상자수 (추정) | 현재 투여된 선량 2021년[224][225] 10월 26일 오후 11:59 | 상황 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1조 | ||||
| 1a | 국경/MIQ 인력 | 66,451 | 1회 투여량: 66,767 복용량 2: 65,205 | 진행중 |
| 1b | 가족 및 가정 연락처 | |||
| 2조 | ||||
| 2a | 돌봄 제공 중 코로나19에 노출될 수 있는 일선 의료인(비국경) | 661,183 | 1회 투여량: 661,231 2회 투여량: 621,689 | 진행중 |
| 2b | 코로나19에 취약계층 노출 가능성이 있는 일선 의료인 | |||
| 2b | 코로나19 전염이나 노출 위험이 높은 환경에서 생활하는 위험자 | |||
| 2b | 뉴질랜드 방위군[226] | |||
| 2b | 백신 접종 프로그램을[227] 직접 지원하는 고객 및 운송 및 물류 서비스를 제공하는 일선 직원 | |||
| 3조 | ||||
| 3a | 75세 이상인 사람들 | 1,700,000≈[228] | 1회 투여량 : 793,481 용량 2: 746,741 | 진행중 |
| 3b | 65세 이상 인구 | |||
| 3c | 근본적인 건강 상태나 장애를 가진 사람들, 또는 | |||
| 3c | 사용할 수 없습니다. 장애가 있는 사람을 돌보는 위치에 있거나, 임신 중이거나(임신 중이거나), 어른이 된 거라고 생각해요 | |||
| 4조 | ||||
| 4 | 60세이상자 | 2,136,481[229] | 용량 1: 2,136,491 용량 2: 1,585,195 | 진행중[230] |
| 55세이상자 | ||||
| 50세이상자 | ||||
| 40세이상자 | ||||
| 30세이상자 | ||||
| 12세 이상인[231] 자 | ||||
| 기타그룹 | ||||
| – | 뉴질랜드 올림픽 대표팀 | 220[232] | 용량 1:220 복용량 2:220 | 완료된 |
| – | 뉴질랜드 패럴림픽 선수단 | 29[233] | 용량 1:29 복용량 2:29 | 완료된 |
| – | 코카코[234] 작전의 특수부대 | 80[235] | 용량 1:80 복용량 2:80 | 완료된 |
조기 백신 접종을 위해 고려할 수 있는 해외여행 사유는 다음과 같습니다.[236]
- 뉴질랜드에서 본인 또는 부양가족이 이용할 수 없는 중요한 의료 서비스를 이용할 수 있습니다.
- 죽어가는 직계 가족을 방문하다
- 당신의 자녀와 같은 부양가족을 위한 중요한 보살핌과 보호를 제공합니다.
- 뉴질랜드의 자치권의 안전과 안전을 보호하기 위해
- 뉴질랜드의 해외 원조, 국제 재난 대응 또는 태평양 및 영역 국가들의 코로나19 팬데믹으로부터의 회복 지원에 대한 약속의 일환으로 정부가 승인한 인도주의적 노력에 대하여
- 뉴질랜드를 대표하기 위해 여행이 필요한 주요 국제 행사에 참가하는 것
- 국가적으로 중요한 무역 협상을 위해.
여론
이 섹션을 업데이트해야 합니다.(2022년 8월) |
정부대응승인
2020년 3월 1일부터 2일까지 실시된 Uting Research 여론조사에 따르면 응답자의 47%가 코로나19 사태에 대한 정부의 전반적인 대응에 만족하고 있으며, 34%는 불만족하고 19%는 불확실한 것으로 나타났습니다.[237]봉쇄 발표 전인 3월 21일부터 22일까지 실시된 후속 여론조사에서 응답자의 62%가 응답에 만족하는 것으로 나타났습니다.[238]그러나 37%는 뉴질랜드에서 대규모 발병이 예방될 수 있다고 확신하지 못했고, 26%는 확신하지 못했고 36%는 확신하지 못했습니다.[238]
2020년 5월 8일부터 16일까지 실시된 Newshub-Reid Research 여론조사에서 3~4월 전국 레벨 4 재택 명령을 이행하는 것이 "적절한 요청"인지 질문했으며 91.6%가 "그렇다", 6%가 "아니오", 2.5%가 "모름"[239]이라고 응답했습니다.
2020년 8월 9일, 호라이즌 리서치 여론조사에 따르면 코로나19 범유행을 관리하는 보건부와 정부의 능력에 대한 신뢰는 82%로 2020년 4월 91%보다 하락했습니다.이번 여론조사에서는 뉴질랜드 국민의 64%가 여전히 정부와 보건부를 '완전하게' 신뢰하는 것으로 나타나 지난 4월의 75%보다 감소했습니다.[240]
2021년 2월 16일부터 17일까지 스티키비크 포 더 스핀오프가 실시한 여론조사에 따르면 79%의 사람들이 정부의 대응을 "우수" 또는 "좋다"고 평가한 반면 12%의 사람들은 "나쁘다" 또는 "끔찍하다"고 평가했습니다.마찬가지로 2월 14일 오클랜드를 경보 3단계로 변경하기로 한 결정에 대해 79%가 찬성했고 12%는 반대했으며 나머지 국가를 2단계로 변경하는 것에 대해 67%가 찬성했으며 19%는 반대했습니다.[241]
2021년 8월 18일부터 22일까지 스티키비크가 실시한 여론조사에서 84%의 사람들이 8월 17일에 경보 레벨 4로 전환하기로 결정한 것을 지지하고 10%가 반대하는 것으로 나타났습니다.84% 중 72%가 이번 결정을 강하게 지지했습니다.전체적으로 79%의 사람들이 바이러스에 대한 정부의 대응을 지지하고 12%는 반대했습니다. 이 수치는 지난 2월 조사 때와 변함이 없습니다.[242]
8월 초 뉴질랜드 정부는 델타 변이 바이러스를 막기 위해 국가를 봉쇄했지만, 초기에는 정부의 대응을 지지했지만, 봉쇄가 계속되면서 여론이 크게 감소했고, 정부는 초기에 제거 전략을 포기하기를 거부했습니다.2021년 11월에 조사된 10월 여론조사에 따르면 델타 변이 바이러스를 막기 위해 진행 중인 봉쇄로 인해 정부에 대한 지지와 대응에 대한 신뢰가 일정 부분 하락한 것으로 나타났습니다.[243]
2022년 11월 17일부터 11월 28일까지 뉴질랜드 헤럴드는 여론조사 회사 다이너타에 의해 두 개의 여론조사를 의뢰했고, 두 개 모두 1,000명을 대상으로 설문조사를 실시했습니다.1차 조사에서는 응답자의 51%가 뉴질랜드의 코로나19 대응이 나라를 분열시켰다고 생각했고 37%는 코로나19 대응이 나라를 분열시켰다고 생각했습니다.두 번째 조사에서는 응답자의 57%가 뉴질랜드의 코로나19 대응이 "잘 판단되고 적절했다"고 생각하는 것으로 나타났습니다.반대로 25%는 반대했고 18%는 이 문제에 대해 결정하지 못했습니다.[244]
저신다 아던 사임
그녀가 팬데믹을 다루는 것에 대한 조기 승인에도 불구하고, 느린 백신 출시, 지속적인 코로나19 제한 및 뉴질랜드의 비 코로나19 관련 문제들은 특히 아던 총리직에 대한 극우 단체들의 강력한 반대를 만드는 데 도움이 되었습니다.그녀는 국제적으로 인기를 유지했지만, 2023년 1월 그녀의 사임은 저신다 아던이 2023년 10월 선거에서 승리하기 위한 정치적 지지를 받지 못한 것으로 보여 일부 환영 받는 반응을 얻었습니다.[245]
| 날짜. | 여론조사기관 | 표본크기 | 승인 | 불승인 | 확실하지 않음 | 이끌다 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022년11월17일-28일 | 뉴질랜드 헤럴드 다이나타 | 1,000 | 57 | 25 | 18 | 27 |
| 2021년10월29일-11월3일 | 탈보트 밀스 리서치 | 1,023 | 46 | 26 | 28 | 20 |
| 2021년 9월 28일~10월 5일 | 탈보트 밀스 리서치 | 1,200 | 60 | 16 | 24 | 44 |
| 2021년 8월 18일~22일 | 스핀오프-스티키비크 | 79 | 12 | 11 | 57 | |
| 2021년 2월 16~17일 | 스핀오프-스티키비크 | 601 | 79 | 12 | 10 | 57 |
| 2020년 7월 14일~19일 | 호라이즌 폴 | 1,762 | 82 | 17 | 1 | 65 |
| 2020년 5월 16일~20일 | 콜마 브런튼 | 1,003 | 92 | 7 | 2 | 85 |
| 2020년 4월 20~21일 | 콜마 브런튼 | 601 | 87 | 8 | 5 | 79 |
| 2020년 4월 3~5일 | 콜마 브런튼 | 601 | 84 | 9 | 6 | 75 |
| 2020년 3월 21~22일 | Uting Research/Stuffing | 3,133 | 62 | 22 | 16 | 40 |
| 2020년 3월 1~2일 | Uting Research/Stuffing | 1,900 | 47 | 37 | 16 | 10 |
| 2020년 2월 8일~12일 | 콜마 브런튼 | 1,004 | 62 | 25 | 12 | 37 |
백신 의무화
2021년 10월 Talbot Mills 여론조사에 따르면 직장 백신 의무화에 대한 지지는 보건 종사자 79%, 해외 여행객 76%, 교사 72%, 환대 종사자 71%, 슈퍼마켓 직원 및 국내 여행객 70%로 나타났습니다.[246]2021년 11월 1일 뉴스-콜마 브런튼 여론조사에 따르면 응답자의 74%가 현재 시행 중인 직장용 백신 의무화를 지지하고 있으며, 20%는 반대했습니다.[247]
미디어 인식
저신다 아던 총리의 리더십과 신속한 대처를 높이 평가한 국내외 언론은 코로나19 팬데믹에 대한 뉴질랜드 정부의 대응을 집중 보도했습니다.[248][249]워싱턴포스트의 피필드는 그녀가 인터뷰와 기자회견, 소셜미디어를 자주 이용하는 것을 "위기 소통의 달인 수업"이라고 묘사했습니다.[250]게다가 토니 블레어 영국 정부의 언론인이자 고문인 알라스테어 캠벨은 아던이 코로나바이러스 팬데믹으로 인한 인간적인 결과와 경제적인 결과를 모두 언급한 것에 대해 칭찬했습니다.[251]2020년 뉴질랜드 총선에 이어 옵저버즈 로이와 그레이엄 맥레이는 제6대 노동당 정부의 압승을 아던의 코로나19 팬데믹에 대한 "재치 있는 대처"와 과학 및 전문가에 대한 "절대적 신념"의 결과로 돌렸습니다.[252]
매일 오후 1시 언론 브리핑을 많이 보기 때문에, 많은 사람들이 반복적이거나 공격적인 질문 라인과 "잡혔다"는 비난과 함께, 기자들의 질문의 행동과 라인은 대중으로부터 정밀 조사를 받았습니다.기자 토마스 코글란은 "어디에서도 온 것 같지 않다"는 비판과 이러한 행동들은 "정말로 항상 그래왔던 것"이라며, 방법론이 기자회견의 많은 시청률로 인해 의문이 제기되었을 뿐이라고 답했습니다.[253]뉴스룸에 기고하는 TV 프로듀서 로빈 패터슨은 "일부 지역 언론인들의 공격적인 입장이 대중의 반발로 이어지고 있다"고 언급했고, 이는 "이미 고통스러워하는 대중들의 불안 수준을 높이고 깊은 불안감을 조성한다"그녀는 저널리즘 베스트 프랙티스에 대한 2019년 그리피스 대학의 연구가 언론인들에게 재앙적인 사건의 영향을 받는 사람들의 필요를 고려하거나 그렇지 않으면 득보다 실이 많을 위험이 있다고 권고했다고 언급했습니다.[254]
2021년 4월 말 블룸버그가 발표한 코로나19 회복력 순위에서 뉴질랜드는 79.6점을 받아 코로나19 팬데믹 기간 중 두 번째로 좋은 곳으로 꼽혔습니다.더딘 백신 접종률로 인해 한국은 0.1 포인트 하락했습니다.당시 코로나 회복력 순위에서 싱가포르는 79.7점으로 1위를 차지했습니다.[255][256]
제한수준
경보단계체계
뉴질랜드는 2020년 3월부터 2021년 12월까지 4단계 경보 수준 시스템으로 운영되었으며, 3단계와 4단계는 봉쇄의 형태입니다.레벨 1에서는 국내 제한이 없고, 레벨 2에서는 모임 제한이 있고, 레벨 3에서는 목적이 있는 여행만 허용되고 모임 제한이 엄격합니다. 레벨 4에서는 필수적인 여행만 허용되고 모임이 금지됩니다.
신호등체계
2021년 10월 15일, 아던은 경보 수준 시스템이 공식적으로 COVID-19 Protection Framework라고 불리는 "신호등" 시스템을 선호하여 곧 폐지될 것이라고 발표했습니다.이 3단계 시스템은 백신 접종률을 사용하여 필요한 제약 수준을 결정합니다.[257]그녀는 처음에 모든 DHB가 자격 인구의 90%가 백신을 완전히 접종하는 대기록에 도달하면 이 시스템이 전국적으로 채택될 것이며 3개의 DHB가 90%[258]를 달성하면 오클랜드 지역에서 발생할 것이라고 말했습니다.그러나 11월 22일, 아던은 90% 목표를 달성할 필요가 없을 것이라고 말했고, 뉴질랜드가 12월 3일에 이전 경보 수준 시스템을 대체하는 "신호등 시스템"에 진입할 것이라고 확인했습니다.오클랜드와 백신 접종률이 낮은 지역은 적색으로, 나머지 지역은 오렌지색으로 시작합니다.[259][260]
의료 시스템에 과부하가 걸릴 위험이 있는 경우에는 빨간색, 의료 시스템에 압력이 있는 경우에는 주황색, 입원 수준을 관리할 수 있는 경우에는 녹색의 세 가지 레벨이 있습니다.[261]
지지대거품

팬데믹 초기에 정부는 "지지 거품" 개념을 시작했습니다.[262]버블은 신체적으로 밀접한 접촉을 하는 사람들의 집단으로 정의됩니다.거품이 낀 사람들은 서로 사회적 거리두기를 실천할 필요가 없습니다.전체 거품은 하나의 가구로 간주됩니다.[263][264][265]
장기효과
2020년 4월 뉴질랜드 재무부는 뉴질랜드가 4주 동안 봉쇄 상태를 유지할 경우 13.5%의 실업률을 경험할 수 있으며, 봉쇄가 연장될 경우 17.5%에서 26% 사이의 범위를 가질 수 있다고 전망했습니다.[266]봉쇄 전 실업률은 4.2%[267]였습니다.그랜트 로버트슨 재무장관은 정부가 실업률을 10%[268] 이하로 유지할 것이라고 약속했습니다.
2020년 2분기 실업률은 0.2%포인트 하락한 4%를 기록했지만, 저활용률(노동시장 예비능력 척도)은 전분기 대비 1.6%포인트 상승한 12%로 사상 최대치를 기록했고, 근로시간은 10% 감소했습니다.[269]
2020년 1분기 국내총생산 1.[270]6% 감소뉴질랜드 통계청이 2020년 2분기 국내총생산(GDP)이 12.2% 감소했다고 발표한 후 9월 공식적으로 경기침체에 진입했습니다.[271]2분기 위축은 숙박·식음료 서비스가 47.4%, 운수·우편·창고업이 38.7%, 건설업이 25.8% 위축된 것이 주도했습니다.[272]2020년 3분기 GDP는 14.0% 반등했습니다.[273]
2021년 11월 3일, 뉴질랜드 통계청은 코로나19의 영향에도 불구하고 실업률이 3.4%로 떨어졌으며, 이는 해당 기관이 보고를 시작한 이래 가장 낮은 수치라고 발표했습니다.[274]지지대거품
팬데믹 이후
뉴질랜드는 부분적으로 코로나19 팬데믹의 여파로 인해 2023년 중반에 침체기에 접어들었습니다.[275]팬데믹 대처에 대한 왕립위원회는 현재 진행 중이며 2024년 중반에 보고될 것으로 예상됩니다.[276]
테스트
요구 사항들
2020년 3월 초, 코로나19 검사가 영향을 받은 국가에서 돌아온 증상을 가진 사람들이나 확진자와 접촉한 사람들에게만 시행되는 것에 대한 우려가 있었습니다.[277]증상이 있지만 이 범주에 맞지 않는 일부 사람들은 검사를 받지 않았습니다.[278]4월에 뉴질랜드 미생물학 네트워크는 노인 돌봄 제공자로 또는 노인 돌봄 제공자 간의 이전을 검사하지 말 것을 권고하였는데,[279] 이는 돌봄 시설에서 발생했음에도 불구하고 유지한 입장이며, ETU 연합과 노인 돌봄 협회의 선별 검사를 요구하고 있습니다.[280]
코로나19 검사를 받을 수 있는 경우의 정의는 "기침, 인후통, 호흡곤란, 코리자, 발열 또는 발열 없이 무통증 중 하나 이상을 동반한 급성 호흡기 감염"입니다.[281]
3월 14일부터 4월 3일까지 시험에 대한 이전의 사례 정의는 다음 기준 중 적어도 하나를 충족하는 것이었습니다.[282]
- 증상(fever 또는 기침, 호흡곤란 또는 인후통) 및 여행력
- 증상(fever 또는 기침, 호흡곤란 또는 인후통) 및 용의자와의 밀접하거나 가벼운 접촉, 가능성이 있거나 확인된 사례
- 폐렴에 걸린 의료 종사자들
- 중증 호흡기 질환으로 중환자실에서 치료를 받는 사람들
이 사례 정의에 맞지 않는 경우에는 의사가 환자를 검사할지 여부를 판단하는 것이 좋습니다.[283]
8월 18일, 뉴스허브는 한 고위 검역 관리가 검역 직원들이 정기 검사 "정권"을 여러 번 요청했지만 그들의 우려는 무시되었다고 밝혔다고 보도했습니다.아던 총리가 처음에는 일부 근로자들이 꺼린다고 주장했지만, 크리스 힙킨스 보건장관은 브리핑에서 국경 직원들의 테스트가 불완전하다는 것을 알고 있었다는 것을 인정하면서 "테스트를 거절당하지 말았어야 했다"고 말했습니다.야당 지도자 주디스 콜린스는 정부의 이 문제 처리를 비판했습니다.[284]
2021년 7월 9일, 크리스 힙킨스 COVID-19 대응부 장관은 출발 전 검사의 절반이 "용량 제약"으로 인해 확인되었다고 인정했습니다.최근 뉴사우스웨일스주를 방문한 사람을 포함해 20명 이상이 호주에서 출발 전 테스트를 받지 않고 입국한 것으로 알려졌습니다.[285]
2021년 8월 26일, 지역 보건 제공업체 와나우 와이파레이라는 오클랜드와 웰링턴에 있는 250명의 직원들을 대상으로 타액 검사를 시작했습니다.이 단체의 최고경영자인 존 타미히어 씨도 의료 제공자들이 사용하고 있는 더 일반적인 코 면봉 검사에 대한 대안으로 코 면봉 검사를 대중에게 확대할 계획이 있다고 확인했습니다.[286]
2021년 9월 초, 애슐리 블룸필드 보건국장은 정부가 오클랜드 레벨 4 국경 교차로에서 타액 검사를 확대할 계획이라고 확인했습니다.[287]이 발표는 예일 대학교의 연구 과학자이자 타액 검사 옹호자인 앤 와일리가 타액 검사 제공업체인 아시아 퍼시픽 헬스케어 그룹의 검사 방법에 대해 비판한 이후에 나온 것입니다.[288][289]
2022년 2월 28일까지 보건부는 뉴질랜드가 1,400만 개의 신속항원검사(RATS) 키트를 받았다고 확인했습니다.이 키트는 뉴질랜드 전역의 지역사회 테스트 센터, 일반 의료인 및 약국으로 배송됩니다.보건부 차관 아이샤 베럴은 정부가 향후 6개월간 1억 8천만 개의 RATS 키트를 주문했다고 확인하기도 했습니다.[290]
결과.

2021년[update] 11월 21일 기준: 관리 격리 시설에서 401,966건의 검사를 포함하여 총 4,664,080건의 검사가 완료되었으며 양성률은 0.21%입니다.[1]테스트 비율이 가장 높은 민족은 태평양으로 100명당 170.2개의 테스트 비율을 보였으며, 아시아인 97.1개, 마오리인 83.1개, 마지막으로 유럽/MELAA/기타인 80.4개로 [e]총 4,664,080명 [292]중 뉴질랜드 인구(5,126,300명)의 91%에 해당하는 테스트 비율이 가장 높았습니다.[293]
2020년 4월 16일부터, 바이러스의 지역사회 전파가 여전히 존재하는지에 대한 정보를 제공하기 위해 전국의 일부 슈퍼마켓에서 무작위 자발적인 지역사회 검사가 실시되었습니다.[294][295]이 테스트는 4월 20일까지 1000명 중에서 양성 결과가 나오지 않았습니다.[296]
2021년 3월 19일, 뉴스허브는 과학자들이 크라이스트처치에 있는 관리 격리 시설의 호텔 복도 입구에 있는 환기되지 않은 공간에 격리된 상태로 머문 후 양성 반응을 보인 두 명의 코로나19 환자를 추적했다고 보도했습니다.[297]
통계
이 섹션을 업데이트해야 합니다.최근 또는 할 수 본 기사 . (2022년 10월) |
경우들
뉴질랜드는 팬데믹 기간 동안 2,274,370명(2,217,047명 확진, 57,323명 발생 가능)의 코로나19 확진자가 발생했습니다(2023년 4월 3일까지).[1]전국 인구 추정치 4,966[298],000명을 기준으로 할 때, 이 수치는 인구 백만 명당 422,409.6명의 확진자를 제공합니다(인구 백만 명당 430,679.4명의 확진자와 발생 가능성이 있음).
2023년[update] 4월 3일 기준 지역 보건 위원회(DHB)별 분류:[1]
| DHB | 경우들 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 총 | 데스 | 리커버리 | 활동적인 | |
| 오클랜드 | 216,385 | 178 | 215,242 | 965 |
| 만 오브 플렌티 | 101,507 | 130 | 100,907 | 470 |
| 캔터베리 | 297,169 | 379 | 294,543 | 2,247 |
| 캐피털 앤 코스트 | 159,401 | 121 | 158,403 | 877 |
| 마누카우 주 | 259,929 | 208 | 258,869 | 1,032 |
| 호크스베이 | 77,734 | 126 | 76,140 | 280 |
| 허트 계곡 | 77,140 | 77 | 77,642 | 386 |
| 호수 | 45,616 | 77 | 45,318 | 221 |
| 미드센트럴 | 83,433 | 148 | 82,859 | 426 |
| 넬슨 말버러 | 67,974 | 93 | 67,427 | 454 |
| 노스랜드 | 70,066 | 91 | 69,665 | 310 |
| 사우스캔터베리 | 29,420 | 31 | 29,181 | 208 |
| 남부 | 165,568 | 220 | 164,133 | 1,215 |
| 타이라휘티 | 23,162 | 30 | 23,033 | 99 |
| 타라나키 | 56,820 | 104 | 56,341 | 375 |
| 알 수 없는 | 1,804 | 3 | 1,766 | 35 |
| 와이카토 | 179,815 | 264 | 178,664 | 887 |
| 와이라라파 | 21,950 | 49 | 21,782 | 119 |
| 와이테마타 | 268,274 | 279 | 266,731 | 1,264 |
| 웨스트코스트 | 13,794 | 15 | 13,609 | 167 |
| 황가누이 | 29,746 | 58 | 29,551 | 137 |
| 앳 더 보더 | 27,295 | 6 | 27,289 | 0 |
| 뉴질랜드 | 2,274,370 | 2,687 | 2,259,509 | 12,174 |
채텀 제도와[300] 뉴질랜드의 관련 주(쿡 제도 536명,[301] 니우에[302] 1명)에서 사례가 보고되었습니다.
토켈라우의[303] 종속 지역에서는 아직 보고된 사례가 없으며, 토켈라우는 이 질병으로 인한 감염이 확인되지 않은 마지막 국가 또는 종속 국가입니다.[304]
봉쇄 기간 동안 뉴질랜드에서는 주간 전체 사망자가 예년에 비해 감소했습니다.[305]그 감소는 교통사고, 대기오염, 업무상 부상, 호흡기 감염, 선택 수술로 인한 사망자 감소와 관련이 있다고 생각됩니다.[305]
클러스터


팬데믹의 제거 단계 동안, 발병은 추적되고 다양한 클러스터로 통합되었으며, 대부분은 완전히 억제되었습니다.
다음 클러스터가 닫혔습니다.모든 환자가 격리를 완료한 날로부터 2번(즉, 28일) 동안 새로운 환자가 발생하지 않은 경우 클러스터는 닫힌 것으로 간주됩니다.[306]
- 2021년 8월 커뮤니티, 오클랜드 – 10,006[306]
- 오클랜드 8월 클러스터,[307] 2020년[308] 11월 3일 ~ 2020년 11월 179년
- 웨딩, 블러프 – 98[306]
- 오클랜드 매리스트 칼리지 96[306][310][311]
- 성 패트릭의 날 모임, 리덥바, 마타마타 – 77[306]
- 로즈우드 휴게소, 크라이스트처치 – 56[306]
- CHT 세인트 마가레츠 휴게소, 오클랜드 – 51[306]
- 전용 기능, 오클랜드 – 40[306]
- 월드 헤리퍼드 컨퍼런스, 퀸스타운 – 39[306]
- 인터내셔널 매리너스, 크라이스트처치 – 33[306]
- 커뮤니티 그룹, 오클랜드 – 30[306]
- 루비 프린세스 유람선, 호크스 베이 – 24[306]
- George Manning Life care rest home, Christchurch – 19[306]
- 바이킹 베이 베셀, 웰링턴 – 18[306]
- 미국, 웰링턴 단체 여행 – 16[306]
- 미국, 오클랜드 – 16 단체[306] 여행
- 리텔턴 매리너 – 16[306]
- 아태어시즈의 집, 해밀턴 – 15[306]
- 오클랜드 2월 클러스터 – 15[306]
- Mattina Vessel, Invercargill – 15[306]
- 커뮤니티 그룹, 크라이스트처치 – 14[306]
- 웨딩, 웰링턴 – 13[306]
- 휴식처, 오클랜드 – 13[306]
- 리오 데 라 플라타 선박, 타우랑가 – 11[306]
캔터베리 DHB 사망 1차 유행(2022년 이전)의 12건은 모두 로즈우드 휴게소 클러스터 내 사례였습니다.이 클러스터는 2022년 이전의 코로나19로 인한 국가 전체 사망자 수의 거의 4분의 1을 차지했습니다.
코로나19의 진행 상황
뉴질랜드의 코로나19 환자 추이, 2020년 3월~2021년 11월:[312]
2021년[update] 11월 30일 기준:
기술적인 문제로 인해 그래프를 일시적으로 사용할 수 없습니다. |
사례들 복구됨 입원중 데스 활성 사례[f]
반로그 플롯 형태의 2020년 3~6월 동일한 그래프 부분:
2020년[update] 6월 30일 기준:
기술적인 문제로 인해 그래프를 일시적으로 사용할 수 없습니다. |
사례들 복구됨 입원중 데스 활성 사례[f]
신규 사례 및 사망자 수
뉴질랜드의 신종 코로나바이러스 감염증(확진 및 발생 가능성) 환자 및 사망자:[312]
일별 신규건수
2020
기술적인 문제로 인해 그래프를 일시적으로 사용할 수 없습니다. |
2021
기술적인 문제로 인해 그래프를 일시적으로 사용할 수 없습니다. |
2022
2022년[update] 7월 24일 기준:
기술적인 문제로 인해 그래프를 일시적으로 사용할 수 없습니다. |
2022년[update] 7월 24일 기준, 세미로그 형태:
기술적인 문제로 인해 그래프를 일시적으로 사용할 수 없습니다. |
일일 신규 사망자 수
기술적인 문제로 인해 그래프를 일시적으로 사용할 수 없습니다. |
참고 항목
각주
- ^ a b c MIQ(Managed Isolation & Quarantine) 시설에 있는 경우를 제외합니다.
- ^ 가능한 사례는 양성 실험실 결과가 없는 사례이지만, 노출 이력과 임상 증상에 따라 확진 사례처럼 취급됩니다.
- ^ a b c 이 날짜에 복구된 사례가 크게 증가한 것은 사례 정의의 변화 때문입니다.2021년 12월 16일부터 21일이 경과하면 활동 중인 환자가 의료인의 허가를 받아야 하는 상황에서 자동으로 회복되는 것입니다.[20]2022년 3월 4일에는 이 기간이 10일로 단축되었고, 3월 18일부터는 7일로 단축되었습니다.
- ^ a b 이 날짜에 보고된 사망자 수의 변화는 코로나 사망자의 재정의 때문입니다.처음에는 코로나19가 확인되거나 가능성이 높은 사망 원인일 때 코로나 사망자가 보고되었습니다.2022년 3월 10일부터 코로나19 양성 판정을 받은 후 28일 이내에 사망하거나 28일 이후 코로나19와 명백한 연관성이 있는 경우에 코로나19 사망자가 자동으로 보고되었습니다.[21]2022년 7월 26일부터 코로나19가 근본적인 원인 또는 원인으로 간주될 때 코로나19 사망자가 보고됩니다. 이전에 보고된 사망자 중 새로운 정의에 부합하지 않는 사람은 전체 코로나 사망자 수에서 제거되었습니다.[22]
- ^ 테스트 데이터는 민족성 우선순위에 따라 보고됩니다.한 사람이 여러 민족을 가진 경우 다음과 같은 우선 순위를 가진 단일 민족으로만 보고됩니다.마오리, 태평양, 아시아, 중동/중남미/아프리카, 기타, 유럽.이것은 여러 민족을 가진 사람이 그들이 동일시하는 모든 민족 집단 아래에서 보고되는 완전한 반응 민족과는 대조적입니다.[291]
- ^ a b 활동 중인 환자 수는 전체 확진자 수와 발생 가능성이 있는 환자 수에서 회복자 수와 사망자 수를 뺀 수치입니다.
- ^ 2022년 3월 10일, 코로나19 관련 사망자의 정의가 변경되어 최고점을 기록했습니다.
참고문헌
- ^ a b c d e f g h i "COVID-19 – current cases". Ministry of Health. 6 October 2023. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020.
- ^ "New Zealand: WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard With Vaccination Data". covid19.who.int. Retrieved 23 October 2021.
- ^ "Quarantine-free travel country". Immigration New Zealand. Retrieved 28 August 2021.
- ^ a b Ainge Roy, Eleanor (23 March 2020). "'Kiwis – go home': New Zealand to go into month-long lockdown to fight coronavirus". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 23 March 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
- ^ a b "Coronavirus live updates: COVID-19 in community, Auckland going to level 3". Newshub. Archived from the original on 12 August 2020. Retrieved 11 August 2020.
- ^ a b "Covid-19 coronavirus: Auckland in alert level 3 lockdown for a week – Jacinda Ardern". The New Zealand Herald. 27 February 2021. Archived from the original on 27 February 2021.
- ^ a b c "New Zealand to enter COVID-19 alert level 4 from midnight Tuesday". Newshub. Retrieved 17 August 2021.
- ^ a b Corlett, Eva (4 October 2021). "New Zealand Covid elimination strategy to be phased out, Ardern says". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 4 October 2021. Retrieved 4 October 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19 Protection Framework". Unite against COVID-19. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ a b "Covid-19: Border reopening for New Zealanders confirmed for end of February - what you need to know". Radio New Zealand. 3 February 2022. Archived from the original on 3 February 2022. Retrieved 3 February 2022.
- ^ a b Whyte, Anna (23 March 2022). "PM reveals changes to mandates, vaccines passes and restrictions". 1 News. Retrieved 23 March 2022.
- ^ a b "New Zealand border reopening fully from end of July". Radio New Zealand. 11 May 2022. Archived from the original on 11 May 2022. Retrieved 12 May 2022.
- ^ a b "Covid-19 traffic light system scrapped: All you need to know". The New Zealand Herald. 12 September 2022. Retrieved 12 September 2022.
- ^ Ensor, Jamie (14 August 2023). "Health Minister Dr Ayesha Verrall announces end of remaining coronavirus restrictions". Newshub. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ "Novel Coronavirus Information Center". Elsevier Connect. Archived from the original on 30 January 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ Reynolds, Matt (4 March 2020). "What is coronavirus and how close is it to becoming a pandemic?". Wired UK. ISSN 1357-0978. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ a b "Crunching the numbers for coronavirus". Imperial News. 13 March 2020. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ "High consequence infectious diseases (HCID); Guidance and information about high consequence infectious diseases and their management in England". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 16 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint : bot : 원본 URL 상태 알 수 없음 (링크) - ^ "World Federation Of Societies of Anaesthesiologists – Coronavirus". wfsahq.org. Archived from the original on 8 April 2020. Retrieved 15 March 2020.
- ^ Forrester, Georgia (15 December 2021). "The 1pm Covid-19 updates are changing. Here is what you need to know". Stuff.co.nz. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ "90% of Wairarapa Māori fully vaccinated; 21,015 community cases; 773 in hospital; 16 in ICU; 1 death". Ministry of Health. 10 March 2022. Retrieved 1 August 2022.
- ^ Morton, Jamie (26 July 2022). "Covid-19: What we've just learned about virus deaths". New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 26 July 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19: News and media updates". Ministry of Health. 6 October 2023.
- ^ a b "COVID-19: Current cases". Ministry of Health. 6 October 2023.
- ^ Cooke, Henry; Chumko, Andre. "Coronavirus: First case of virus in New Zealand". Stuff. Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- ^ "New Zealand confirms case of Covid-19 coronavirus". Radio New Zealand. Archived from the original on 28 February 2020. Retrieved 28 February 2020.
- ^ Hunt, Tom; Wiltshire, Laura; Williams, Katarina (4 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Second confirmed NZ case in Auckland, patient took multiple Air NZ flights". Dominion Post. Archived from the original on 4 March 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ "Watch live: 74 people now recovered from Covid-19 in NZ – Health Ministry". Radio New Zealand. 31 March 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ Satherley, Dan; Quinlivan, Mark (29 March 2020). "Newshub: Coronavirus: First New Zealand death recorded". Newshub. Archived from the original on 29 March 2020. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ^ Manch, Thomas; Devlin, Collette (29 March 2020). "Coronavirus: New Zealand has 514 cases – one person dead on West Coast". Stuff. Archived from the original on 29 March 2020. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ^ "HISO 10001:2017 Ethnicity Data Protocols" (PDF). Ministry of Health. September 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 February 2020. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ^ "COVID-19 – current cases". Ministry of Health NZ. Ministry of Health. 31 July 2020. Archived from the original on 31 July 2020. Retrieved 31 July 2020.
- ^ "Four Covid-19 community cases; Auckland to move to level 3". Newstalk ZB. 11 August 2020. Archived from the original on 11 August 2020. Retrieved 11 August 2020.
- ^ "Jacinda Ardern hails Pasifika community's efforts in Covid crisis – 'They have saved other people's lives'". 1 News. 22 August 2020. Archived from the original on 22 August 2020. Retrieved 22 August 2020.
- ^ "Former Cook Islands PM dies in Auckland after contracting Covid". Radio New Zealand. 5 September 2020. Archived from the original on 15 September 2020. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ Graham-McLay, Charlotte (21 October 2020). "New Zealand records 25 Covid cases amid arrival of foreign fishing crews". The Guardian Australia edition. Wellington. Retrieved 24 October 2020.
- ^ Wade, Amelia (12 November 2020). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Two new community cases, say Chris Hipkins and Ashley Bloomfield". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- ^ "Covid-19: Air New Zealand crew member tests positive after returning from the US". Stuff. 12 December 2020. Archived from the original on 12 December 2020. Retrieved 12 December 2020.
- ^ "COVID-19: Current cases". Ministry of Health. 31 December 2020. Archived from the original on 31 December 2020. Retrieved 31 December 2020.
- ^ Wiles, Siouxsie (22 October 2020). "Siouxsie Wiles & Toby Morris: Covid-19 and the Swiss cheese system". The Spinoff. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- ^ "New Zealand's new COVID case is the South African variant". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ Coleman, Justine (24 January 2021). "New Zealand identifies first community spread of COVID-19 since November". The Hill. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 25 January 2021.
- ^ "Covid 19 coronavirus: Three 'new and active' Covid cases in South Auckland". The New Zealand Herald. 14 February 2021. Archived from the original on 14 February 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19: Current cases". Ministry of Health. 30 July 2021. Archived from the original on 30 July 2021. Retrieved 30 July 2021.
- ^ "Health officials are investigating 1 new case of COVID-19 in the community". Ministry of Health. Archived from the original on 17 August 2021.
- ^ "Covid-19 community case: Nationwide level 4 lockdown". Radio New Zealand. 17 August 2021. Archived from the original on 17 August 2021. Retrieved 17 August 2021.
- ^ "Covid 19 coronavirus Delta outbreak: Covid-19 cases confirmed at Northcote and Lynfield colleges; 11 new cases, 2 in hospital". The New Zealand Herald. 19 August 2021. Retrieved 19 August 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19: Current cases". Ministry of Health. 31 December 2021. Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 31 December 2021.
- ^ Ensor, Blair; Basagre, Bernadette (29 December 2021). "Covid-19: Omicron border case active in the community is DJ Dimension". Stuff. Archived from the original on 29 December 2021. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19: Current cases". Ministry of Health. 31 January 2022. Archived from the original on 31 January 2022. Retrieved 31 January 2022.
- ^ "COVID-19: Current cases". Ministry of Health. 28 February 2022. Archived from the original on 28 February 2022. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ "Covid-19 total: Record rise in cases due to backlog in processing - modeller". Radio New Zealand. 26 February 2022. Archived from the original on 27 February 2022. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ "Novel coronovirus update". Ministry of Health, New Zealand. 27 January 2020. Archived from the original on 28 January 2020. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- ^ "NZ to close doors on foreign travellers from China". Radio New Zealand. 2 February 2020. Archived from the original on 2 February 2020. Retrieved 9 February 2020.
- ^ "Air NZ mercy flight from coronavirus-stricken Wuhan, China arrives in Auckland". TVNZ. 5 February 2020. Archived from the original on 4 March 2020. Retrieved 4 March 2020.
- ^ Walls, Jason. "Coronavirus: NZ shutting borders to everyone except citizens, residents – PM Jacinda Ardern". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ Cooke, Henry (19 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Government shutting borders to all but citizens and residents". Stuff. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ Cheng, Derek (20 March 2020). "Coronavirus: PM Jacinda Ardern outlines NZ's new alert system, over-70s should stay at home". The New Zealand Herald. ISSN 1170-0777. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ Sachdeva, Sam (20 April 2020). "Ardern: NZ to leave lockdown in a week". Newsroom. Archived from the original on 20 April 2020. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- ^ Cooke, Henry (11 May 2020). "Coronavirus: New Zealand will start to move to level 2 on Thursday". Stuff. Archived from the original on 11 May 2020. Retrieved 11 May 2020.
- ^ a b Cheng, Derek (25 May 2020). "Live: Mass gatherings to increase to 100 max from noon Friday". Newstalk ZB. Archived from the original on 25 May 2020. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- ^ a b "Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern reveals move to level 1 from midnight". Radio New Zealand. 8 June 2020. Archived from the original on 8 June 2020. Retrieved 8 June 2020.
- ^ Wade, Amelia (14 May 2020). "Covid-19 coronavirus: Controversial bill passed to enforce alert level 2 powers". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 13 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ a b "Covid-19 live updates, May 13: Alert level two law passes; changes to rules for funerals and tangi". The Spinoff. 13 May 2020. Archived from the original on 14 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ Andelane, Lana (30 August 2020). "COVID-19: Auckland to move to 'level 2.5' on Sunday – what you need to know". Newshub. Archived from the original on 30 August 2020. Retrieved 30 August 2020.
- ^ Wade, Amelia (21 September 2020). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Auckland moving to alert level 2 and NZ to level 1 – Jacinda Ardern". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 21 September 2020. Retrieved 21 September 2020.
- ^ Franks, Josephine (5 October 2020). "Covid-19: Auckland to move to alert level 1 from midnight Wednesday". Stuff. Archived from the original on 5 October 2020. Retrieved 5 October 2020.
- ^ "Isolation hotel vouchers now required to enter NZ, with pre-Christmas period completely booked". 1 News. 3 November 2020. Archived from the original on 2 November 2020. Retrieved 2 November 2020.
- ^ "Covid 19 coronavirus: Cook Islands, New Zealand travel bubble without quarantine from early next year". The New Zealand Herald. 12 December 2020. Archived from the original on 11 December 2020. Retrieved 11 December 2020.
- ^ Taylor, Phil; Remeikis, Amy (14 December 2020). "Jacinda Ardern: New Zealand and Australia to launch travel bubble in early 2021". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 14 December 2020. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- ^ Walls, Jason (14 February 2021). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Auckland to level 3 tonight; rest of country at level 2". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 14 February 2021. Retrieved 14 February 2021.
- ^ Wade, Amelia (17 February 2021). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Auckland to level 2, rest of NZ to level 1 – despite another new Covid case". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 17 February 2021. Retrieved 17 February 2021.
- ^ Wade, Amelia (22 February 2021). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Auckland back to alert level 1 from midnight – face masks on public transport still mandatory throughout country". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 22 February 2021.
- ^ "Covid-19 briefing: Waikato joins Auckland in alert level 3 from tonight". Radio New Zealand. 3 October 2021. Archived from the original on 3 October 2021. Retrieved 3 October 2021.
- ^ Cooke, Henry (22 November 2021). "Covid-19: New Zealand to enter traffic-light system on December 3, opening up Auckland". Stuff. Archived from the original on 22 November 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ^ "Official Covid-19 vaccine certificate to go live". Radio New Zealand. 16 November 2021. Archived from the original on 17 November 2021. Retrieved 17 November 2021.
- ^ "Mandate legislation pushed through Parliament amid fierce opposition". Radio New Zealand. 24 November 2021. Archived from the original on 24 November 2021. Retrieved 24 November 2021.
- ^ "COVID-29: Omicron outbreak would push New Zealand back to red traffic light setting, says Jacinda Ardern". Radio New Zealand. 17 January 2022. Archived from the original on 17 January 2022. Retrieved 18 January 2022.
- ^ "Government announces three phase public health response to Omicron". Unite against COVID-19. Ministry of Health. 26 January 2022. Archived from the original on 10 February 2022. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ Daalder, Marc (18 October 2022). "Lockdowns scrapped, but seven-day isolation to stay as Ardern seeks balanced response". Newsroom. Archived from the original on 18 October 2022. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- ^ "Covid-19 response: Vaccine mandates, MIQ and lockdowns set to be scrapped". Radio New Zealand. 18 October 2022. Archived from the original on 18 October 2022. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- ^ Palmer, Russell (18 October 2022). "Government signals Covid-19 inquiry in the works". Radio New Zealand. Archived from the original on 18 October 2022. Retrieved 19 October 2022.
- ^ Daalder, Marc (17 August 2020). "How genomics will help us track Covid-19". Newsroom. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ^ "PRIME MINISTER'S10.30 AM PRESS CONFERENCE: WEDNESDAY, 12 AUGUST 2020" (PDF). beehive.govt.nz. 12 August 2020. p. 2.
- ^ Welch, David (22 August 2020). "How rapid genome sequencing is changing the way we respond to Covid-19". The Spinoff. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ^ Nine to Noon (13 August 2020). "How genome testing could help reveal the source of community Covid". RNZ. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ^ Checkpoint (25 November 2020). "How Covid-19 genome sequencing maps the spread of the virus". RNZ. Retrieved 5 April 2021.
- ^ Geoghegan, Jemma L.; Ren, Xiaoyun; et al. (11 December 2020). "Genomic epidemiology reveals transmission patterns and dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in Aotearoa New Zealand". Nature Communications. 11 (6351): 6351. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.6351G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20235-8. PMC 7733492. PMID 33311501.
- ^ "Auckland Council to close libraries, pools, recreation centres and major venues". Auckland Council. 20 March 2020. Archived from the original on 20 March 2020. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ^ Andelane, Lana (20 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Auckland Council to close pools, recreation centres, major venues". Newshub. Archived from the original on 20 March 2020. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ^ "DCC closes libraries, pools". Otago Daily Times. 21 March 2020. Archived from the original on 21 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Christchurch City Council Closing All Community Facilities" (Press release). 21 March 2020. Archived from the original on 21 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Wellington, Christchurch and Dunedin councils close community facilities". 1 News. 21 March 2020. Archived from the original on 21 March 2020. Retrieved 21 March 2020.
- ^ "Coronavirus: Councils across New Zealand close facilities indefinitely". Stuff. 21 March 2020. Archived from the original on 21 March 2020. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
- ^ "Covid 19 coronavirus lockdown: Your questions answered". The New Zealand Herald. 24 March 2020. Archived from the original on 24 March 2020. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
- ^ Titchall, Alan (14 April 2020). "Councils chase project funding". LG: NZ Local Government Magazine. Archived from the original on 15 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- ^ "Coronavirus: Otago mayors donating 10 per cent of salaries". Stuff. 15 April 2020. Archived from the original on 15 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- ^ Kronast, Hannah (10 July 2020). "Auckland Council to cut over 500 permanent jobs". Newshub. Archived from the original on 10 July 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- ^ a b "Auckland councillor Efeso Collins calls for amnesty for people with expired visas". Radio New Zealand. 27 August 2020. Archived from the original on 27 August 2020. Retrieved 27 August 2020.
- ^ Wade, Amelia (12 November 2020). "Covid-19 coronavirus: Auckland CBD staff should work from home if they can, new case's movements revealed". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- ^ Block, George; Xia, Lucy (12 November 2020). "Auckland mystery Covid-19 case: Owner of store at centre of controversy speaks". Stuff. Archived from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- ^ "Covid-19 coronavirus: Infected student says health officials made mistakes with her movements". The New Zealand Herald. 13 November 2020. Archived from the original on 13 November 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- ^ Block, George (13 November 2020). "Covid-19: Shop employee diagnosed with coronavirus says she never called in sick". Stuff. Archived from the original on 13 November 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- ^ "Northern part of Northland to move to alert level 3 – Hipkins". Radio New Zealand. 2 November 2021. Archived from the original on 2 November 2021. Retrieved 2 November 2021.
- ^ Russell, Emma (19 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Urgent calls for retired doctors and nurses to step up". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 24 March 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- ^ McKenzie-McLean, Jo (19 March 2020). "Coronavirus: 'Call to Arms' for retired doctors and nurses to help hospitals fight infection". Stuff. Archived from the original on 21 March 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- ^ "Covid 19 coronavirus: St John facing staff cuts, aims to save $30 million". The New Zealand Herald. 10 June 2020. Archived from the original on 10 June 2020. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ^ Macfarlane, Andrew (10 June 2020). "Jobs will be lost as St John Ambulance looks to slash $30m due to Covid-19, CEO says in memo". 1 News. Archived from the original on 11 June 2020. Retrieved 11 June 2020.
- ^ New Zealand Nurses Organisation (20 August 2021). "NZNO concerned for nurse wellbeing in renewed COVID climate". Scoop. Archived from the original on 20 August 2021. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- ^ Tan, Quiyi (11 September 2021). "Nurses take Auckland DHB to task over visitor policy". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 12 September 2021. Retrieved 14 September 2021.
- ^ Kerr-Lazenby, Mina (11 October 2021). "Covid-19: Pharmac signs deal for experimental treatment pill molnupiravir". Stuff. Archived from the original on 11 October 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "Pharmac secures the antiviral baricitinib, another medicine for treating Covid-19". RNZ. 5 November 2021. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
- ^ "Pharmac signs deal for new drug to fight Covid-19". RNZ. 31 October 2021. Retrieved 5 November 2021.
- ^ "Covid: New Zealand unveils phased border reopening plan". BBC News. 3 February 2022. p. 1. Retrieved 3 February 2022.
- ^ Bhamidipati, Soumya (13 October 2021). "SIQ funding in early stages". Wairarapa Times-Age. Archived from the original on 12 October 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ Harvey, Helen (22 October 2021). "Taranaki isolation facility ready if needed, manager appointed". Stuff. Archived from the original on 11 November 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19 isolation at home". Auckland District Health Board. 23 November 2021. Archived from the original on 23 December 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ Houlahan, Mike (8 December 2021). "SIQ options for Queenstown discussed". Otago Daily Times. Archived from the original on 10 December 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ MacLean, Hamish (15 December 2021). "Whanganui DHB to have SIQ facilities in four regional locations". Whanganui Chronicle. The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 15 December 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ MacLean, Hamish (22 December 2021). "Former holiday park confirmed as isolation centre". Otago Daily Times. Archived from the original on 22 December 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ^ "Health staff vote to strike twice next month after pay offer rejected". Radio New Zealand. 17 February 2022. Archived from the original on 19 February 2022. Retrieved 24 February 2022.
- ^ "Burnt out laboratory staff working in poor conditions, institute says". Radio New Zealand. 20 February 2022. Archived from the original on 19 February 2022. Retrieved 24 February 2022.
- ^ Thomas, Rachel (16 May 2022). "Striking allied health workers say 'we need to be valued'". Stuff. Archived from the original on 24 May 2022. Retrieved 3 June 2022.
- ^ Ryder, Wyatt (3 June 2022). "Hospital closed to visitors". Otago Daily Times. Retrieved 3 June 2022.
- ^ Murray, Georgina (2006). "The New Zealand Interlocks of Power". Capitalist Networks and Social Power in Australia and New Zealand. Corporate social responsibility series. Aldershot, Hampshire: Ashgate Publishing, Ltd. p. 123. ISBN 9780754647089. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
New Zealand has been described as a mixed economy [...] and it works from free market principles.
- ^ 예를 들어,
- ^ 예를 들어,
- ^ "BNZ Markets Outlook" (PDF). www.bnz.co.nz/research. Bank of New Zealand. 6 April 2020. p. 2. Archived (PDF) from the original on 27 April 2020. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
On Tuesday, we get NZIER's Quarterly Survey of Business Opinion. NZIER tells us that the responses were complete by March 20. So, there will be the first signs of concern in the data but it will predate the big hit the economy has since suffered. We expect a drop in confidence but recognize that it will be just a step along the way to a much bigger fall.
- ^ 예를 들어,
- ^ 예를 들어,
- ^ "Covid-19: GDP results show NZ officially in first recession in a decade". Radio New Zealand. 17 September 2020. Archived from the original on 17 September 2020. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
- ^ Pullar-Strecker, Tom (17 September 2020). "NZ in recession as Covid shrinks GDP by 12.2%". Stuff. Archived from the original on 17 September 2020. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
- ^ Roy, Eleanor (16 September 2020). "New Zealand in Covid recession after worst quarterly GDP fall on record". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 17 September 2020. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
- ^ Clent, Danielle (1 March 2020). "Coronavirus: 'Zero' hand sanitisers, face masks at Auckland pharmacies". Stuff. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ "Wellington supermarket limits hand sanitiser sales to two items per customer". The New Zealand Herald. 18 February 2020. Archived from the original on 4 March 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ Deguara, Brittney (1 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Retailers confident of supply chain despite 'panic' buying". Radio New Zealand. Archived from the original on 2 March 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ Deguara, Brittney (29 February 2020). "Coronavirus stockpiling: Customer demand forces Auckland wholesaler to close its doors". Stuff. Archived from the original on 3 March 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ Sherwood, Sam (17 March 2020). "Dunedin student 12th positive coronavirus case – high school to close". Stuff. Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- ^ Moodie, Kim (23 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Four Auckland schools linked to Covid-19 in one day". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
- ^ Wade, Amelia (23 March 2020). "Coronavirus lockdown: What it means for schools, universities and other education facilities". The New Zealand Herald. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
- ^ MacManus, Joel; Chumko, Andre (25 April 2020). "Victoria University halls charging rent despite locking students out". Stuff. Archived from the original on 6 June 2020. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ Hudson, Daisy (6 May 2020). "Hall charges under fire from Green MP". Otago Daily Times. Archived from the original on 19 August 2020. Retrieved 12 May 2020.
- ^ Stewart, Indira (17 March 2020). "NZ churches back govt restrictions, cancel mass gatherings. Except Destiny". Radio New Zealand. Archived from the original on 28 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ Angeloni, Alice (19 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Church plans multiple Sunday services, others 'likely' to cancel after gathering ban". Stuff. Archived from the original on 19 March 2020. Retrieved 28 March 2020.
- ^ "Bishops Conference Pastoral Letter regarding Covid-19". Catholic Diocese of Christchurch. 20 March 2020. Archived from the original on 23 March 2020. Retrieved 23 March 2020.
- ^ Hall, Kristin (28 March 2020). "Concern among Muslims that halal butcher closures will see them miss out in lockdown". Archived from the original on 9 April 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ Andelane, Lana (29 March 2020). "Jacinda Ardern 'aware of' issues for people accessing halal meat". Newshub. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ Keogh, Brittany (31 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Community safety trumps access to halal meat, Muslim man says". Stuff. Archived from the original on 15 April 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ Mohammad, Rizwan (12 May 2020). "FIANZ circular confirms Eid prayers will not be held in New Zealand this year". The Indian Weekender. Archived from the original on 20 May 2020. Retrieved 22 May 2020.
- ^ "Covid-19: Churches in New Zealand to re-open without religious services". Vatican News. 12 May 2020. Archived from the original on 14 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ Bhatia, Ripu (12 May 2020). "Coronavirus: Destiny Church leader Brian Tamaki says Sunday service will go ahead". Stuff. Archived from the original on 14 May 2020. Retrieved 14 May 2020.
- ^ "PM Jacinda Ardern reveals move to gatherings of 100 under alert level 2". Radio New Zealand. 25 May 2020. Archived from the original on 25 May 2020. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- ^ Devlin, Collette (25 May 2020). "Coronavirus: Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern says gathering limits to increase to 100". Stuff. Archived from the original on 25 May 2020. Retrieved 25 May 2020.
- ^ Bradley, Anusha (10 September 2020). "Churches with links to the US being blamed for spreading Covid-19 misinformation". Radio New Zealand. Archived from the original on 9 September 2020. Retrieved 10 September 2020.
- ^ Williams, Caroline; Biddle, Donna-Lee (24 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Iwi across NZ step up tourist blockades, close huts and walkways". Stuff. Archived from the original on 1 April 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ Graham-McLay, Charlotte (23 March 2020). "New Zealand's Māori tribes set up checkpoints to avoid 'catastrophic' coronavirus deaths". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 27 April 2020. Retrieved 31 March 2020.
- ^ Walton, Steven (21 April 2020). "Coronavirus: Illegal checkpoints being dealt with, but ones with support OK – minister". Stuff. Archived from the original on 28 April 2020. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- ^ Castles, Helen (30 April 2020). "Some iwi-led checkpoints causing tension as they continue through Alert Level 3". 1 News. Archived from the original on 6 May 2020. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- ^ Burrows, Matt (6 May 2020). "Coronavirus: Local iwi's 'travel permits' at Bay of Plenty community roadblocks mean nothing, police say". Newshub. Archived from the original on 6 May 2020. Retrieved 6 May 2020.
- ^ "Covid-19: Far North iwi says road checkpoints will return". Stuff. 26 January 2021. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- ^ Piper, Denise (28 January 2021). "Covid-19: Northland checkpoint operated by iwi shut down by police". Stuff. Archived from the original on 28 January 2021. Retrieved 28 January 2021.
- ^ Wiltshire, Laura (19 March 2020). "Anzac Day services cancelled due to coronavirus". Stuff. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ^ "New Zealand protests live: Protester ties himself to US Embassy in Wellington". The New Zealand Herald. 1 June 2020. Archived from the original on 1 June 2020. Retrieved 1 June 2020.
- ^ Block, George; Kenny, Lee; Flahive, Brad; Piper, Denise (1 June 2020). "Black Lives Matter marches: Thousands of Kiwis peacefully protest against racism". Stuff. Archived from the original on 1 June 2020. Retrieved 1 June 2020.
- ^ "New Zealand protests live: Social distancing concerns as thousands attend protests". The New Zealand Herald. 1 June 2020. Archived from the original on 2 June 2020. Retrieved 1 June 2020.
- ^ Cheng, Derek (1 June 2020). "Act's David Seymour: Protest makes a mockery of level 2 rules". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 2 June 2020. Retrieved 1 June 2020.
- ^ "'We are in a global pandemic' – Ardern gives Black Lives Matter protestors telling off for flouting Covid-19 restrictions". 1 News. 2 June 2020. Archived from the original on 2 June 2020. Retrieved 2 June 2020.
- ^ Pearse, Adam (13 August 2020). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Lockdown protest stops traffic in Whangārei". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 16 August 2020. Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- ^ "Anti-lockdown protestors gather in Auckland's Aotea Square before march down Queen St". 1 News. 22 August 2020. Archived from the original on 22 August 2020. Retrieved 22 August 2020.
- ^ Bayer, Kurt (5 September 2020). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Hundreds turn out for anti-lockdown protests". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 5 September 2020. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ Palmer, Scott (10 October 2020). "Conspiracy theorists, anti-COVID-19 'freedom fighters' march through Auckland". Newshub. Archived from the original on 10 October 2020. Retrieved 10 October 2020.
- ^ Decent, Tom (14 March 2020). "All Super Rugby matches to be cancelled after Sunday's fixtures". Sydney Morning Herald. Archived from the original on 15 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ "Warbirds Over Wanaka International Airshow – Cancelled 15.3.20". Warbirds Over Wanaka. 15 March 2020. Archived from the original on 3 April 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- ^ "Halberg Awards celebrating decade of champions postponed after Auckland's move to Alert Level 3". 1 News. 15 February 2021. Archived from the original on 15 February 2021. Retrieved 15 February 2021.
- ^ "Covid-19 alert level change: Which events have been affected". Radio New Zealand. 17 February 2021. Archived from the original on 17 February 2021. Retrieved 17 February 2021.
- ^ "Live updates: Anti-mandate protest enters third day at Parliament". Radio New Zealand. 10 February 2022.
- ^ Bradbury, Martyn (27 February 2021). "UPDATE: Does the latest outbreak suggest we are getting it wrong in South Auckland?". Daily Blog. Archived from the original on 28 February 2021. Retrieved 2 March 2021.
- ^ Andelane, Lana (19 February 2020). "Coronavirus: 157 Wuhan evacuees permitted to leave quarantine in Whangaparaoa". Newshub. Archived from the original on 4 March 2020. Retrieved 4 March 2020.
- ^ "New Zealanders from cruise ship anxious to get home". Radio New Zealand. 29 March 2020. Archived from the original on 29 March 2020. Retrieved 30 March 2020.
- ^ Manch, Thomas (6 April 2020). "Coronavirus: Mercy flight for Kiwis stranded in Peru". Stuff. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 6 April 2020.
- ^ "Covid 19 coronavirus: Kiwis stranded on cruise ship in Uruguay coming home". The New Zealand Herald. 11 April 2020. Archived from the original on 11 April 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ^ Earley, Melanie (15 April 2020). "Coronavirus: Kiwis stranded in Peru arrive home on repatriation flight". Stuff. Archived from the original on 15 April 2020. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- ^ "Government announces repatriation flights for New Zealanders in India". Radio New Zealand. 3 May 2020. Archived from the original on 24 April 2020. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- ^ a b Devlin, Collete (24 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Foreign Minister Winston Peters urges New Zealanders abroad to take shelter as PM warns there will be no way home". Stuff. Archived from the original on 24 March 2020. Retrieved 24 March 2020.
- ^ "New Zealanders in India 'just want to get home'". Radio New Zealand. 27 April 2021. Archived from the original on 1 May 2021. Retrieved 11 May 2021.
- ^ Earley, Melanie; Basagre, Bernadette (28 April 2021). "Covid-19: New Zealand citizens stuck in India due to travel bans in transit countries". Stuff. Archived from the original on 8 May 2021. Retrieved 11 May 2021.
- ^ "Government extends temporary work visas by six months". Radio New Zealand. 7 July 2020. Archived from the original on 7 July 2020. Retrieved 7 July 2020.
- ^ Moir, Jo. "Govt's emergency welfare fund depletes with foreigners still stranded". Radio New Zealand. Archived from the original on 2 June 2020. Retrieved 2 June 2020.
- ^ "New border exemption sees some international students allowed back into NZ". 1 News. 12 October 2020. Archived from the original on 12 October 2020. Retrieved 12 October 2020.
- ^ Bayer, Kurt (10 July 2020). "Christchurch mosque shooting: Border exceptions for victims based overseas to attend gunman's sentencing". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 10 July 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- ^ Dillane, Tom (13 November 2020). "UK family whose son died at sea praise Jacinda Ardern for New Zealand entry decision reversal". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 13 November 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- ^ Harris, Dominic (25 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Plans for new flights a lifeline for tourists stranded in NZ". Stuff. Archived from the original on 26 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ Tuckey, Karoline (4 April 2020). "Overseas travellers relieved to be heading home". Radio New Zealand. Archived from the original on 4 April 2020. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
- ^ "Covid 19 coronavirus: Stranded foreigners to start leaving NZ tomorrow". The New Zealand Herald. 2 April 2020. Archived from the original on 2 April 2020. Retrieved 2 April 2020.
- ^ "Kiwis who helped stranded German travellers thanked with Auckland flyover by Lufthansa". 1 News. 10 April 2020. Archived from the original on 10 April 2020. Retrieved 10 April 2020.
- ^ Wade, Amelia (13 May 2020). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Winston Peters tells struggling migrant workers 'you should probably go home'". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 15 May 2020. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- ^ Robson, Sarah (9 May 2021). "Millions spent to bring home Kiwis stranded during pandemic". Stuff. Archived from the original on 10 May 2021. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Bonnett, Gillian (28 May 2021). "Covid-19 border closure: Millions spent on attracting migrants". Stuff. Archived from the original on 31 May 2021. Retrieved 14 June 2021.
- ^ Corlett, Eva (10 August 2021). "New Zealand should take phased approach to border reopening, experts advise". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 11 August 2021. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ^ Malpass, Luke; Cooke, Henry (11 August 2021). "Covid-19 NZ: Government advisory group says borders can open in 2022 without forgoing elimination strategy". Stuff. Archived from the original on 10 August 2021. Retrieved 11 August 2021.
- ^ Tahana, Jamie (25 August 2021). "World Politics Pacific Te Ao Māori Sport Business Country Local Democracy Reporting Comment & Analysis In Depth Weather TE AO MĀORI COVID-1925 Aug 2021 Iwi say trust in police damaged after Northland Covid-19 checkpoints set up 7 days into lockdown". Radio New Zealand. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 28 August 2021.
- ^ Ali, Imran (27 August 2021). "Covid 19 Delta outbreak: Northland police clarify checkpoint confusion". Northern Advocate. The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 26 August 2021. Retrieved 28 August 2021.
- ^ "Covid-19 Omicron: Chris Hipkins reveals decision on borders, boosters amid Omicron threat". The New Zealand Herald. 21 December 2021. Retrieved 21 December 2021.
- ^ "Covid-19: Border reopening for New Zealanders confirmed for end of February - what you need to know". Radio New Zealand. 3 February 2022. Archived from the original on 3 February 2022. Retrieved 3 February 2022.
- ^ "Jacinda Ardern provides post-Cabinet briefing on border restrictions, Ukraine". Radio New Zealand. 28 February 2022. Archived from the original on 28 February 2022. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ "MIQ exemption extended to more unvaccinated, including Australians". Radio New Zealand. 3 May 2022. Archived from the original on 3 May 2022. Retrieved 25 May 2022.
- ^ "New Zealand border reopening fully from end of July". Radio New Zealand. 11 May 2022. Archived from the original on 11 May 2022. Retrieved 25 May 2022.
- ^ "New Zealand border fully reopening by July 2022". Immigration New Zealand. 11 May 2022. Archived from the original on 11 May 2022. Retrieved 25 May 2022.
- ^ "World Health Organization praises New Zealand's response to Covid-19 again". 1 News. 17 October 2020. Archived from the original on 8 September 2020. Retrieved 17 October 2020.
- ^ Creitz, Charles (28 October 2020). "Victor Davis Hanson laments New Zealand's COVID-19 quarantine 'camps' as end of personal freedom". Fox News. Archived from the original on 28 October 2020. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- ^ Braae, Alex (29 October 2020). "The Bulletin: Idiots abroad infuriated by NZ's Covid response". The Spinoff. Archived from the original on 29 October 2020. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- ^ Ensor, Jamie. "Who is Laura Ingraham? A look at the Fox News host whose 'quarantine camps' comments shocked NZ". Newshub. Archived from the original on 29 October 2020. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- ^ Hurley, Sam; Bayer, Kurt (5 May 2020). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Judge overrules lockdown and allows son to visit dying dad, PM orders review of refusals". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 4 May 2020. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ^ Gower, Patrick (4 May 2020). "Coronavirus: Jacinda Ardern orders review into quarantined people wanting exemption to visit dying relatives". Newshub. Archived from the original on 5 May 2020. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- ^ O'Brien, Tova (6 May 2020). "Kiwi in quarantine granted exemption to see dying mother". Newshub. Archived from the original on 7 May 2020. Retrieved 7 May 2020.
- ^ Nichol-Williams, Kate (19 August 2020). "Early stages of Covid-19 Level 4 lockdown ruled unlawful by High Court". 1 News. Archived from the original on 19 August 2020. Retrieved 19 August 2020.
- ^ Mitchell, Jonathan (19 August 2020). "High Court rules some of Covid-19 level 4 lockdown was unlawful". Radio New Zealand. Archived from the original on 19 August 2020. Retrieved 19 August 2020.
- ^ "Government signs agreement to purchase 1.5m Covid-19 vaccines, enough for 750k people". 1 News. 12 October 2020. Archived from the original on 12 October 2020. Retrieved 12 October 2020.
- ^ "Pfizer vaccine signed off by Government, with rules about who will get it". 1 News. 10 February 2021. Archived from the original on 10 February 2021. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ Leahy, Ben (20 February 2021). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Health officials give presser as first Kiwis receive vaccinations". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 20 February 2021. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- ^ "New Zealand's first ever 'Vaxathon' launches". Ministry of Health NZ. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ^ "Live Covid-19 updates: Super Saturday Vaxathon". RNZ. 16 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19 vaccine rollout plan". Unite against COVID-19. 10 March 2021. Archived from the original on 17 March 2021. Retrieved 11 March 2021.
- ^ Daalder, Marc (4 August 2021). "Charting New Zealand's vaccine rollout". Newsroom. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- ^ MoH는 백신 접종 자격이 있는 사람은 누구나 백신을 맞을 수 있기 때문에 그룹 번호 업데이트를 중단했습니다.
- ^ "Defence Force service members told to get vaccinated or face being fired". RNZ. 23 April 2021. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ "Covid-19: Essential supermarket workers start getting vaccinations at work". Stuff. 24 August 2021. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- ^ 그룹 3에 속한 사람들은 그룹 4에서 복용량 수가 실제보다 더 낮아지도록 식별할 수 있습니다.
- ^ 그룹 3에 속한 사람들은 그룹 4에서 실제보다 복용량 수가 더 많아지게 할 수 있습니다.
- ^ "COVID-19: The vaccine rollout". Ministry of Health NZ. Retrieved 19 August 2021.
- ^ 2021년 8월 20일부터 부모 또는 보호자가 접종 대상자가 되었을 때 12세에서 15세 사이의 사람들이 접종 대상자가 되었습니다.
- ^ "New Zealand Team marks 100 days until Tokyo, calls for Kiwis to Get on Board". New Zealand Olympic Team. 14 April 2021. Retrieved 26 April 2021.
- ^ "Tokyo 2020 - Paralympics New Zealand". Archived from the original on 23 March 2020.
- ^ 아프가니스탄에서 뉴질랜드 국민, 그들의 가족, 비자 소지자들에 대한 군 철수
- ^ "New Zealand Army's role in evacuation mission involved - NZDF". Archived from the original on 31 August 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19: Applying for an early vaccine for travel overseas". Ministry of Health NZ. Retrieved 26 April 2021.[영구 데드링크]
- ^ Cooke, Henry; Malpass, Luke (5 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Kiwis want more border control, don't think Govt can stop outbreak". Stuff. Archived from the original on 5 March 2020. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
- ^ a b Cooke, Henry; Malpass, Luke (25 March 2020). "Coronavirus: Poll shows Kiwis back harsh measures but are extremely worried about virus". Stuff. Archived from the original on 24 March 2020. Retrieved 25 March 2020.
- ^ Lynch, Jenna (18 May 2020). "Newshub-Reid Research Poll: Overwhelming number of Kiwis back Government's lockdown decision". Newshub. Archived from the original on 21 May 2020. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
- ^ "Covid 19 coronavirus: New Zealanders' trust in Government's pandemic management falls". The New Zealand Herald. 9 August 2020. Archived from the original on 9 August 2020. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- ^ Manhire, Tom (18 February 2021). "Exclusive poll: NZ support for Covid-19 response remains sky high". The Spinoff. Retrieved 18 February 2021.
- ^ Manhire, Toby (23 August 2021). "Exclusive poll: Resounding popular support for decision to take NZ into strict lockdown". The Spinoff. Retrieved 23 August 2021.
- ^ "Jacinda Ardern's popularity plunges as New Zealand reckons with new era of endemic Covid". the Guardian. 11 November 2021. Retrieved 26 October 2022.
- ^ Gabel, Julia; Knox, Chris (2 December 2022). "Divided NZ? Exclusive poll reveals how divided we feel – and what we agree on". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 2 December 2022. Retrieved 2 December 2022.
- ^ Clark, Emily (19 January 2023). "Jacinda Ardern's resignation may have shocked the world. But at home, it wasn't as surprising". ABC News. Retrieved 28 July 2023.
- ^ "Majority support for 'no jab, no job' across several sectors – new poll". NZ Herald. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
- ^ "Covid 19 Delta: Poll reveals public support for vaccine mandates". NZ Herald. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
- ^ Ensor, Jamie (24 April 2020). "Coronavirus: Jacinda Ardern's 'incredible', 'down to earth' leadership praised after viral video". Newshub. Archived from the original on 21 April 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ Khalil, Shaimaa (22 April 2020). "Coronavirus: How New Zealand relied on science and empathy". BBC News. Archived from the original on 22 April 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ Fifield, Anna (7 April 2020). "New Zealand isn't just flattening the curve. It's squashing it". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 23 April 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ Campbell, Alastair (11 April 2020). "Jacinda Ardern's coronavirus plan is working because, unlike others, she's behaving like a true leader". The Independent. Archived from the original on 23 April 2020. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- ^ Roy, Eleanor (17 October 2020). "Jacinda Ardern to govern New Zealand for second term after historic victory". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 26 January 2021. Retrieved 28 February 2021.
- ^ Brettkelly, Sharon (15 September 2020). "The 1pm news scramble". Newsroom. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- ^ Patterson, Robyn (5 September 2020). "The watchdog role of our journalists". Newsroom. Retrieved 16 September 2020.
- ^ "Coronavirus Pandemic: Ranking The Best, Worst Places To Be". Bloomberg News. 25 April 2021. Retrieved 27 April 2021.
- ^ Deguara, Brittney (27 April 2021). "Covid-19: Singapore overtakes New Zealand as the pandemic's most resilient country". Stuff. Archived from the original on 27 April 2021. Retrieved 27 April 2021.
- ^ Hall, Kristin (15 October 2021). "Govt to ditch alert levels for new traffic light system". 1 News. TVNZ. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ^ Neville, Alice (22 October 2021). "How NZ's new traffic light Covid-19 vaccine target system works". The Spinoff. Archived from the original on 2 November 2021. Retrieved 22 October 2021.
- ^ Cooke, Henry (22 November 2021). "Covid-19: New Zealand to enter traffic-light system on December 3, opening up Auckland". Stuff. Archived from the original on 22 November 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ^ "Explained: What the traffic light system is and how it works". Radio New Zealand. 22 November 2021. Archived from the original on 22 November 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19 Protection Framework". Unite against COVID-19. Retrieved 27 November 2021.
- ^ 수시 와일스 & 토비 모리스:그 거품들이 왜 그렇게 중요한가요?
- ^ 서포트 버블: 그들은 어떻게 일하고 누가 당신 안에 있습니까? 2020년 12월 21일 www.bbc.com 2020년 12월 31일 접속
- ^ 뉴질랜드의 "버블 컨셉"은 사람들이 천천히 다시 사회를 이루도록 하고 있습니다. 미국에서도 통할까요?2020년 5월 6일 slate.com 2020년 12월 31일 접속
- ^ 방역 거품 - 올바르게 되었을 때 - 코로나바이러스 위험을 제한하고 외로움과 싸우는 데 도움이 되는 2020년 6월 17일 theconversation.com 2020년 12월 31일 접속
- ^ Walls, Jason (14 April 2020). "Jobless rate could reach 26% if lockdown extended, according to the Treasury". The New Zealand Herald. ISSN 1170-0777. Archived from the original on 31 August 2020. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- ^ "Unemployment rate Stats NZ". 16 May 2020. Archived from the original on 16 May 2020. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- ^ "Coronavirus: Treasury models paint dire economic picture, mass unemployment Stuff.co.nz". 13 April 2020. Archived from the original on 13 April 2020. Retrieved 16 May 2020.
- ^ Hargreaves, David (5 August 2020). "Statistics New Zealand says unemployment rate actually FELL to 4%, but the 'underutilisation' rate had a record climb, up to 12%, employment fell by 11,000 jobs and 37,000 people left the workforce". Interest.co.nz. Archived from the original on 7 August 2020. Retrieved 4 September 2020.
- ^ "Covid-19 took 1.6 per cent chunk out of GDP by end of March". Stuff. 17 June 2020. Retrieved 18 June 2020.
- ^ Pullar-Strecker, Tom (17 September 2020). "NZ in recession as Covid shrinks GDP by 12.2%". Stuff. Stuff Ltd. Retrieved 17 September 2020.
- ^ "Gross domestic product: June 2020 quarter Stats NZ". www.stats.govt.nz. Retrieved 28 September 2020.
- ^ "GDP jump of 14 per cent completes NZ's 'V'-shaped recovery". Stuff. 16 December 2020. Retrieved 22 January 2021.
- ^ "Unemployment and underutilisation continue to fall". Statistics New Zealand. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Clark, Emily (15 June 2023). "New Zealand is officially in a recession. These charts show how Australia compares". ABC News. Retrieved 28 July 2023.
- ^ Corlett, Eva (5 December 2022). "New Zealand announces inquiry into Covid-19 response". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 28 July 2023.
- ^ Morton, Jamie (5 March 2020). "Coronavirus testing: Five questions answered". The New Zealand Herald. ISSN 1170-0777. Archived from the original on 5 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ "Coronavirus: Auckland mum's request to be tested for virus rejected". Stuff. 13 March 2020. Archived from the original on 14 March 2020. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ "Coronavirus: How Covid-19 unfolded at Rosewood". Stuff. 15 April 2020. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "Rosewood exposes broken elderly care model". Newsroom. 15 April 2020. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "Case definition of COVID-19 infection – 3 April 2020" (PDF). Ministry of Health NZ. 3 April 2020. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 April 2020. Retrieved 8 April 2020.
- ^ "Case definition of COVID-19 infection". Ministry of Health NZ. Archived from the original on 17 March 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint : URL(링크) 부적합 - ^ "PM to doctors: test more people for Covid-19". Newsroom. 17 March 2020. Archived from the original on 29 July 2020. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
- ^ Morrah, Michael (18 August 2020). "Coronavirus: Senior quarantine whistleblower says staff were refused regular testing programme despite pleas". Newshub. Archived from the original on 18 August 2020. Retrieved 18 August 2020.
- ^ Cooke, Henry; Ensor, Blair (9 July 2021). "Covid-19 NZ: Minister blames 'capacity constraints' as just half of pre-departure tests are checked". Stuff. Archived from the original on 9 July 2021. Retrieved 9 July 2021.
- ^ Cann, Geraden (26 August 2021). "Covid-19: Auckland community health provider rolls out saliva testing to staff". Stuff. Archived from the original on 1 September 2021. Retrieved 8 September 2021.
- ^ Fonseka, Dileepa (9 September 2021). "Covid-19: Saliva testing at the Level 4 Auckland boundary". Stuff. Archived from the original on 8 September 2021. Retrieved 8 September 2021.
- ^ Cheng, Derek (8 September 2021). "'Fumbling over saliva testing': Expert scientist questions whether Jacinda Ardern has been misinformed". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 8 September 2021. Retrieved 8 September 2021.
- ^ "Saliva test developer 'frustrated' by Government's slow uptake". 1 News. TVNZ. 6 September 2021. Archived from the original on 6 September 2021. Retrieved 8 September 2021.
- ^ "Plane delivering tonnes of RATs touches down in Christchurch". 1 News. TVNZ. 28 February 2022. Archived from the original on 2 March 2022. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "HISO 10001:2017 Ethnicity Data Protocols" (PDF). Ministry of Health. September 2017. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 February 2020. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
- ^ "COVID-19 – Testing by region". Health.govt.nz. New Zealand Government. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ "National population estimates: At 30 September 2021 – Infoshare tables Stats NZ". stats.govt.nz. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
- ^ Quinn, Rowan (17 April 2020). "Random testing to give insight into Covid-19 spread". Radio NZ. Archived from the original on 17 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ Hayward, Michael; Lines-MacKenzie, Jo (17 April 2020). "Coronavirus: Wider Covid-19 testing starts in Christchurch, Waikato". Stuff. Archived from the original on 22 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ Ainge Roy, Eleanor (20 April 2020). "New Zealand plans to ease coronavirus lockdown in a week". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 20 April 2020. Retrieved 21 April 2020.
- ^ Satherley, Dan (19 March 2021). "Coronavirus: Christchurch MIQ COVID-19 transmission mystery solved using CCTV". Newshub. Retrieved 19 March 2021.
- ^ "COVID-19 – Testing by region". Health.govt.nz. New Zealand Government. Archived from the original on 1 May 2020. Retrieved 27 August 2020.
- ^ a b "COVID-19: case demographics". Health.govt.nz. Ministry of Health. 6 October 2023.
- ^ "Chatham Island records first Covid cases two years into pandemic". The Independent. 7 March 2022. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
- ^ "Cook Islands COVID-19 Response". covid19.gov.ck. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
- ^ "Niue records first Covid-19 case in arrival from NZ". 1 News. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
- ^ "WHO COVID-19 Dashboard". 17 April 2020. Archived from the original on 16 April 2020. Retrieved 17 April 2020.
- ^ WHO 코로나바이러스(COVID-19) 대시보드.세계보건기구(WHO)로부터."데이터 테이블" 탭을 누릅니다.로딩될 때까지 기다립니다.표에는 국가별 사례 및 사망자에 대한 공식 데이터가 있습니다.매일 업데이트됩니다.인터넷 보관소에는 지난 몇일간의 시간이 있습니다.
- ^ a b "Weekly deaths declined in NZ's lockdown – but we still don't know exactly why – Public Health Expert, University of Otago". Archived from the original on 12 August 2020. Retrieved 9 August 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x "COVID-19 – Significant clusters". Ministry of Health NZ. 6 October 2023. Retrieved 5 October 2021.
- ^ Martin, Hannah (24 August 2020). "Coronavirus: Auckland cluster largest in NZ, PM warns of Covid's 'long tail'". Stuff. Archived from the original on 26 August 2020. Retrieved 26 August 2020.
- ^ "Five new Covid-19 cases in NZ today, Auckland August cluster closed". Radio New Zealand. 3 November 2020. Archived from the original on 9 November 2020. Retrieved 12 November 2020.
- ^ Owen, Catrin (26 August 2020). "Coronavirus: Five new cases and a new 'mini cluster' at Auckland church". Stuff. Archived from the original on 26 August 2020. Retrieved 26 August 2020.
- ^ Martin, Hannah (15 June 2020). "Coronavirus: Marist College cluster officially 'closed', health authorities say". Stuff. Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ^ Kirkness, Luke (15 June 2020). "Covid 19 coronavirus: Marist College cluster officially closed by Ministry of Health". The New Zealand Herald. Archived from the original on 15 June 2020. Retrieved 15 June 2020.
- ^ a b "The New Zealand Ministry of Health". Health.govt.nz. Archived from the original on 23 April 2020. Retrieved 23 May 2020.
외부 링크
- covid19.govt.nz , 주요 뉴질랜드 정부 웹사이트
- 뉴질랜드 보건부, COVID-19 (신종 코로나바이러스)
- 세계보건기구 코로나바이러스병(코로나19) 상황 보고 (국가별 공식 확진자 수)
- 존스 홉킨스 대학의 코로나바이러스 COVID-19 글로벌 사례와 역사적 데이터
- 뉴질랜드에서 코로나19 전파의 성공적인 제거, M. Baker, N. Wilson, A.앵글마이어.2020년 8월 20일, 뉴잉글랜드 의학저널
- 위키 다양성:COVID-19/모든 원인 사망/뉴질랜드






