2021년 영국 천연가스 공급업체 위기
2021 United Kingdom natural gas supplier crisis2021년 8월부터 높은 유럽 천연가스 도매가격이 영국에 심각한 영향을 미치기 시작했다.아시아에서의 가스 수요 급증, 러시아로부터의 유럽 시장으로의 가스 공급 감소, 저가스 비축량, 각종 전기 설비의 연쇄 고장으로 인해 영국의 소비자들은 급격한 가스 가격 상승에 직면했다.
소비자, 전력회사, 그리고 이산화탄소에 의존하는 기업들 모두가 영향을 받았다.이 위기로 인해 영국의 일부 소규모 국내 공급업체가 폐업하여 2021년 10월 14일 현재 약 200만 명의 소비자가 피해를 입었다.
원인들
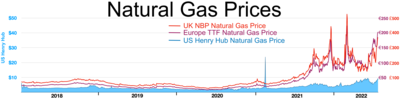
가격 상승의 주된 원인은 전 [1]세계 천연가스 도매가격의 급등이다.국내 공급은 영국 [1]수요의 약 40%에 불과하고 나머지는 노르웨이, 네덜란드 등 인접국으로부터 수입되며 카타르와 미국에서도 러시아로부터 영국 시장의 [2][1]약 5%를 공급받고 있다.2021년 1월과 9월 사이에 가스 가격이 250% 상승했으며, 8월 [3]한 달에만 70%가 상승했습니다.이러한 가격 상승은 COVID-19로 인한 경기침체, 특히 [4][5]아시아의 강력한 에너지 수요로 인해 전 세계적으로 수요가 급증했기 때문이다.
러시아는 보통 유럽연합(EU)의 소비량의 40%~50%를 공급하고 알제리, 노르웨이, LNG 수입품은 [6][2]나머지 대부분을 차지한다.러시아는 위기 직전 유럽에 공급한 가스는 장기 계약에 따라 공급했지만 현물시장에서는 추가 공급하지 않았다.이코노미스트 인텔리전스 유닛(Economic Intelligence Unit)은 러시아의 추가 가스 수출 능력이 제한적인 것은 생산 정점에 근접한 높은 국내 수요와 기술적 [2][7]문제 때문이라고 보고했습니다.2021년 1월부터 6월까지 러시아는 유럽에 2020년 같은 달보다 약 22% 더 많은 가스를 공급했으며, 2019년과 거의 같은 양이었다.알제리도 그 몇 달 동안 공급을 늘렸지만 노르웨이, 영국,[8] 네덜란드를 포함한 다른 나라들은 공급을 줄였다.
날씨가 조건 또한 영국에 가게에게 불리하게:영국의 추운 날씨 2020/21 겨울은 더 많은 천연 가스 중앙 난방을 위해 평소보다 사용될 때, 전기 발전을 위한 여름, 2021년까지에 대한 여분의 가스 요건에 의해 원자력 발전 정지, 그 shutd의 시리즈 때문에 악화되었다 stockpiles,[4] 병들게 초래되었습니다.자신의프랑스로부터 전기를 가져오는 HVDC 크로스 채널 상호 접속 화재와 러프 저장 시설의 폐쇄로 인해 영국은 장기 [9]비축량을 유지할 수 없게 되었다.이는 1961년 [10][2]이후 바람이 가장 적게 부는 여름 중 하나로 인해 영국에서 더욱 악화되어 풍력발전이 평소보다 낮았다.
많은 가스 회사들이 예를 들어 1년 동안 일정 기간 동안 고정 요금 계약을 판매했지만, 미래의 가스 도매 가격 상승에 대한 충분한 포워드 헤지를 하지 못했기 때문에, 이러한 고정 요금 [11]계약에서 큰 손실을 보고 있었다.또한, 일반 가스 회사가 소비자에게 요금을 부과할 수 있는 최대 법적 제한은 이러한 가격 인상을 이러한 소비자들에게 완전히 전가할 수 없다는 것을 의미했다.그 결과 2021년 9월부터 일부 소규모 가스공급업체들이 [12][3][13]부도로 문을 닫았다.
영향들
2021년 초 [14]영국에는 약 70개의 국내 가스 공급 업체가 있었다.2021년 11월 22일 현재, 총 20개의 가스 공급 회사가 진행 중인 위기의 직접적인 결과로 거래를 중단했으며,[15][16] 약 350만 명의 고객에게 영향을 미쳤다.여기에는 Avro Energy와 Bulb가 포함되어 있습니다.Avro Energy는 지금까지 거래를 중단한 최대 공급업체로 약 1,700,000명의 [17]고객에게 영향을 미쳤으며, Avro Energy의 종말은 580,000명의 고객에게 영향을 미쳤습니다.벌브는 영국에서 7번째로 큰 에너지 회사였고 약 1,000명의 [18]직원이 있었다.일부 업계 분석가들에 따르면 적어도 35개 이상의 공급 업체가 [18]붕괴 위험에 처해 있는 것으로 생각되고 있다.실패한 회사의 고객들은 가스 및 전기 시장 사무국 메커니즘에 의해 새로운 가스 회사에 재할당되었고, 때로는 더 비싼 [19]요금으로 전환되었다.2021년 10월, 어려움을 겪고 있는 상업용 가스 소비자들은 정부의 [20]개입을 요청했습니다.고유가 때문에 전기요금에 큰 영향을 미쳐 일부 전동차 운영자는 일시적으로 디젤열차로 [21]전환했다.
가스 가격 상승의 결과로 CF Industries는 티사이드와 체셔에 [22]있는 비료 공장의 생산을 중단했다.순수한 이산화탄소의 생산은 질소 비료를 만드는 데 사용되는 Haber 공정의 부산물이며 CF 비료 또한 이 나라에서 가장 큰 상업용 이산화탄소 생산국 중 하나였습니다. 그 결과, 폐쇄는 상업적으로 이산화탄소의 부족으로 이어져 식품 가격이 [23]상승했습니다.9월 21일 정부는 CF비료와 생산을 재개하고 공급망에 이산화탄소를 재도입하는 계약을 체결했다.다만,[24] 그 날짜 이후의 3주를 커버하는 것은 단기적인 긴급 계약일 뿐이다.2022년 6월 CF인더스트리는 계속되는 고유가와 환경세 [25]때문에 체셔주 잉스에 있는 비료 공장을 영구 폐쇄했다.
2021년 12월 1일 현재 28개 에너지 공급 회사가 고장났습니다.벌브에너지는 정부의 효과적인 지원을 받아 에너지 공급 회사 경영에 들어갔고, Ofgem 이전 [26]체제 하에서 27개사가 새로운 공급업체에 인수되었습니다.2022년 1월 투게더에너지는 27번째로 [27]파산했다.한 분석가는 시스템의 [28]유통 사용을 통해 소비자가 손실을 충당하게 되어 있기 때문에 이러한 결함으로 인해 소비자가 34파운드의 비용을 부담하게 될 것으로 예상했습니다.
정부 대응
Kwasi Kwarteng 에너지 장관은 "불이 꺼지고 사람들이 집을 데울 수 없다는 것은 의심의 여지가 없다"고 말했다.콰르탱은 [29]또 정부는 실패한 기업들을 구제하지 않을 것이라고 말했다.실패나 관리 [30]실패에 대한 보상은 없습니다.
보리스 존슨 총리는 에너지 가격의 상승은 COVID-19 경기 [31]침체 이후 "세계 경제가 살아나면서" 야기된 "단기적인" 문제라고 말했다.
영국 정부는 카타르에 [32]액화천연가스(LNG)의 균형 있는 공급을 보장하기 위한 장기 가스 계약을 모색하기로 했다.존슨 총리는 2021년 [33][34]9월 유엔 총회에서 셰이크 타밈 빈 하마드 알 타니 카타르 국왕에게 도움을 요청했다.
결과
2021년 10월 28일 러시아가 11월 8일 러시아 저장소가 채워진 후 오스트리아와 독일에 대한 공급을 늘리겠다고 발표한 이후 유럽의 천연가스 가격은 12% 하락했다.노르웨이는 가스 생산량을 늘리고 중국의 석탄 가격을 낮춘 것도 가스 가격 하락에 일조하고 있다.영국의 물가는 유럽 물가를 면밀히 추적하고 있지만,[35][36] 평상시보다 약 4배 높은 수준을 유지할 것이다.2021년 11월 16일, 독일의 에너지 규제 기관이 러시아에서 [37][38][39]독일로 가는 노르트 스트림 2 천연가스 파이프라인의 승인을 중단한 후, 영국의 천연가스 가격은 17% 상승했다.
유럽의 높은 가격은 LNG를 세계의 다른 지역으로부터 수송하도록 끌어들였다.특히 미국-아시아 화물은 가격 외에도 여행 시간이 단축된 점이 매력적이었다.러시아로부터의 LNG 수송량도 증가했다.추가 [40][41]공급으로 인해 12월 마지막 주에 가격이 다소 하락했다.
2022년 4월 영국의 에너지 가격 상한선을 감독하는 Ofgem은 상한선을 54%(일반 가정의 경우 2,017파운드)로 인상했습니다.이것은 "난방"과 "식사" 중 하나를 재정적으로 선택해야 하는 고객들을 위해 몇몇 의원들과 대변인들에 의해 격렬한 항의를 이끌어냈다.2022년 6월 현재 Ofgem은 10월에 에너지 가격 상한선을 연간 최대 2980파운드까지 51% 인상할 예정입니다.Ofgem은 또한 가격 상한선을 6개월마다에서 3개월마다 변경하는 빈도를 줄일 계획을 제시했습니다.이렇게 하면 도매가격이 상승할 경우 더 빨리 이익을 가져와 에너지 회사를 보호할 수 있습니다.이것은 도매 가격이 떨어지면, 고객들도 그들의 청구서가 더 빨리 떨어지는 것을 볼 수 있다는 것을 의미할 것이다.
Ofgem은 또한 영국 가정이 단열재를 추가하고 난방 시스템을 업그레이드하여 가정의 에너지 효율을 개선하기 위한 보조금을 신청할 수 있는 에너지 회사 의무 제도를 감독한다.에너지회사 의무(ECO4)의 4단계는 4월보다 늦춰진 뒤 2022년 7월에 공식적으로 시작된다.
「 」를 참조해 주세요.
레퍼런스
- ^ a b c "Where does Britain get its gas from and why does Russia matter?". The Independent. 8 October 2021. Archived from the original on 17 October 2021. Retrieved 14 October 2021.
- ^ a b c d Horton, Jake (14 October 2021). "Europe gas prices: How far is Russia responsible?". BBC News. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 17 October 2021.
- ^ a b Choi, Chris (21 September 2021). "Why are gas prices surging and what happens if your energy firm goes bust?". ITV News. Archived from the original on 22 September 2021. Retrieved 22 September 2021.
- ^ a b Ambrose, Jillian (19 September 2021). "UK energy market crisis: what caused it and how does it affect my bills?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 20 October 2021. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ^ Valle, Sabrina (10 September 2021). "Asian spot prices hit all-time seasonal high". Reuters. Archived from the original on 8 October 2021. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ^ "Europe's soaring gas prices: does Russia hold solution to crisis?". the Guardian. 7 October 2021. Archived from the original on 17 October 2021. Retrieved 14 October 2021.
- ^ Mazneva, Elena (3 September 2021). "Russia Has a Gas Problem Nearly the Size of Exports to Europe". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 17 October 2021.
- ^ Yermakov, Vitaly (September 2021). Big Bounce: Russian gas amid market tightness (PDF) (Report). Oxford Institute for Energy Studies. pp. 9–13. Archived (PDF) from the original on 11 October 2021. Retrieved 1 November 2021.
- ^ Bradshaw, Michael (20 September 2021). "Gas price spike: how UK government failures made a global crisis worse". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 14 October 2021.
- ^ "Britain's last coal power stations to be paid huge sums to keep lights on". the Guardian. 13 September 2021. Archived from the original on 22 October 2021. Retrieved 14 October 2021.
- ^ "How the UK's reliance on gas turned an energy furore into an energy crisis". Greenpeace UK. 28 September 2021. Archived from the original on 30 September 2021. Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- ^ "Profiling the 11 UK energy companies that ceased trading in the past year". Archived from the original on 8 October 2021. Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- ^ Morales, Alex; Morison, Rachel; Mathis, Will (20 September 2021). "U.K. Won't Bail Out Failed Companies Amid Crisis: Power Update". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 16 October 2021. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ^ McCann, Jaymi (24 September 2021). "Who are the 'Big 6' energy companies? The UK's biggest suppliers explained and why gas prices have gone up". i. Associated Newspapers. Archived from the original on 27 September 2021. Retrieved 27 September 2021.
- ^ "Check who's taken over your energy supply". www.citizensadvice.org.uk. Archived from the original on 8 October 2021. Retrieved 7 October 2021.
- ^ "How you're protected when energy firms collapse". Ofgem. Archived from the original on 4 November 2021. Retrieved 4 November 2021.
- ^ Millard, Rachel (24 September 2021). "Collapsed Avro Energy paid directors £2.2m despite £28m loss". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 24 September 2021. Retrieved 24 September 2021.
- ^ a b "Energy firm Bulb set to go into administration". BBC News. 22 November 2021. Archived from the original on 22 November 2021. Retrieved 22 November 2021.
- ^ "Your energy supplier has gone bust". Citizens Advice. Archived from the original on 6 October 2021. Retrieved 7 October 2021.
- ^ "British industry warns of factory closures without help on fuel costs". Reuters. 9 October 2021. Archived from the original on 11 October 2021. Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "Press Comment on Use of Electric Traction in Rail Freight". Rail Freight Group. 13 October 2021. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 19 October 2021.
- ^ Thomas, Nathalie; Sheppard, David (16 September 2021). "Gas price surge triggers UK fertiliser plant closures and crop warnings". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 17 October 2021. Retrieved 14 October 2021.
- ^ Lorch, Mark (20 September 2021). "CO₂ shortage: why a chemical problem could mean more empty shelves". The Conversation. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 14 October 2021.
- ^ Younger, Rachel (22 September 2021). "Food prices rising over CO2 shortage as supply deal covers just three weeks". ITV News. Archived from the original on 22 September 2021. Retrieved 22 September 2021.
- ^ Cahill, Helen; Wallace, Tim (8 June 2022). "UK food supply 'vulnerable' after fertiliser factory closes permanently". The Daily Telegraph. Retrieved 8 June 2022.
- ^ "Check who's taken over your energy supply". Ofgem. Archived from the original on 22 December 2021. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "Together Energy becomes latest supplier to collapse amid surging energy prices". The Independent. 18 January 2022. Archived from the original on 18 January 2022. Retrieved 18 January 2022.
- ^ Lempriere, Molly (16 February 2022). "Cost of failed energy suppliers adding £34.36 to domestic electricity bills". Current. Archived from the original on 16 February 2022.
- ^ "Where does the UK get its gas and is it facing a shortage this winter?". BBC News. Archived from the original on 19 October 2021. Retrieved 28 September 2021.
- ^ "UK gas supply issues will not see 'lights going out', business secretary Kwarteng says". The Irish Times. 20 September 2021. Archived from the original on 28 September 2021. Retrieved 28 September 2021.
- ^ "Boris Johnson dismisses fears over tough winter". BBC News. Archived from the original on 6 October 2021. Retrieved 28 September 2021.
- ^ "Why Boris Johnson's Qatar gas plan is a cop out". Evening Standard. 17 November 2021. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ "UK asks Qatar to become gas 'supplier of last resort' amid energy crisis". Doha News. 7 November 2021. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ "UK seeks long-term gas deal with Qatar, asks to become 'supplier of last resort' -FT". Reuters. 6 November 2021. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ Millard, Rachel (28 October 2021). "Gas prices slump as Putin boosts supplies to Europe". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 28 October 2021.
- ^ "Russia seen starting to fill Europe's gas storage after Nov. 8". Euronews. 27 October 2021. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 28 October 2021.
- ^ "Natural-Gas Prices Jump as Germany Pauses Certification of Russian Pipeline". The Wall Street Journal. 16 November 2021. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ "European Natural Gas Prices Surge on Nord Stream 2 Delay — LNG Recap". Natural Gas Intelligence. 16 November 2021. Archived from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ "European Gas Storage Levels". BFY Group. 1 December 2021. Archived from the original on 8 December 2021. Retrieved 8 December 2021.
- ^ Burton, Lucy; Millard, Rachel (28 December 2021). "Gas price falls as cargo ships divert to UK". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on 29 December 2021. Retrieved 29 December 2021.
- ^ "It's going to cost EUR62 Billion to meet new EU gas storage legislation". Retrieved 28 March 2022.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint :url-status (링크)