13 모노케로티스
13 Monocerotis| 관측 데이터 에폭 J2000 이쿼녹스 J2000 | |
|---|---|
| 별자리 | 모노케로스 |
| 우측 상승 | 06h 32m 54.22948s[1] |
| 탈위임 | 7° 19′ 58.6942″[1] |
| 겉보기 크기 (V) | 4.498[2] |
| 특성. | |
| 스펙트럼형 | A0 Ib[2] |
| U-B색지수 | −0.217[2] |
| B-V색지수 | +0.007[2] |
| 변수형 | 의심스러운[3] |
| 아스트로메트리 | |
| 방사 속도 (Rv) | +11.80km[4]/s |
| 고유 운동 (μ) | RA: -0.20[1] mas/yr Dec.: -3.48[1]mas/yr |
| 시차 (π) | 0.83 ± 0.46[1] 마스 |
| 거리 | 780[5] pc |
| 절대치수 (MV) | −4.80[6] |
| 세부 사항 | |
| 미사 | 12.0[7] M☉ |
| 반지름 | 34[6] R☉ |
| 표면 중력 (log g) | 2.15[2] cgs |
| 온도 | 만[2] K |
| 금속성 [Fe/H] | -0.18[8] 덱스 |
| 회전 속도 (v sin i) | 0km[2]/s |
| 나이 | 16MYR[7] |
| 기타 지정 | |
| 데이터베이스 참조 | |
| 심바드 | 자료 |
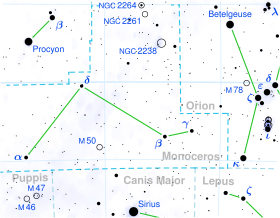
13 Monocerotis (13 Mon)는 Monoceros 별자리에 있는 등급 A0 Ib (흰색 초거성) 별이다. 겉보기 크기는 4.5이며 대략 780파섹(2,500리) 떨어져 있다.
13 Mon은 로제트 성운과 NGC 2264 사이의 중간인 [6]Monoceros OB1 항성조합 내에 있으며, 약 780 파섹의 거리에 있다.[5] 이 성운은 Van den Bergh 81 (VdB 81)로 나열된 작은 반사 성운에 둘러싸여 있다.[9]
13 모노케로티스(Monocerotis)는 A0 Ib 스펙트럼 등급의 표준 항성으로 사용되어 왔다.[10]
1997년부터 2000년까지 13개의 모노케로티스의 연장된 사진 측정은 최대 0.04개의 불규칙한 변동을 보여주며 또한 이 기간 동안 점점 희미해지는 약간의 추세를 보인다.[11] 히파르코스 위성 데이터를 이용해 분석한 밝은 A0 - A5 슈퍼자이언트는 모두 가변성이 있는 것으로 나타났지만, 13 Mon이 가장 덜 가변적인 것으로 나타났다.[12]
참조
- ^ a b c d e Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. S2CID 18759600. Vizier 카탈로그 항목
- ^ a b c d e f g Firnstein, M.; Przybilla, N. (2012). "Quantitative spectroscopy of Galactic BA-type supergiants. I. Atmospheric parameters". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 543: A80. arXiv:1207.0308. Bibcode:2012A&A...543A..80F. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219034. S2CID 54725386.
- ^ Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/GCVS. Originally Published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1. Bibcode:2009yCat....1.2025S. Vizier 카탈로그 항목
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759–771. arXiv:1606.08053. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065. S2CID 119231169.
- ^ a b Hovhannessian, R. Kh.; Hovhannessian, E. R. (2001). "Gas—Dust Shells around Some Early-Type Stars with an IR Excess (of Emission)". Astrophysics (English Translation of Astrofizika). 44 (4): 454. Bibcode:2001Ap.....44..454H. doi:10.1023/A:1014244720865. S2CID 118532665.
- ^ a b c Verdugo, E.; Talavera, A.; Gómez De Castro, A. I. (1999). "Understanding A-type supergiants. I. Ultraviolet and visible spectral atlas" (PDF). Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement. 137 (2): 351. Bibcode:1999A&AS..137..351V. doi:10.1051/aas:1999487.
- ^ a b Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (2011). "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 410 (1): 190–200. arXiv:1007.4883. Bibcode:2011MNRAS.410..190T. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x. S2CID 118629873. Vizier 카탈로그 항목
- ^ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. S2CID 119257644. Vizier 카탈로그 항목
- ^ Van Den Bergh, S. (1966). "A study of reflection nebulae". Astronomical Journal. 71: 990. Bibcode:1966AJ.....71..990V. doi:10.1086/109995.
- ^ Morgan, W. W.; Roman, Nancy G. (1950). "Revised Standards for Supergiants on the System of the Yerkes Spectral Atlas". Astrophysical Journal. 112: 362. Bibcode:1950ApJ...112..362M. doi:10.1086/145351.
- ^ Adelman, Saul J. (2001). "Differential uvby Photometry of 13 Mon (A0 Ib)". Baltic Astronomy. 10 (3): 385. Bibcode:2001BaltA..10..385A. doi:10.1515/astro-2001-0305.
- ^ Adelman, S. J.; Albayrak, B. (1997). "On the Variability of Early A-Type Supergiants". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars. 4541: 1. Bibcode:1997IBVS.4541....1A.